Large and sweet pepper variety “Big Girl”: reviews from summer residents and their growing secrets
Bell pepper Big Girl shows high productivity both in the open air and in greenhouse conditions. Gardeners value the variety for its juicy taste and high content of vitamins and minerals. The vegetable makes nutritious salads and snacks, winter preparations and side dishes. To get a rich harvest, follow a number of simple rules. Let's look at the main ones and identify the distinctive features of the Big Girl sweet pepper.
What type of pepper is this?
An early ripening Big Girl grows in 100-105 days. Harvest in mid to late August. The variety is resistant to major crop diseases and can withstand hot and dry summers without consequences. Planting a vegetable by seedlings or seeds in open ground.
Characteristics and description of the variety
The bushes are semi-standard, reaching a height of 50-70 cm. There are a lot of leaves, so the plant needs timely formation. From 8 to 10 large and juicy fruits grow on one bush.
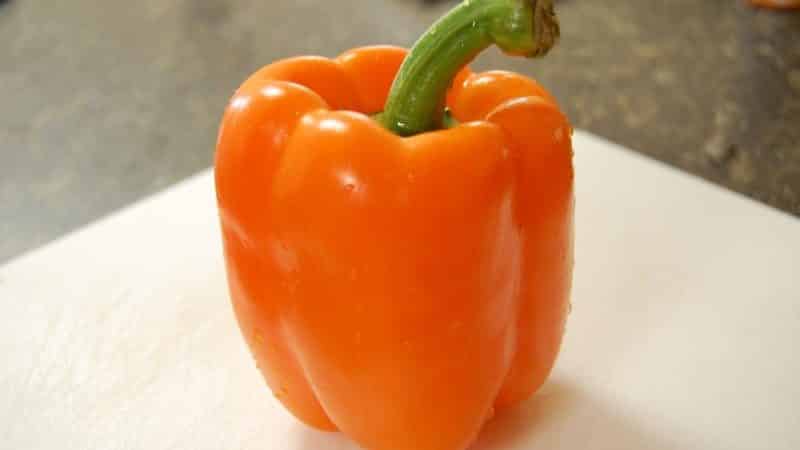

Fruit characteristics and yield
The weight of the vegetable is from 120 to 200 g, in some cases reaching 300 g. The color is bright orange, the pulp is high in sugar. The wall thickness is 7-9 mm, so the peppers are perfectly stored. From 1 square meter, summer residents collect about 7 kg of beautiful and aromatic vegetables.
Interesting! Big Girl peppers make an excellent base for stuffing. The peppers are peeled from the stem and seeds, stuffed with vegetables, meat, and herbs. The appetizer will decorate any holiday table and will be a tasty addition to the first and second courses.
Preparation for cultivation
For growing peppers provide fertile warm beds. In the fall, the soil is dug up and cleared of weeds and debris. With the arrival of spring, the procedure is repeated, then fertilized with peat or compost. If the soil has a high level of acidity, liming is carried out: the beds are sprinkled with a mixture of dry wood ash and lime.
Next, prepare the seeds. They are inspected for external defects and disinfected with a boric acid solution. After disinfection, the seeds are germinated: placed on a warm, damp cloth and stored in a warm place. Germination accelerates seed germination and strengthens their immunity.
Important! Experienced gardeners prepare the soil for seedlings in advance. Use ready-made compounds or soil from the garden. It is recommended to disinfect the soil with a solution of potassium permanganate and clean it of debris, insects and their larvae.
Growing seedlings
Seedlings are prepared 2-3 weeks before planting on the site. To do this, purchase a container, for example peat tablets or plastic cassettes with trays. Pour soil into a clean container, make small grooves and place 3-4 seeds in each hole. The grooves are sprinkled with earth and watered generously with warm water.
Place the container in a warm sunny place and water it every 5-7 days. 2 weeks after planting, the seedlings are fertilized with ash or a solution of Bordeaux mixture. Fertilizing improves the plant's immunity and prevents the occurrence of diseases. The next fertilizer is applied after 10 days.
Important! Pepper seedlings are sensitive to lack of light, so summer residents organize additional lighting using fluorescent lamps.
When growing peppers in small containers, after 3 weeks they pick and place the seedlings in larger containers.To do this, the sprouts are carefully removed from the container, leaving a lump of earth on the roots and placed in a new container in the ground so that the root system has enough space for healthy development. Also, digging into new soil can save you from fungi and bacteria living in the soil.
Planting peppers in open ground
Peppers are planted after legumes or greens; it is not recommended after potatoes or tomatoes. The optimal distance between the grooves is from 40 to 60 cm. The seedlings are watered abundantly, each seedling is removed and moved to the garden bed. In the first week, the seedlings are covered with polyethylene or film, this helps young peppers quickly adapt to climatic conditions.
Further care
The beds are moistened every 7 days, the amount of water depends on weather conditions. In hot and humid summers, 1 liter is consumed per bush; in drought, from 1.5 to 2 liters. For convenience and water saving, a drip irrigation system is used. Once a week, instead of watering, use nettle infusion. The folk remedy protects against pests and stimulates the healthy development of plants. Water the beds in the morning or evening to avoid sunburn.
Caring for sweet peppers is impossible without organic and mineral fertilizers. From organic matter, compost, humus, wood ash, and liquid manure are used. Fertilizers improve the taste and quality of fruits and saturate the soil with nutrients. Superphosphate, ammophos, nitrophoska, and ammonium nitrate are used as mineral fertilizers. If there is a lack of useful elements, the plants dry out, leaves curl and turn yellow.
Features of growing the variety and possible difficulties

