What is a potato tuber: botanical description, development and application
The scientific name for potatoes is nightshade. But usually both the tubers and the plant as a whole are called potatoes. We will talk about the anatomical structure of potato tubers. This information will help beginning farmers use their harvest wisely and obtain valuable seed material.
What is a potato tuber?
What is a potato tuber? This is a vegetative thickening, or an overgrown bud on the root of a plant, suitable for food.
Essentially, the tuber is a modified shoot of the tuberous nightshade. It develops at the top of a stolon - a side shoot with elongated internodes and underdeveloped leaves.
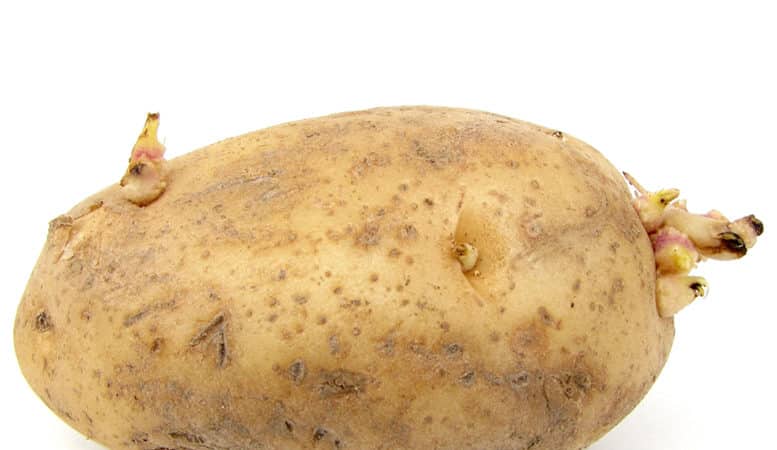

What does it look like
Depending on the variety, tubers are round, oval, oblong and spindle-shaped. The pulp is white, yellow, cream, orange. Thick skin - pink, yellow, beige, brown or purple.
Interesting! The Explosion potato variety has dark purple flesh and skin with a nutty flavor and aroma.
Tuber structure
The pulp consists of thickened, starchy, dense tissue. The tuber is covered with a corky crust, which becomes rougher as it ages (see photo).
On a note! The homeland of tuberous nightshade is South America, where it was first cultivated.
Internal
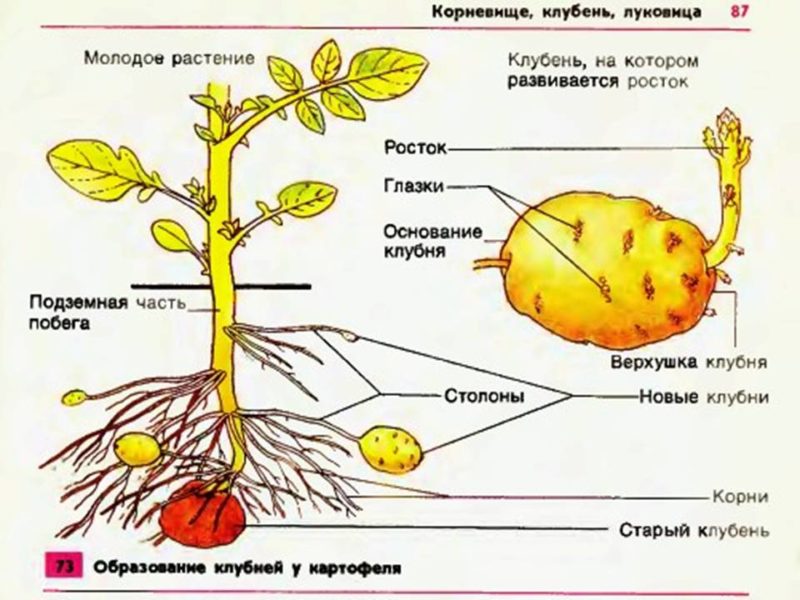
You can only examine the internal structure of a potato using a fresh cut. The underground stem in section includes the following layers:
- epidermis - suberized cells of the periderm;
- cortex - parenchyma cells with starch grains;
- cambium - cambial cells with xylem elements;
- core - parenchyma cells with radial rays.
The core contains the least amount of starch grains. This is the coarsest part of the pulp.
External
Tuber is seed material for vegetative propagation of potatoes. On its surface there are 7-15 ocelli, 3 buds with rudiments of leaves and roots in each. Only the central bud grows, from which above-ground shoots and roots develop.
