How to deal with scab on potatoes and cure the soil
Scab is one of the most common fungal infections of potatoes. The disease spoils not only the appearance of the tubers. Taste quality deteriorates and storage is reduced. Fungal spores quickly multiply and capture more and more plants, so it’s worth understanding the reasons for its appearance and learning how to get rid of scab on potatoes. Photos and descriptions of scab types will help to more accurately diagnose the disease and take effective measures in time.
What is potato scab
Outwardly, it resembles scabs on tubers. The lesion begins with small ulcers - if you do not pay attention to them in time, the disease reaches its extreme manifestation - the appearance of deep cracks with torn edges. Bacteria develop in such tubers and the potatoes rot.

Spread of the disease
The disease mainly affects tubers, extremely rarely spreads to tops and roots.
Fungus spreads by spores from one bush to another and gradually takes over the entire field if measures are not taken in time. The spores survive in the ground for up to three years, which is why it is so important to change the planting site.
The fungus can be spread by using fresh organic matter.: Scab spores remain viable after passing through the animal’s digestive tract. The cause of the disease may be incomplete disposal of infected potato tops in the fall.
During potato growth, it is impossible to notice scabTherefore, it is important to take into account the presence of fungus on tubers during harvest and take preventive measures for the next year.
Causes of potato infection
The main reasons for the defeat of culture:
- non-compliance with crop rotation - it is important to change the planting site at least once every three years;
- planting affected tubers;
- increased nitrogen content in the soil;
- hot (25-30°C) dry weather promotes the growth of fungus;
- improper application of organic fertilizers;
- weak soil acidity;
- improperly equipped potato storage facility - elevated temperatures and humidity, large volume of potatoes with poor ventilation.
Reference. Loamy and sandy loam soils are more susceptible to scab. Before planting, the tubers must be pickled. Plant potatoes deeper to prevent excess oxygen.
How does scab appear on potatoes?
There are several types of scab depending on color, shape and signs of damage.
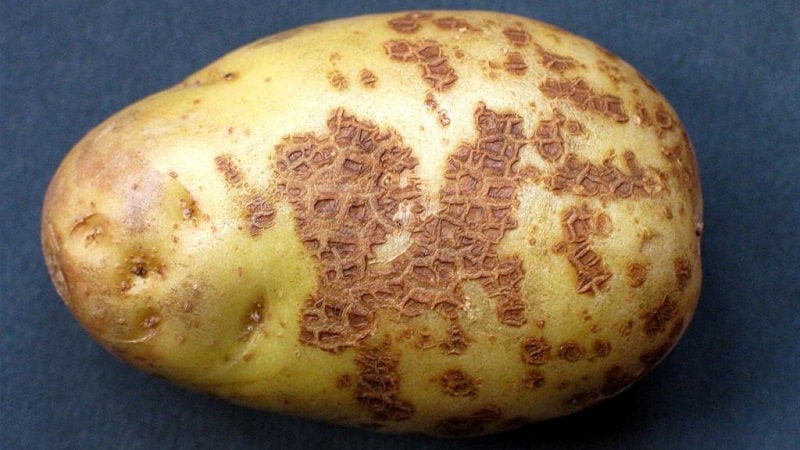
Ordinary
 Spots on tubers in the form of hard sores with a dry rim of dark yellow or brown color. They can cover entire potatoes or individual areas. Common scab occurs due to shallow planting and access of air to the tubers, due to improper application of lime and wood ash to the soil. It manifests itself in soils poor in moisture.
Spots on tubers in the form of hard sores with a dry rim of dark yellow or brown color. They can cover entire potatoes or individual areas. Common scab occurs due to shallow planting and access of air to the tubers, due to improper application of lime and wood ash to the soil. It manifests itself in soils poor in moisture.
Spores enter the tuber through mechanical damage to the skin. Varieties with red thin skin are often affected by the fungus. The affected vegetable is poor in minerals, vitamins and amino acids.
