Is it necessary to remove stepsons from peppers: arguments for and against, step-by-step instructions for removing stepsons and useful tips
Pepper is a delicate and whimsical plant that requires constant care. Among the main principles of agricultural technology for growing peppers is mandatory pinching during the period of intensive growth and ovary formation. With strict observance of pinching rules, the quantity and quality of fruits increases several times without additional watering and fertilizing.
What is stepsoning
Stepchildren are shoots growing from the axils of the leaves from the main stem of the plant. Pinching is the manual removal of excess side shoots.
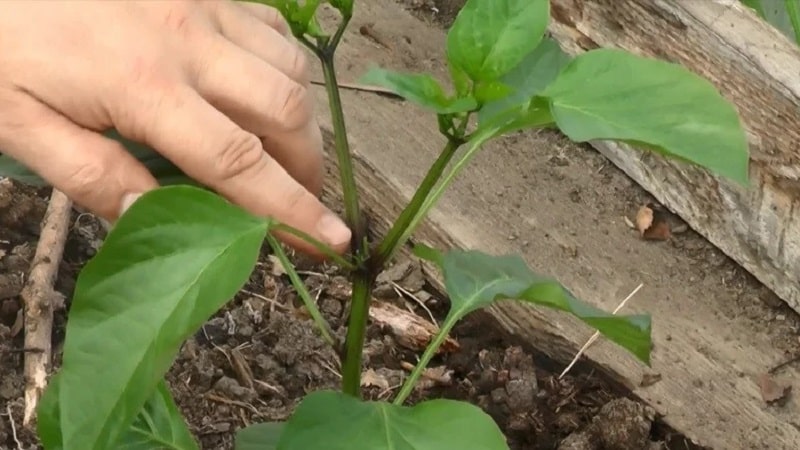

Why do stepchildren cut off
Removing excess shoots on the bush helps the plant retain a lot of strength and nutrients that go into the formation of vegetative mass. After eliminating unnecessary parts, the bush instantly produces a lot of high-quality ovaries.
Is it necessary to chop peppers?
The need for pinching pepper directly depends on weather conditions.
In hot and rainy weather, pepper actively forms side shoots and thickens the bush. Abundant vegetation prevents sunlight and increases the risk of infection with fungal spores. In this case, pinching not only increases productivity, but also prevents the development of late blight on the site.
During dry periods, the bushes produce a small number of shoots. A sparse crown does not sufficiently shade the stem and root zone.The soil dries out quickly due to the lack of shade from the leaves; the beds require mandatory mulching.
Important! Experienced vegetable growers recommend pinching all tall and hybrid varieties of peppers. Varieties with a bouquet type of fruiting, such as Winnie the Pooh and Kapitoshka, do not bear stepson under any growing conditions.
Points for and against
Pepper is a delicate and vulnerable vegetable crop. Before removing stepchildren, it is worth weighing all the arguments and take into account the comments of agronomists.
The advantages of removing shoots from a bush include:
- prevention of the development of fungal diseases of nightshade crops;
- intensive appearance of ovary on bushes and increased yield;
- increasing the flowering period of the bush in open ground.
You should be careful when removing side shoots from diseased plants.. Weakened pepper bushes often cannot withstand the traumatic procedure and die. Beginners often do not know how to properly thin out and carelessly remove important ovaries.

