Why is tomato anthracnose so scary: we study the disease and effectively fight it ourselves
Beginning gardeners often encounter diseases tomatoes. In such cases, it is important not to miss time to fight, otherwise the entire crop may die. In this article we will talk about a common disease - anthracnose of tomatoes. What kind of disease is this, can it be cured and what preventative measures exist? Read the advice of experienced summer residents and photos of plants infected with anthracnose in our article.
Anthracnose - what kind of disease is it?
This fungal disease, caused by pathogens of the genus Colletotrichum, is more typical for ripe and overripe tomatoes. It can spoil the presentation of the fruit and even destroy the entire harvest.
Most often, anthracnose develops in regions with high humidity, both in open ground and in film greenhouses. Affects tomatoes, potatoes, cucumbers, pepper, eggplant, melons, shrubs and fruit trees. Can be widespread.
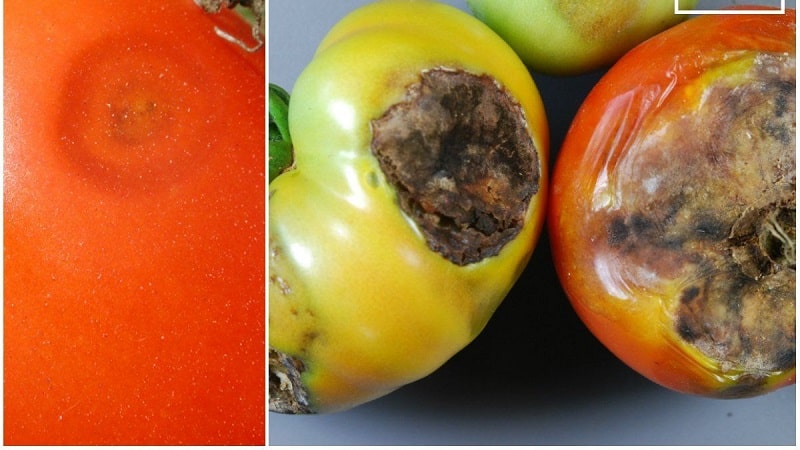

How does it affect tomatoes?
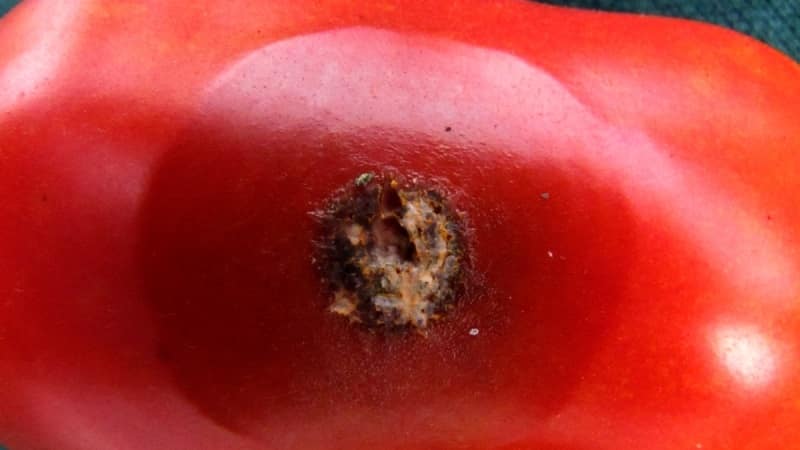
The photo shows that tomato fruits infected with anthracnose lose their attractive appearance. Spots of various shapes appear on them, under which rotting and tissue destruction occurs.
The formations may acquire a dark color due to the fact that hairs begin to appear on the body of the pathogenic fungus. When the fruit is cut, a mucous, jelly-like mass of pink color appears, containing spores of the microorganism.
Important! The disease can also affect green fruits.
Description of symptoms and external signs
There are two types of anthracnose: affecting leaves or fruits. At risk are plants that have mechanical damage through which the fungus gets inside.
The causative agent of green mass disease is a fungus Colletotrichum atramentarium, adult plants suffer from it. First, the upper leaves wither and the roots weaken; the tomato can be pulled out without difficulty. Small black sclerotia appear on the diseased plant, while the central cylinder is exposed.
Anthracnose of fruits is caused by fungi Colletotrichum phomoides.
