A step-by-step guide to treating tomatoes with metronidazole against late blight: fighting the disease and preventing it
Late blight is the scourge of tomatoes. This disease can completely destroy the crop. Vegetable growers use many means to combat its pathogen: from folk remedies to chemicals. Practice has shown that tomatoes can be saved with the help of an inexpensive pharmaceutical drug - Metronidazole.
How effective is treating tomatoes with Metronidazole against late blight, how often to use the drug for spraying and what nuances should be taken into account - you will learn all this from our article.
What kind of drug is this
Metronidazole is an antibacterial drug used to treat many diseases.. However, this remedy has also found use in the garden due to its pronounced antifungal properties.

The principle of action in the fight against late blight
The drug contains the active ingredient metronidazole. Coming into contact with late blight, it actively affects the DNA of the pathogen cell, slows down protein synthesis and the formation of nucleic acids, which leads to the cessation of fungal reproduction.
Differences from "Trichopol"
The drug "Trichopol" is an analogue of "Metronidazole", there are no special differences between them. It is also based on the active ingredient metronidazole. The dosage in these two drugs is also identical - 250 mg.
“Trichopol” is the trade name of the drug, and “Metronidazole” is the international nonproprietary name.In fact, these are the same medicine, just under different names. There is no difference in which tablets to use in the garden.
Efficiency
Metronidazole destroys pathogenic fungi and bacteria, it is equally effective against most known strains. Keep in mind that fungal microorganisms have the ability to quickly adapt to drugs, so you cannot use the product regularly.
Important! The drug is a medicinal drug - it has contraindications and dosage.
Metronidazole is used in the treatment of the following diseases:
- late blight;
- brown spot;
- powdery mildew;
- Alternaria blight;
- fusarium;
- anthracnose;
- rot - white, gray, dry;
- blackleg.
Pros and cons of using
Like any other drug, Metronidazole has a number of its strengths and weaknesses.
Advantages of the drug:
- high efficiency;
- affordable price;
- ease of use;
- absence of pesticides.
Disadvantages of Metronidazole:
- the drug is not officially included in the list of products for the treatment of agricultural crops;
- promotes the development of pathogen resistance;
- the need for replacement or search for combinations with other means;
- the effect of the substance on plants has not been studied;
- the hazard class for humans has not been established.
How to prepare a solution for treatment
 It is very simple to prepare the correct solution based on Metronidazole — just dissolve 20 tablets in 10 liters of water. Gardeners recommend first making a concentrate, using warm water for dilution. As soon as the drug dissolves, the volume is adjusted to the required 10 liters. The solution cannot be stored; it must be used on the day of preparation.
It is very simple to prepare the correct solution based on Metronidazole — just dissolve 20 tablets in 10 liters of water. Gardeners recommend first making a concentrate, using warm water for dilution. As soon as the drug dissolves, the volume is adjusted to the required 10 liters. The solution cannot be stored; it must be used on the day of preparation.
Rules for preparing the solution:
- the drug is diluted in water not lower than +30° C;
- To quickly dissolve, the tablets are crushed;
- the solution is ready for use 30 minutes after preparation.
Important! Increasing the dosage of the drug can lead to the death of the plant.
Many vegetable growers combine the drug With brilliant green or iodine — these tools make processing more effective. Metronidazole acts on the fungus, brilliant green heals and disinfects damage, iodine nourishes the plant.
Thanks to such combinations, tomatoes receive double protection. First, prepare a solution with Metronidazole, then add 1 bottle of pharmaceutical brilliant green or 15-20 drops of iodine into it.
How to treat tomatoes with Metronidazole
Tomatoes can be treated with the preparation at the stage of sowing seeds. - this will protect the seedlings not only from late blight, but also other fungal diseases. To do this, the seeds are soaked in the prepared solution for 30 minutes, then they are dried and planted in a planting box.
Step-by-step instruction
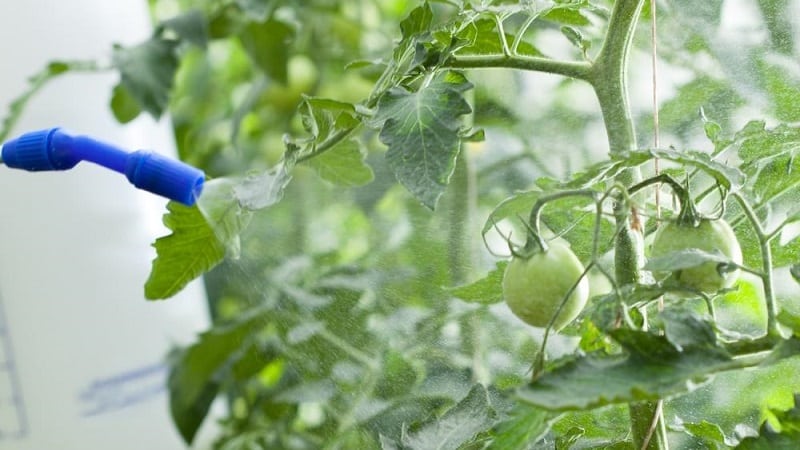
The drug is most often used for spraying:
- Prepare the solution.
- Spraying is carried out in the first half of a dry, windless day.
- For the procedure, a fine spray is used.
- Process the stem and leaves on both sides, paying special attention to the lower branches.
- Additionally, water the seedlings at the root with the solution - 50 ml per bush.
- If precipitation occurs after spraying, the procedure must be repeated.
Important! When working with metronidazole, you must use personal protective equipment - a mask and gloves. It is not recommended to stay in the greenhouse for a long time after treatment.