Attention! If the shoots from the central shoot are damaged, replacement occurs due to the lateral buds. But such shoots are always weaker and do not tolerate unfavorable weather conditions during the intensive growing season.
Does it depend on the variety?
The general structure of the potato tuber is the same for all varieties. The only difference is in the color of the potato pulp and skin and the ratio of the internal layers in thickness.
Other components of the plant

The above-ground part of the potato includes:
- Stems. Erect, fleshy, with appressed hairs, height from 30 to 140 cm. Usually 4-7 stems are formed on the bush.
- Leaves. Discontinuously unpaired, pinnately dissected, with 6-10 ovoid, pointed leaflets. Smooth on the outside and pubescent, ribbed on the inside. Arranged on the stems in a spiral.
- Flowers. Five-membered, collected at the top in inflorescences-curls. The calyx consists of 5 sepals. The corolla is sphenoletal, white, yellow, pink, purple. After pollination, the pistil turns into a fruit.
- Fetus. Green berry, spherical, 1.5-2.2 cm in diameter, not edible.
What is the root system of potatoes?
The potato root system is fibrous, extending to a depth of 30-50 cm from the soil surface.The roots reach their maximum development at the time of budding of the bush; when the tubers are fully mature, they gradually die off.
Comprises:
- primary roots, which form at the beginning of tuber germination;
- near-bottom roots, located in groups of 4-5 pieces;
- stolon roots.
A potato tuber is a thickened and shortened stem covered with a protective cork tissue.
How many cotyledons
Potatoes belong to the class of dicotyledons. Upon germination, the seed forms two cotyledons.
Biological features of the tuber
The formation of new tubers occurs in the lower leaf axils and takes 40-70 days from the moment of planting.
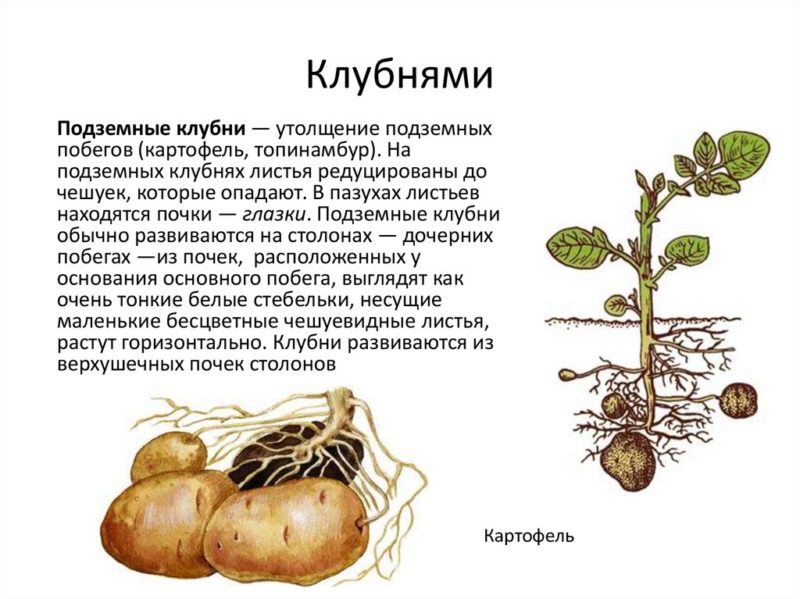
How is it formed
The beginning of potato germination is characterized by the activation of cellular metabolism to form the vegetative mass of the plant. The bush forms up to 20-30 tubers, but only 5-15 of them turn into full-fledged ones, retaining all varietal characteristics.
Development algorithm
Development is divided into conditional periods:
- During the process of photosynthesis, the green part of the plant accumulates nutrients and sends them to the root system, due to which tubers are formed in 30-45 days landings.
- Stolons develop from the lateral subsoil buds.
- With the onset of favorable conditions, initiation occurs and the elongation of the stolon stops.
- During the flowering phase, the subapical part of the stolon swells, which leads to the accumulation of starch and protein.
- After 3-4 weeks, overall metabolic activity decreases and the vines die.
- The skin thickens, the speed of cellular processes is suppressed.
At the time of harvest, the tubers are ready for long-term storage in basement conditions.
Why is it considered a modified shoot?
Stolons with tuberous thickenings in the apical part are a continuation of the aboveground stem. However, the structure of the tuber tissue differs from the structure of the tissues of the aerial part. The presence of scale-like leaf blades indicates their vegetative origin.
