Step-by-step instructions for beginner gardeners: how to pinch watermelons in open ground
Growing watermelons requires certain skills and knowledge. In order for the fruits to have time to ripen and be sweet, it is important to grow them correctly from the very beginning. Beginning gardeners often have a question: how to pinch watermelons in open ground and is it necessary to do this?
Why pinch watermelons?
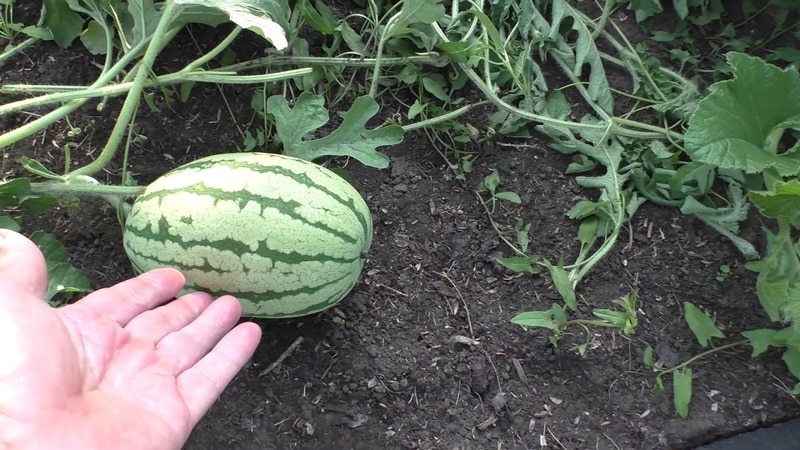

To limit the number of ovaries, plants are pinched. When a lot of fruits form on the vine, they become smaller and do not have time to ripen. Pinching watermelons is reminiscent of pinching peppers or melons. The procedure is especially relevant in areas with colder climates when summers are short.
Important! Watermelons that have been pinched grow less green mass. They are more convenient to process, weed and water, since you do not have to step on the leaves and stems, which grow strongly.
Is it possible to do without it?
Be sure to pinch plants in cold regions, in northern Russia. Southern cultures manage without it. Sometimes the procedure is not carried out in greenhouses, where the fruits have time to ripen during the season.
For watermelons growing in open ground, pinching is mandatory.
When to carry out
Pinching at the wrong time will have a detrimental effect on the crop. In the northern regions, plants receive less heat and sunlight - there the procedure is done earlier.
Excess shoots are removed when the watermelons begin to grow and shade each other. This is done if secondary processes are noticeable.
Attention! In wet weather, the procedure is not carried out, otherwise the stems will rot. Choose only sunny days.
How many times per season
The procedure is carried out at least twice during the season. It depends on the specific varieties. In the southern regions, heat-loving watermelons Chill, Nice, Favorite and others are rarely pinched; in the northern regions, cold-resistant plants (Ogonyok, Sugar baby, Helen F1, Siberian Lights) - more often.
How to pinch correctly