Growing sweet bell peppers
No more than 10-12 fleshy peppers can fully form and ripen on a pepper bush. A larger number of fruits will yield a harvest with low technical indicators. The peppers will be rough-skinned, bitter in taste, small and gnarled.
Acute
Hot pepper varieties such as Tabasco, Habanero, Flame, Confetti, have small fruits and grow into lush bushes. They look decorative and bush abundantly and do not require pinching. Hot peppers with large fruits are grown similarly to tall salad peppers.
How and when to plant peppers
Growing sweet and bitter peppers is carried out with extreme caution.so as not to damage delicate and whimsical plants.As a rule, the optimal period for removing excess shoots occurs with the appearance of full 10-11 leaves on the bush.
Attention! Until the bush reaches 30 cm, removing stepsons is strictly prohibited due to the weakness of the plant.
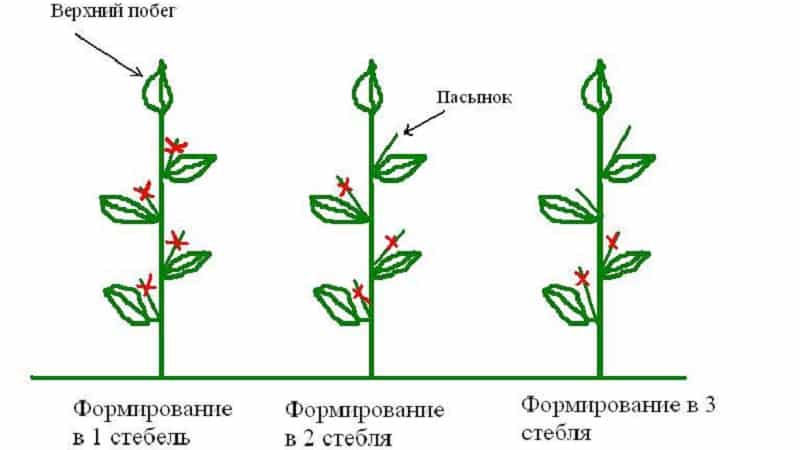
Scheme
The scheme for pinching a pepper bush is extremely simple.:
- Upon careful examination of the bush, 2-3 leading shoots are selected, which will become the basis.
- When cleaning a bush, remove all the stepsons, flowers and leaves that grow on the stem up to the first fork.
- After sanitary cleaning of the stem, the growing points of the remaining 2-3 shoots are pinched to stimulate lateral branching.
- On the forks of the second order we leave one flower at a time, the rest are removed.
It is recommended to remove those flowers that look inside the plant.. Thus, as the fruit ripens outside the plant, the bush will become better ventilated.
Optimal scheme of the formed bush - these are three main branches on the main stem and 4-5 flowers on each of them.
Required Tools
Tall varieties of peppers and peppers growing in a greenhouse are pruned using sharp garden pruners with long thin blades. It is recommended to pinch the growing point manually, without cutting tools.
In a garden with beds of 20-30 bushes, pinching is done manually, without additional tools.
Step-by-step instruction
The process of cleaning a plant looks like this:
- The bush is carefully examined.
- Choose 2-3 main shoots.
- Remove leaves and flowers up to the fork.
- Clean the crown, pinch the growth point.
Stumps 2-3 mm long, no more, are left on the stem. The sprouts do not need wound treatment.
Interesting things on the site:
When to pick peppers in a greenhouse
The nuances of pinching in open ground
In the garden, in the field, peppers are not protected as much as in a greenhouse. The intensity of thinning is less than in closed greenhouses, but the scheme is the same.
In the greenhouse
In protected soil conditions, crops grow actively and thicken quickly. Excessive development of the vegetative part harms the yield; thinning is carried out intensively. The top of the bush is pinched closer to the end of the season, and not in the spring.
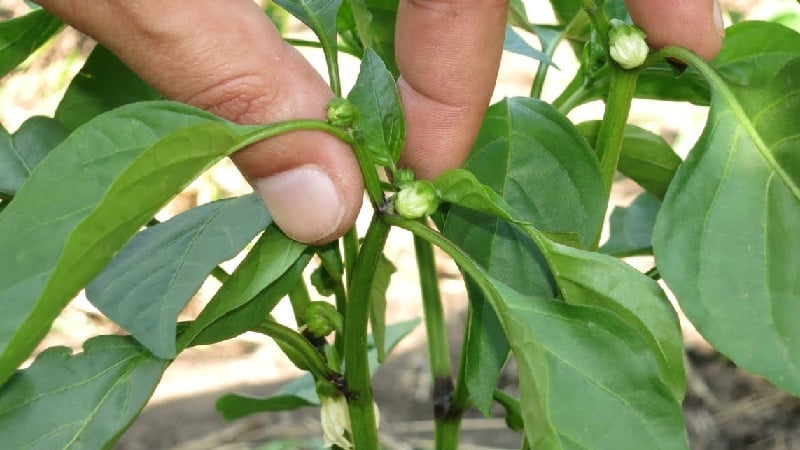

Advantages and disadvantages of stepsoning
In addition to increasing the overall yield, pinching creates additional favorable conditions for the growth and development of pepper.
Bushes after removing excess parts:
- well ventilated, especially indoors;
- receive sufficient sunlight and moisture.
Well-groomed beds are easy to look after, identify diseases and pests at the initial stage of damage.
Pinching is stressful for any plant, especially peppers.. After removing the vegetative part, the bush gets sick for some time and recovers. It is recommended to carry out the first cleaning of seedlings within a strictly specified period (9-10 real leaves). Otherwise, the plant will begin to form extra shoots, which will lead to a reduction in yield by 30-40%.
Inexperienced gardeners often damage fragile plant stems, remove strong buds, form a thickened crown. Regular practice will help you avoid such mistakes.
Useful tips from experienced summer residents
Summer residents with extensive experience have noticed the following:
- Pepper is a collective crop and grows better in proximity to each other. If the bushes are planted at a considerable distance, gentle pinching is carried out.
- If the pepper is sick or damaged by pests, cleaning will lead to the death of the plant.
- You should not leave limp and small buds on the bush, which will not bear fruit, but will take away the strength of the plant.
It is recommended to carry out pinching in dry, fine weather. weather at sunset.
Conclusion
Growing peppers is the most important agrotechnical procedure. With proper practice, a careful and responsible approach to business, the question of whether it is necessary to pluck peppers disappears by itself. And the harvest pleases the hardworking vegetable grower with quality and quantity.