What is potato ring rot and methods of combating it
Potato tubers, rich in water and starch, are a favorable environment for the development of bacteria and fungi. Potato diseases, in particular ring rot, can completely destroy the crop. For this reason, they begin to fight the disease when the first signs are detected.
In this article we will describe in detail what ring rot of potatoes is, we will provide a description of the symptoms of the disease and methods of treating it.
Description of the disease
Potato ring rot is dangerous because it affects both the tops and tubers. Affected potatoes begin to rot even before harvesting. And through infected tops, healthy tubers become infected when dug up.
Characteristic
Ring rot is a bacterial disease, widespread in all areas where the crop is grown.
The disease can be detected by cutting the tuber. If the potato is infected, a vascular ring is visible under the skin. The tissues in the ring area are soft and yellow-brown in color. When pressed, light yellow mucus emerges from the affected tissues.
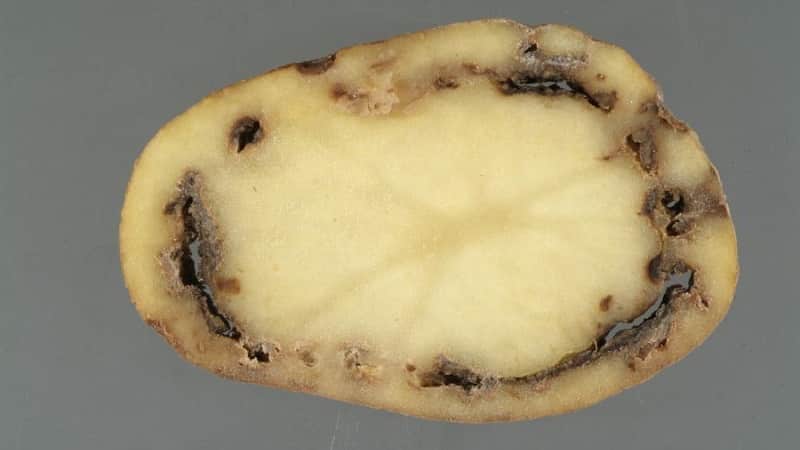
As the disease develops, rot spreads to adjacent tissues, covering the entire tuber. The potato pulp rots and turns into a slimy substance with an unpleasant odor.
Attention. The disease develops slowly. At the initial stages of development, the pathogen can only be identified using laboratory methods.
If the problem is not detected in time and measures are not taken, crop losses can be 40-50%.
Infected bushes are dug up and destroyed. It is no longer possible to cure these plants. Therefore, prevention plays a special role in the fight against infection.
Development conditions
Harmful bacteria actively develop at moderate temperatures (from +20°C) and high humidity. In heat and drought, the development of the disease stops. The main source of infection persistence and transmission to new generation tubers is already affected tubers.
Pathogen
The causative agent of the disease is bacteria. It is noteworthy that they do not survive in the soil and are not able to overwinter in it. However, they remain viable in vegetable stores, on plant debris, and on garden tools. But the main source of infection is infected tubers placed in storage.
The pathogen is capable of remaining dormant for several generations.until suitable conditions for development arrive. Therefore, even from apparently healthy tubers, diseased plants are sometimes obtained.
It can be useful:
What to do if the potatoes inside become empty
Transfer methods
Tubers become infected with bacteria during growth, in the early stages of tuberization. The causative agent of the disease penetrates from the vessels of the diseased bush through the stolons into the potatoes of the new crop.
Another way for bacteria to spread is through infection during cleaning.. The causative agent of infection reaches the surface of the tuber through contact with infected tops, cut diseased potatoes or tools used during harvesting.
During storage, healthy tubers can also become infected through contact with diseased tubers.. Especially if the first ones have damage to the skin, scratches or cuts. For this reason, all damaged potatoes are stored separately from the main crop and processed first.
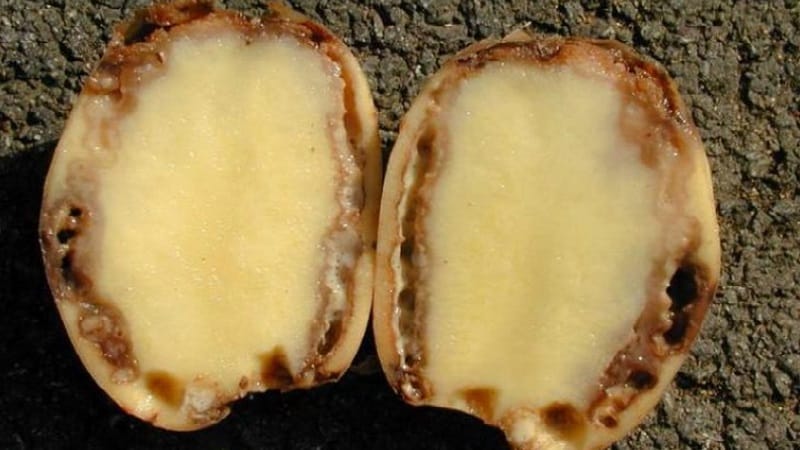
Forms of the disease
Ring rot develops in two forms: pit rot and ring rot itself.