Summer residents recommend forming peppers 3 weeks after planting. The procedure improves yield and has a positive effect on fruit size.It is enough to remove weak and growing shoots. To prevent the plant from breaking under the weight of heavy fruits, it is tied to a wooden peg installed near each bush.
Also, special attention is paid to the dosage of minerals. An excess of nitrogen leads to the wilting of the plant, an excess of potassium leads to the development of infections. You cannot add minerals and ash at the same time; because of this, green mass increases and the fruits remain small. Abundant watering and sprinkling the beds with wood ash will help solve the problem of overabundance.
Typical diseases and pests
Pepper yields are affected by whiteflies and aphid. The flying little bugs are difficult to see with the naked eye, so it is recommended to regularly lift the leaves and inspect their back side. Pests gather in flocks and suck the juice from the plant, which is necessary for healthy development. As preventive measures, the rules of disinfection and crop rotation are observed. For treatment, spraying with ash or whey solution is used.
Another well-known pest is the Colorado potato beetle.. Both adults and larvae are dangerous. Insects live in the ground, and with the arrival of summer they appear on the bushes. The striped pest can destroy up to 100% of the crop. They get rid of the beetle using professional preparations “Tornado” or “Fundazol”. 
Late blight is a typical disease for pepper. The fungus develops in hot and humid summer conditions. It appears as brown spots on the leaves and drying out. For prevention purposes, ash or iodine solution is used; for treatment, a solution of copper sulfate or Bordeaux mixture is chosen.
In addition to late blight, black bacterial spot is found on the beds. Dark spots appear on the pepper and stem, which become larger over time. If infected, plants are removed from the garden bed and burned. For preventive purposes, spraying with infusion on burdock leaves is used.
Advantages and disadvantages of the variety
The Big Girl variety has stable yields. The vegetable is successfully planted both in open ground and in a greenhouse. The fruits are large, with a dense peel. The harvest is stored for up to 3-5 months and does not lose its taste and beneficial properties.
Universal in use, it is prepared from pepper preparations for the winter, stuffed, used for preparing appetizers, vegetable salads, side dishes. The commercial quality of the Big Girl variety is excellent; it attracts with its bright color and pronounced aroma.
Among the disadvantages, the need to form a bush is noted. If this is not done in time, then many unnecessary shoots appear, and the fruits do not have enough nutrition for healthy development.
A variety with a similar name - Big Boy

The main difference between the Big Girl and Big Boy varieties is the color of the fruit and a more elongated shape.. If the Big Girl has an attractive orange color, then the second peppers are painted in a deep red color.
The fruits of the Big Boy variety are slightly larger, the average weight of the vegetable varies from 150 to 300 g. The taste is sweet, without bitterness. The thickness of the peel is about 8 mm. Like Big Girl, red vegetables are actively used in cooking. They make tasty and healthy fermented dishes, as well as lecho and salads.
Important! The cultivation technology of the varieties is similar. In the northern regions they use the seedling method, in the southern regions they plant seeds in open ground. Care consists of timely watering and fertilizers. I harvest in August, when the fruits become firm.
Reviews from gardeners
To find out what gardeners think about the Big Girl variety, let’s study several comments from popular gardening forums.
Natalya, Sochi: “I have been growing Big Girl bell peppers for two seasons in a row. I like the juicy and sweet pulp, it is tasty and goes well with other vegetables. The walls of the vegetable are dense, I store the harvest in the basement until winter.”
Pavel, Moscow: “I put Big Girl in a greenhouse. The vegetables started growing quickly, but the fruiting period came late. I took care of it as usual, watered it and fertilized it with nitrogen-containing fertilizers. From 3 sq. m collected only 7 kg of pepper.”
Olga, Volgograd: “Big Girl orange pepper is my favorite. It is unpretentious in care, and the harvest is always rich. A month after planting, I form a bush and water it with organic matter 2-3 times during the season. I recommend it to everyone."
Conclusion
Bright pepper Big Girl does not require special care. Seedlings are prepared at the end of March and planted in open ground after frost. Pepper loves warmth and light, so choose spacious and well-heated beds for planting. Water the vegetable only with warm water; for convenience, a drip system is built. Fertilize the beds with liquid manure, ash, Bordeaux mixture, and superphosphate.
Harvest after the peppers turn orange. The vegetable is picked along with the stalk, wiped with a dry cloth and stored in the basement. The vegetable is great for stuffing and preparing healthy and dietary dishes.