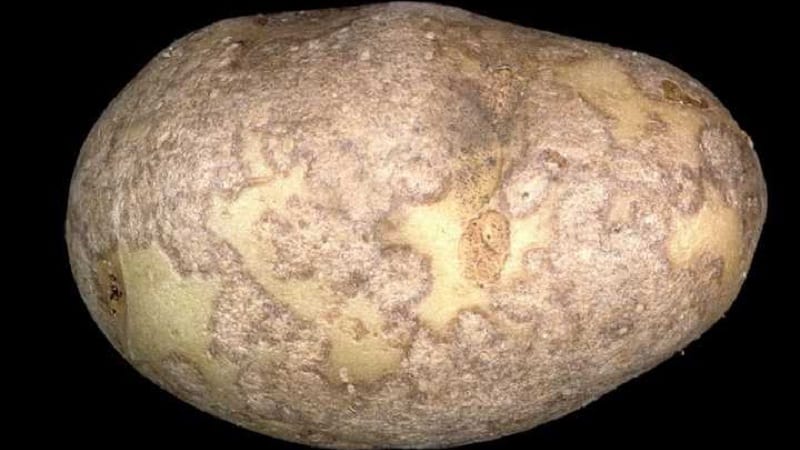
Silver
A distinctive feature is the appearance in the form of silvery spots. First, brown spots or spots that look like black soot form. When the skin peels off, a gray spot appears in its place. The tuber becomes wrinkled.The size of the spot can cover up to 40% of the entire tuber.
This type of fungus dries out the tops, which leads to early death of the entire plant., softens the affected tuber, drying it. The taste of such potatoes is unpleasant and they are not suitable for planting. The development of the fungus begins at a temperature of +3°C and high humidity (80-90%).

Other potato diseases:
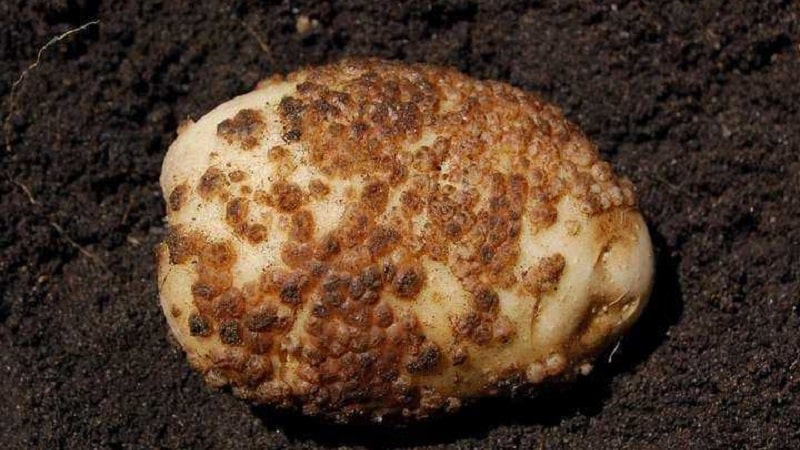
Powdery
Symptom: small focal growths on the stem. The tubers have white growths that turn brown over time. The ulcers contain brown dust from fungal spores and remnants of tuber tissue. Subsequently, the potatoes rot.
Sources of the disease - infected planting material, manure, humus, chicken droppings. Another reason is the soil is too wet. This type of scab affects the roots and stems of vegetables. Tubers become susceptible to late blight and dry rot.

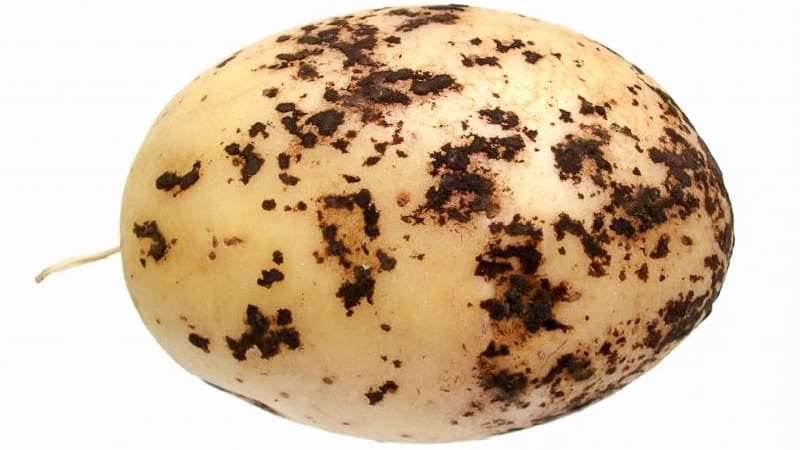
Black, or rhizoctonia
Develops at high humidity and affects the plant from the tuber to the leaves.. This type of fungus looks like black loose spots, similar to stuck lumps of earth. Cover the tuber in small areas no more than 5 mm in girth. If the disease becomes active in the early stages of plant development, it can destroy the entire bush.