Additional evidence that a tuber can be considered a shoot is its ability to green. When exposed to sunlight, potatoes quickly change color, despite the absence of chlorophyll in the cells.
What diseases and pests threaten potato tubers?
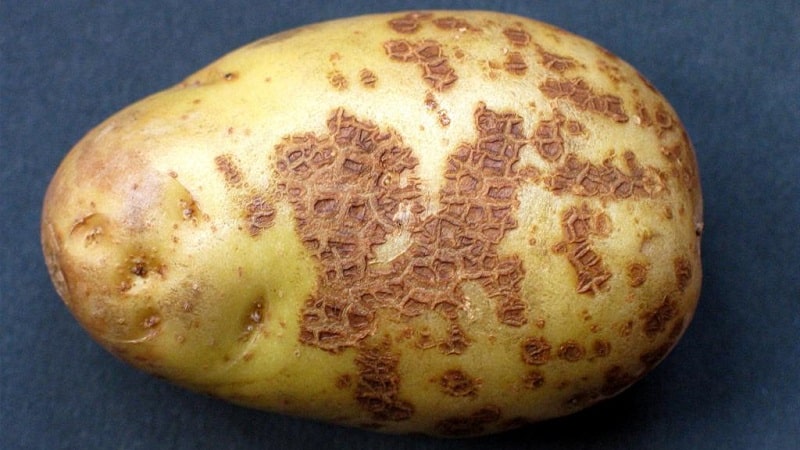

The following diseases affect tuberous nightshade:
- Late blight - a fungal infection that successfully overwinters in the soil and on crops in a cold room. Appears as black spots. The control method is spraying the plantings with Acidan, Tattu, and Bordeaux mixture.
- Fomoz - depressed spots on the surface with a diameter of up to 3 cm. Lead to rotting and cracking of potatoes. The control method is spraying with Trichodermin, Fitodoctor, and Fitosporin.
- Oosporosis - rounded pustules on the skin that damage the eye. Drugs for fighting - “Remontal”, “Stark”, “Doc Pro”.
The most famous potato pests are the Colorado potato beetle, nematode, mole cricket, and slugs. Insecticides will help in the fight against pests - “Aktara”, “Aktofit”, “Bingo Milady”.
Chemical composition and properties
The chemical composition depends on the potato variety, the quality of the soil at the place of growth and the degree of maturity.
Potato tubers contain:
- 73% water;
- 15% starch;
- 2% crude protein;
- 5.5% sugars;
- 1% fiber;
- 0.1% fat;
- 0.5% pectin components;
- 0.3% titratable acids;
- 0.1% phenolic compounds;
- 1.5% organic compounds;
- 1.2% minerals.
The nutritional value
The calorie content of potatoes boiled in their skins reaches 70 kcal. In crushed form (puree) - 60-65 kcal per 100 g.
The main nutrient is the complex carbohydrate starch. In the gastrointestinal tract, it is broken down and converted into glucose, which releases energy when oxidized. On average, the starch content varies between 15-25%.
Potatoes contain a lot of fiber and pectin, which do not irritate the mucous membrane of the stomach and small intestine. The pulp contains vitamins C, B1, B2, B6, K, PP, potassium, sodium, iron, magnesium, copper, zinc, manganese, iodine.
The benefits and harms of potatoes
100 g of potatoes contains:
- 400 mg of potassium, which is necessary for the functioning of the heart muscle and normalization of water metabolism in the body;
- 20 mg of vitamin C, or ascorbic acid, which is responsible for the state of immunity and general resistance to viral diseases, prevents scurvy;
- up to 2% easily digestible protein tuberin (100% digestible by the body).
Harm to the body can be caused by eating green potatoes, which, under the influence of sunlight, intensively accumulate solanine, a poison that causes poisoning.
Application of tubers
Potatoes are grown as an annual crop. The bulk grown crop used for cooking. In addition, potatoes are suitable for feeding domestic animals, producing ethanol and food starch.
This is interesting:
Top leading countries in potato production worldwide.
We are looking into the questions of why a child eats raw potatoes and whether it is harmful.
Conclusion
From the standpoint of biological classification, a tuber is considered a vegetative thickening on the root. It is not the fruit of Nightshade, but it is used to propagate the plant.Simple cultivation technology and high nutritional value have determined its important place in the human diet.