The disease can be recognized by the following external manifestations:
- the appearance on ripe fruits of spots of various shapes with a diameter of 5-15 mm;
- darkening of the affected areas;
- formation of pink sporulation on the spots;
- rotting and destruction of fetal tissue.
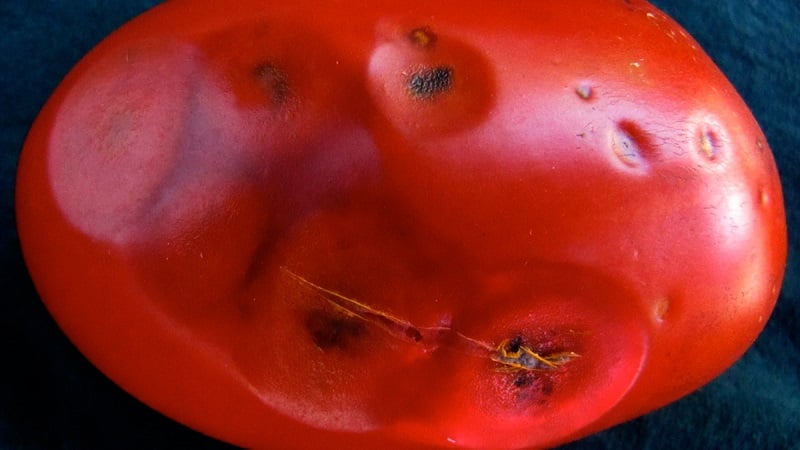
Reference. The disease affects only those fruits that touch the ground; the crop on the upper branches remains intact.
A sick fetus may become re-infected. This happens when cracks appear in damaged areas that contain fungal spores.
The fungus also penetrates green fruits, in which case the disease appears after harvest. When cleaning the area, you need to pay attention to the stems and foliage of tomatoes: if the plant is infected with anthracnose, then small lesions will remain on it.
Important! Infected ones cannot be used seeds, otherwise you will grow a fungus along with the tomato.
As they ripen, small round and depressed spots will form on the green fruits, which will later become darker in color.
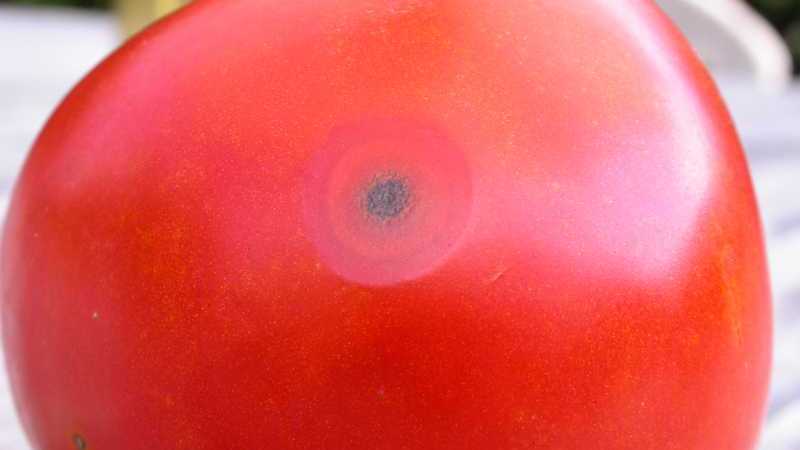

Causes of appearance and infection
The infection spreads very quickly throughout the area. It affects not only tomatoes, but also other crops.Anthracnose can often be seen on fruit plants.
The causative agent of the disease
Favorable conditions for the functioning of the fungus are moderate air temperatures up to 30 degrees and high humidity. Fruits with reduced disease resistance are susceptible to anthracnose.
Factors contributing to the development of the disease are lack of phosphorus and potassium and increased soil pH.
Terms of distribution
The disease is transmitted through gardening tools, containers, plant remains, seeds, and is also carried by insects. Low air temperatures do not kill the fungus - it overwinters in the ground. Spread occurs through rain, wind, dew and watering.
The pathogen poses a particular danger during periods when the fruits and leaves of a plant remain wet for a long time - at the end of summer and autumn.
How and with what to treat
If diseased plants are found, the infected areas must be removed and burned. Then treat the rest of the bush along with the fruits with preparations.
Chemicals
Anthracnose is a fungal disease that is treated with fungicides. Every year the number of drugs increases, some of them are banned due to the presence of dangerous compounds.