Tubers are poorly stored, rot does not develop deeply, but other types of rot often form on it, which completely destroys the crop. Early detection of potato rhizoctonia will help start treatment on time.

Tuberous
Only tubers are affected - tubercles appear, which then turn into pits with putrefactive contents. It appears most clearly in the third or fourth month of storage.Poorly dried tubers suffer the most.
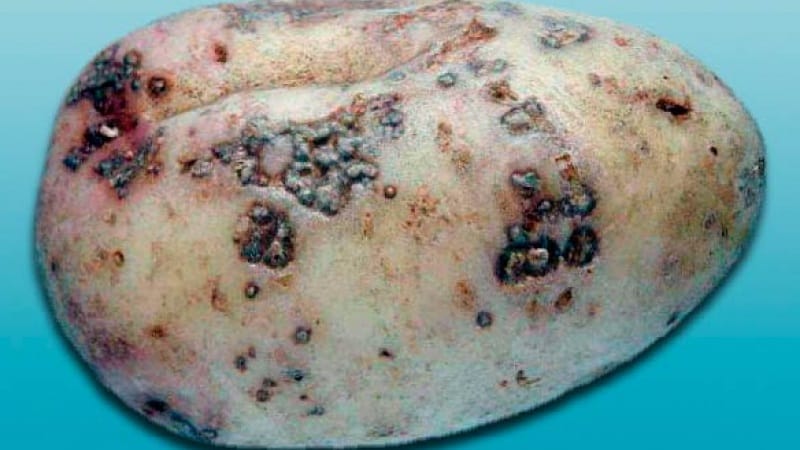
How to deal with scab
There are many methods to combat scab - folk recipes, chemicals and biological methods.
Traditional methods
Use available organic fertilizers and herbal remedies, increasing the resistance of tubers to scab. At different stages of growth, the following medicinal compositions are used (the ratio of the mass of fertilizer and water is indicated):
 before germination, planting material is sprayed with a 1.5% solution of boric acid;
before germination, planting material is sprayed with a 1.5% solution of boric acid;- when planting, add 1 liter of bird droppings solution (1:15) to each hole;
- during the period of stem growth - water 1 bush with 0.5 liters of liquid mullein or bird droppings (0.5:10 liters);
- during the formation of the bush - watering 1 liter of nettle infusion per bush per week (10 kg: 100 l);
- during the budding period, pour 1 liter of ash solution (3 tbsp: 10 l) under the bush;
- during flowering, add 0.5 liters of mullein solution per bush (2 cups: 10 liters).
Chemical and biological methods
In addition to traditional methods, the use of the following drugs is effective:
- "Maksim". The drug is sprayed on tubers in the fall before storage (2:50 ml of water) and in the spring before planting.
- "Prestige KS". The tubers are treated before germination (70-100 ml of the drug is dissolved in 1 liter of water).
- "Fitosporin M". To treat tubers before planting, dilute 10 g of the drug in 5 liters of water. During the season, 3 treatments are carried out with watering the bushes.
- "Agate-25". Spray the seed potatoes before planting and treat the bushes (7g per 500 ml of water).
- "Quadris". Serves to treat the soil and protects it for two months (3 ml per 10 liters of water). The composition is enough to spray 10 m² of land.