Processing times and frequency
Spraying with Metronidazole is carried out no more than 3 times a season:
- the first spraying after planting seedlings in the garden bed;
- the procedure is repeated 2 weeks before the start of harvest;
- if there are no signs of disease, then there is no need for treatment.
Gardeners do not recommend using the drug to treat tomatoes 2 weeks before harvest.. Despite the fact that the hazard class for humans of the drug has not been established, to protect health it is better not to shorten the waiting period.
Use for prevention and treatment
Metronidazole is used not only for treatment, but also for prevention purposes. It should be used by those who have already encountered diseases on their property last season.
Preventive measures begin even before planting seedlings. An undiluted tablet of the drug is added to each well. As soon as the plant is established, the beds are treated once every 10 days. The following solution is used: 5 tablets of water are dissolved in 10 liters of water. Spraying with the drug can be alternated with other drugs and folk remedies.
Important! In the garden, a tablet dosage of 250 mg is used.
At the first appearance of symptoms of late blight, treatment is carried out every day. A stronger solution is used - 20 tablets per 10 liters of water. You can spray the bush, apply the solution under the bush, or carry out spot treatment of damage.

Reviews from vegetable growers
There is no clear opinion from experts about whether Metronidazole should be used on the site. However, more and more gardeners, having tried this cheap pharmaceutical product, are replacing pesticides with it.
Irina, Armavir: “I heard from friends about the effect of Metronidazole against late blight. At first, I was afraid to use it on the site, because it is a “human” medicine. I decided to try it anyway and was not disappointed. I am very pleased with the result - despite the rainy summer there was no late blight on the tomatoes.Next season I want to try combining metronidazole with brilliant green.”.
Ruslan, Moscow region: “I treat the beds with Metronidazole and add iodine to the solution - this is additional nutrition for the tomatoes. This season I want to try treating seeds with the drug".
Galina, Saratov: “The drug did not save my tomatoes from late blight. I planted tall varieties, regularly treated them with a solution, and repeated the procedure after rain. I had to uproot the bushes and burn them. The fungus probably adapted to the medicine.".
Conclusion
Metronidazole is a popular remedy against late blight. Many gardeners are convinced that the drug can stop and prevent the disease. It is important to consider that the drug leads to the development of pathogen resistance, so from time to time it needs to be changed or combined with other agents.
Often, due to the resistance of fungi and bacteria developed during preventive treatments, the crop suffers. Each gardener decides for himself whether to treat tomatoes with Metronidazole or not, taking into account risk factors and the current condition of the plants.
Need to try!