Pit rot is the primary form of the disease. It develops when an infection gets on the potato skin during harvesting (through contact with diseased tops or tubers).
In this case, round, oily yellow spots 2-3 mm in size appear on the tubers during storage. Gradually they increase to 1-2 cm in diameter. At first, no symptoms of the disease are visible. The disease appears only in March-April.
Attention. As the temperature rises (+18…+20°C), the development of pit rot intensifies.
If such tubers are not removed when preparing for planting, then the disease will progress and spread to young tubers.
The second form of the disease is ring rot itself.. Manifests itself in the form of necrosis of the vascular ring on a potato cut. The infection spreads from infected tubers planted in the spring.
Signs of potato infection
You can understand that plantings need help by looking at tuber sections, and by the appearance of the bush.
Advice. Inspect the bushes when hilling and weeding. The first signs of infection become noticeable during the flowering period.
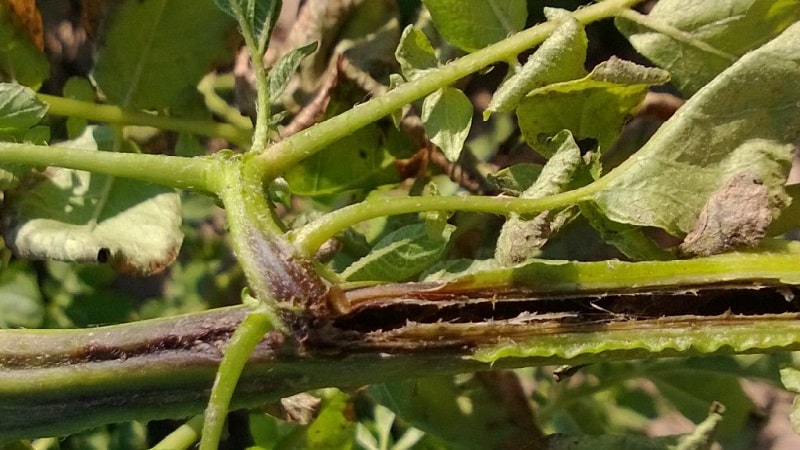
The disease is indicated by the wilting of one or two stems in the bush.. Their falling to the ground is a characteristic sign of ring rot. Brown spots appear on the tips of the leaves of wilted stems.
Important. The causative agent of ring rot, moving from an infected tuber along the roots to the stems, causes clogging of blood vessels.As a result, nutrients do not reach the tops and they wither.
If the tubers are still slightly affected by infection, then they are no different from healthy ones in appearance. But the cut already shows a vascular ring with yellowed and softened tissues.
The photo below shows what the tops of an infected bush look like and what the tuber looks like in the initial phase of infection. As the disease progresses, the potato is completely destroyed and turns into a slimy mass.
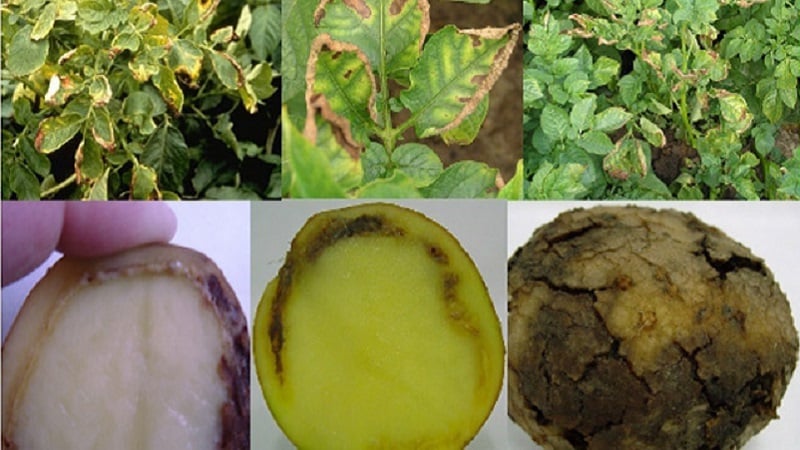

Let us list the main signs of the disease:
- yellow or brown rings on the cut, located close to the peel;
- release of a mucous mass when pressing on a rotten tuber;
- yellowing and curling of potato tops;
- lodging of several stems in a bush, while the stems are difficult to remove and gradually die off;
- Planting heavily infected material leads to dwarf and poorly developed seedlings, the stems of such plants are thin, and the leaves are small and located close to each other.
Causes of rot
If the source of infection is diseased tubers, the disease develops especially quickly.. The bushes wither starting from the top due to lack of moisture. Moisture does not reach the top of the bush due to blockage of blood vessels caused by bacteria.
As a rule, only individual stems wither on a bush. In addition, bacteria release toxins, which also contributes to wilting.