The most effective means:
- "Kuproksat";
- "Oxychom";
- "Acrobat MC";
- "Ridomil Gold";
- "Polyram";
- "Tiovit Jet";
- "Previkur";
- "Skor."
Preparations based on Bacillus subtilis are also suitable for the treatment of tomato anthracnose. You can spray sick plants with Polyrama solution: 2.53 kg will be needed per 1 hectare. Good results are also observed when using Cumulus DF.
You should not expect that the disease will be defeated in one treatment: The procedure will need to be carried out 2-3 times with an interval of one week.To prevent the pathogen from getting used to the current composition of the product, you can change the drugs.
More gentle means will help slow down the spread of anthracnose: "Gamair" and "Fitosporin-M".
Traditional methods
You can try to save the crop with the help of copper oxychloride: 40 g of the substance is dissolved in 10 liters of water. You can also use 1% Bordeaux mixture or colloidal sulfur.
Agrotechnical techniques
You can resist the disease and reduce the rate of its spread if you loosen the soil every time after watering and after rain.
It is also necessary to alternate crops. It is recommended to plant tomatoes in their original place only after 3-4 years.
Preventive measures
In the prevention of anthracnose, general phytosanitary methods are used. To do this you should:
- purchase seed material from trusted producers;
- Before planting, treat the seeds with fungicides or heat them;
- observe crop rotation;
- regularly remove weeds and plant debris from the site;
- do not over-water the plant;
- regularly ventilate the greenhouse;
- do not neglect plant staking;
- treat seedlings with fungicides;
- disinfect garden tools;
- harvest during the period of expert ripeness, avoiding overripening;
- When growing fruits, try to avoid mechanical damage;
- store the crop at a temperature of 5-6 degrees.

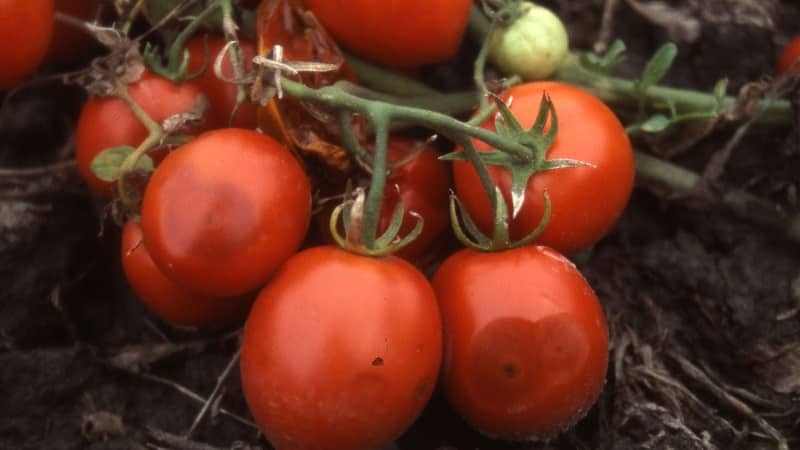
Advice from gardeners
One of the preventive measures is timely harvesting. How to determine the ripeness of a tomato? Expert ripeness is the period when a star-shaped redness appears at the top of the fruit.
In regions with high humidity, many gardeners prefer varieties that are resistant to anthracnose: LSL hybrids F1 Life, Shelf, Longf.
Before planting, you can soak the seeds in solutions of preparations. "Agat-25" (7 g/1 kg) or "Immunocytophyte" (2 ml/1 kg). During the growing season, it is recommended to spray with “Novosil”, and when 2-3 leaves appear – with “Agatom-25” (14 g of product will be needed per 1 hectare).
For prophylaxis, the drugs “Quadris”, “Strobi” and a 1% solution of Bordeaux mixture are used.
Important! To treat the greenhouse, use bleach: 200 g of the substance must be dissolved in 10 liters of water.

Conclusion
Anthracnose is a dangerous disease that makes tomato fruits unfit for consumption. Most often, the disease affects plants grown in greenhouses. It is much easier to make efforts to prevent a disease than to try to cure it.
A novice gardener should not neglect general phytosanitary measures: they can protect the crop not only from anthracnose, but also from other dangerous diseases. If the disease takes you by surprise, you need to burn the damaged bushes and treat healthy plants with effective chemicals.