How to cure soil from scab
How to treat the soil if scab appears on the potatoes? A simple way is to use green manure plants that disinfect the soil..
Example. You can sow mustard. When the shoots are 15-20 cm tall, dig up the soil along with the young greenery. Dry mustard is also scattered between the bushes before watering.
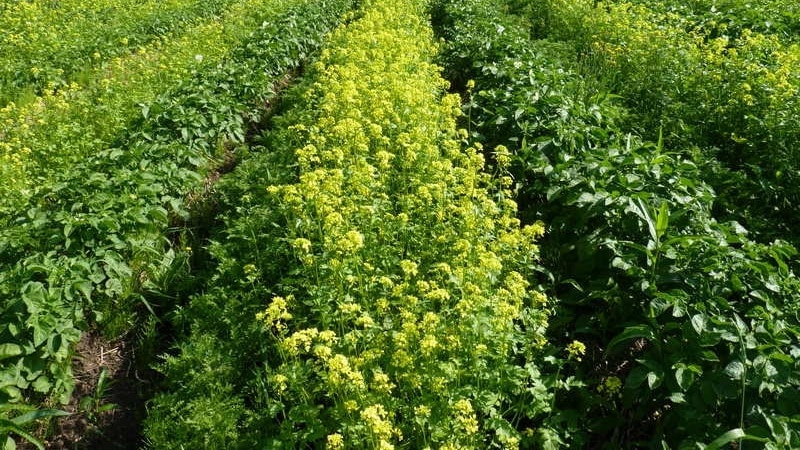

Agrotechnical method: the plot is sown with cereals (oats, rye), legumes (clover, vetch, soybeans), cruciferous crops (mustard, rapeseed, Shrovetide radish) or these crops are sown in the fall. The following year, potatoes are planted in this place.
Alkaline soils require acidification with ammonium sulfate based on 2 tbsp. l. for 10 liters of water. A barrier to fungus will be created by superphosphate, potassium magnesium, potassium permanganate, boric acid and copper sulfate.
Is it possible to eat potatoes with scabs?
Scab does not pose a danger to human health, but the taste of the infected tuber noticeably deteriorates. The starch content in it drops by 2 times, and with it the content of nutrients. Tubers affected by scab are poorly stored and rot.
They also cannot be used for planting, as this will lead to further spread of the disease, the appearance of even more ulcerated tubers, and a decrease in the yield as a whole.
Read also:
Potato varieties resistant to scab
There are no potato varieties that are absolutely resistant to this disease., but gardeners have noted early ripening varieties that are less susceptible to damage: Spring White, Lugovskoy, Zhukovsky early, high-yielding Elizaveta variety with tasty tubers, which is suitable for growing in the middle zone, the Far East and the North Caucasus.Temp is a late-ripening variety characterized by resistance to scab, high yield and good preservation.
Also have variety immunity Yantarny, Domodedovo, Zarechny, Alena, Snow White, Resource, Lasunok.

Infection prevention measures
The improvement of potatoes is carried out in the following directions: protecting tubers and destroying fungus in the soil in the following ways:
- compliance with crop rotation;
- refusal to fertilize the soil with fresh manure;
- drying the crop;
- careful selection of seed potatoes without signs of scab;
- treating seeds with special preparations (polycarbocin or “TMTD”);
- storing potatoes in a cold, dry, ventilated area;
- germinating potatoes in the light - greening (protects not only from scab, but also from many diseases, as well as from rodents and pests);
- regular watering of the bushes during bud formation and flowering;
- choice for planting scab-resistant varieties.
Before sending for long-term storage, potatoes are dried for several hours and the infected ones are immediately destroyed.. Scab spores can spread through the air. This is facilitated by room humidity, so it is important to avoid the formation of condensation in the vegetable storage area.
Conclusion
Scab is a common disease that affects not only potatoes, but also other crops. Having discovered signs of disease, they immediately begin to fight for a healthy harvest. By cultivating the soil and planting tubers, using beneficial vegetation in the potato plot, knowing what actions lead to the spread of the fungus, observing crop rotation, you will definitely achieve positive results and get rid of this disease.