The causative agent of ring rot penetrates into young tubers from affected stems through stolons. Also, tubers become infected through mechanical damage during harvesting and when injured potatoes come into contact with infected tops.
Important. Wet weather conditions combined with moderate temperatures increase the severity of damage.The bushes themselves fade slowly. High temperatures and dry weather are unfavorable for the development of bacteria, but the green part of the infected bush withers quickly.
The main source of the causative agent of ring rot is tubers and plant debris. The pathogen does not persist in the soil. The spread of the disease occurs during harvesting and when diseased tubers get into the mass of healthy ones during storage.
Control measures
Among the measures to combat the scourge highlight folk remedies, biological and chemical preparations.
Folk remedies
 Because the sowing infected tubers is the main route of infection spread, then the main task is to prevent diseased specimens from entering the seed.
Because the sowing infected tubers is the main route of infection spread, then the main task is to prevent diseased specimens from entering the seed.
Warming up in the spring will help identify infected tubers.. The seed material is kept warm for three weeks (at a temperature of +15...+18°C). In a warm environment, bacteria begin to actively develop and appear in the form of foci of rot on the peel. Upon careful examination, identifying and removing infected specimens will not be difficult.
Compliance with the rules of crop rotation allows you to successfully combat the spread of the disease.. Changing the planting location every year improves the soil and allows you to get a healthy harvest.
Experienced gardeners used to combat bacterial and fungal diseases by sowing green manure. This measure is also effective for ring rot. Sowing oats, rye, wheat, barley, corn and tobacco as green manure helps fight the proliferation of bacteria and fungi.
Important. Sowing green manure in a potato field immediately after harvesting potatoes in the fall and before planting them in the spring will reduce the activity of pathogenic bacteria and fungi.
Green manure is sown immediately after digging up the potatoes. In this case, choose fast-growing crops that provide a sufficient amount of green mass before the onset of cold weather.
In early spring, the area for potatoes is planted with mustard or oats.. Before sowing potatoes, green manure is mowed, the soil is loosened and mixed with plant residues. Saprophytes developing in the soil inhibit the development of bacteria.
Read also:
Biological
 Of the biological products against the causative agent of ring rot, “Gamair” is used. This is a biological bactericide intended for the treatment and prevention of both bacterial and fungal plant diseases.
Of the biological products against the causative agent of ring rot, “Gamair” is used. This is a biological bactericide intended for the treatment and prevention of both bacterial and fungal plant diseases.
The drug is used in the summer when watering plantings and in the fall to protect tubers. If autumn is dry, then two weeks before harvesting, water the potatoes with a solution of the drug (2 tablets per 50 liters of water).
If you are storing washed potatoes for winter storage, then during washing you can also add “Gamair” to the water. Or spray the tubers with a solution of the drug before drying.
Chemical
Treating seed potatoes helps get rid of bacteria that cause tuber rotting. fungicides, for example, drugs such as Quadris, Maxim Quatro, Uniform. They are based on the active substance azoxystrobin, a contact and systemic fungicide.
All tools used during harvesting are also treated. Products containing alcohol, chlorine, and kerosene are used as a disinfectant solution. A dark pink solution of potassium permanganate and a 5-10% solution of vitriol also have a disinfecting effect.
Is it possible to eat affected potatoes?
Tubers in which the disease has just begun to develop, are not dangerous to humans and are quite suitable for human consumption. In such potatoes, the dark ring under the skin is not yet clearly visible and the flesh has not lost its taste.
Potatoes with severe signs of damage, pronounced unpleasant odor and soft, slimy pulp can no longer be eaten.

Prevention measures
The following agricultural practices will help prevent damage to plantings:
- The most effective means of prevention is planting zoned resistant varieties. Early potato varieties are most susceptible to ring rot.
- The main source of spread of the disease is affected tubers. Therefore, it is important to obtain healthy seed material, which primarily depends on compliance with cultivation techniques.
- Periodic inspection of plantings during growth and development. Identification and removal of diseased bushes.
- Compliance with crop rotation rules. Potatoes are planted in their original place no earlier than after 3-4 years.
- Long-term drying of potatoes before storing them in storage for two weeks. After this time, all potatoes are inspected and specimens with signs of infection are removed.
- Mowing and removing potato tops from the field 1-2 weeks before digging reduces the likelihood of healthy tubers becoming infected when they come into contact with contaminated greens.
- Disinfection of the cellar before storing vegetables for winter storage.
- Germination of seed material with subsequent identification and removal of diseased tubers.
Varietal qualities and disease resistance of potatoes decrease with non-compliance with crop cultivation technology.
Following these preventive measures will help you prevent the spread of infection and preserve the harvest for many months.
Conclusion
A disease of potato tubers, such as ring rot, can cause serious damage to potato stocks during storage. Therefore, it is imperative to fight the disease.
Maintaining crop rotation, using proven seed material, and choosing varieties resistant to bacterial rot will help preserve the harvest and prevent the development of the disease.