Pinching watermelons in open ground depends on the climate of the area and the area of the plot.
As a rule, the simplest schemes are used:
- watermelons are allowed to grow freely and spread lashes along the ground;
- When ovaries appear, remove excess shoots and lashes that spread to other areas.
Materials and tools
No special tools are required for the procedure. Cut off excess shoots with a sharp knife or pruning shears.
Reference! It is better to pinch the stems not by hand, but with a sharp tool. This way the cut will heal faster and the risk of damage to the plant will be lower.
Scheme
There are 3 schemes for pinching watermelons:
- Growing in one stem. This method is suitable for both varieties and hybrids. The plants are formed into one vine, leaving only the main shoot, all side shoots are removed. From 1 to 4 fruits are left on the central stem, the rest are removed. By pinching the lash, they retreat from the upper fruit by 5 leaves.
- Growing on second-order shoots. This method is a little more complicated - it is important to observe the growing shoots, recognize the extra ones, and pinch them off in time. The technology is more suitable for varieties: they produce watermelons on their side shoots faster than hybrids. In open ground, seedlings are placed freely, and greenery grows quickly.Therefore, pinching is carried out as soon as the lashes begin to extend beyond the edges of the rows. The formation of lashes begins when the fruits reach a diameter of 5–7 cm.
- Formation of bushes with fruits on shoots of the third order. These shoots are the most productive for the crop; the fruits on them ripen earlier. The method is suitable for regions with short summers. When the young sprout produces its 5th leaf, pinch the stem above the third. Of the grown shoots, 2 are selected, the rest are cut off. On these shoots, branches of the third order are formed, on which watermelons will form. They are pinched over the top 5 sheets.
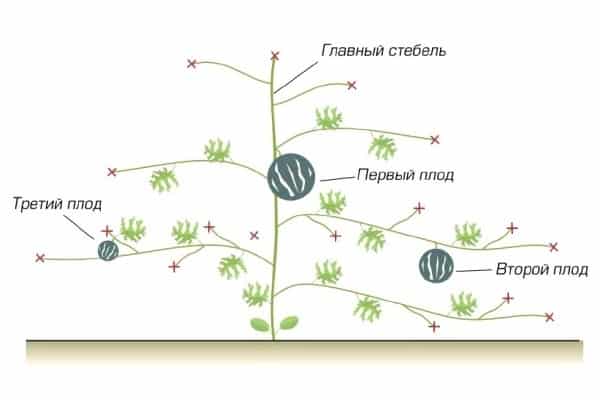
Step by step instructions
Pinching the stem:
- The main stem is left: if it is damaged, the plant will die. Only the stepsons in the leaf axils are harvested.
- No more than 2 shoots are kept on one stem.
- After the procedure, 2 to 6 ovaries are left on each plant. The exact amount depends on the variety. Newly formed fruits are removed.
- Remove all shoots with 5 or more leaves. New shoots are removed before they grow.
- A sprout that does not bear fruit is immediately pinched.
- After the formation of ovaries on the shoot, its upper section is cut off. Only a few leaves are left.
Pinching the top:
- As the watermelon grows, the lashes form.
- The main stem is not touched, only the side shoots are removed.
- Sprouts without fruit or weak ones are pruned after pollination and formation of ovaries.
- On fruiting shoots, only the tops are removed.
The ovaries are pinched in 3 ways:
- With side shoots. This technique is suitable for all varieties. The plant is formed by leaving lateral shoots on the main stem. They are trimmed, leaving 4 leaves. With greenery, the bush continues to develop. 6 ovaries are left on the central stem.As they grow, the lower leaves are cut off.
- No side shoots. The sprouts are cut off, leaving the ovaries on the main stem with an interval of 5 leaves. The growing shoots are removed.
- With side lashes on the main stem. The fruits are formed on the side shoots. All shoots on the main stem are cut off.
No more than 6 fruits are left on the entire plant for better ripening.
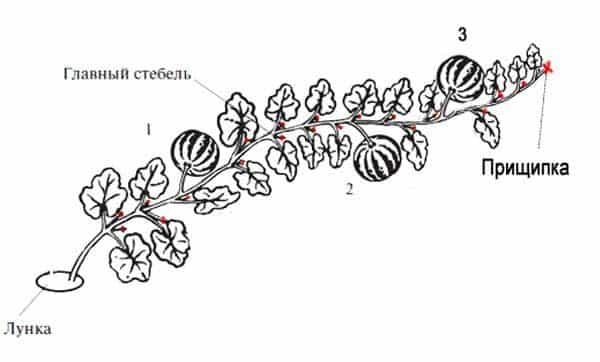
How to trim, shape and plant bushes
Basic methods of plant formation:
- there should not be more than 1-2 fruits per lash;
- all excess ovaries and shoots are carefully trimmed;
- pinching is not carried out when the watermelons begin to grow and fill up: at this time the plant is gaining strength, all procedures will only harm it;
- if there are few leaves left, remove the shoot above the fruit: this stimulates the growth of new leaves;
- choose a specific pinching scheme experimentally.
Pinching in the greenhouse
The culture in closed ground is formed for faster ripening of fruits. Treated plants are easier to care for and space is used more efficiently.
In the greenhouse, 2 procedure schemes are used, since here the plants are tied to trellises.
Formation into one stem:
- Leave the central stem. The sprouts are cut off on the sides.
- The stem is guided along the support, twisting it clockwise.
- 2–5 fruits are left on each bush, the remaining ovaries are removed.
- The top of the main stem is pinched.
In this manner grow watermelons in Siberia and northern regions.
Growing fruits on second-level shoots:
- The number of such shoots is from 1 to 3 pieces. 1-2 ovaries are left on each.
- After the last ovary, 5 leaves are saved and the top is cut off.
- The remaining ovaries and sprouts are removed.
It is important to make sure that the ovaries are growing, and only then pinching. Often fruits the size of a walnut fall off or do not ripen.
Post-procedure care

After pinching, watermelons are carefully looked after:
- Water at least 2 times a week. The amount of water is reduced when the fruits ripen, since waterlogging contributes to cracking of watermelons.
- When the fruits grow to the size of walnuts, they are placed in special nets. This will protect against rotting.
- The soil under watermelons is covered with straw so that the fruits do not touch the ground.
- The culture responds well to mullein, humus, bird droppings, and superphosphate with potassium.
- New shoots are immediately removed so that the plants do not waste their energy on them.
Useful tips
To grow a rich harvest of watermelons, the bushes are formed correctly.
To do this, follow the recommendations of experienced gardeners:
- the crop does not tolerate shading well, so the distance between the fruits and leaves is left no more than 20–25 cm;
- shorten the stems after flowering, when the size of the ovaries reaches 7–9 mm in diameter;
- after the first pinching, supports are placed between the watermelons so that they grow better and do not break;
- After the fruits have ripened, the procedure is not carried out.
Conclusion
With proper pinching of the melon crop, you will be able to get a rich harvest. The watermelon pruning scheme is chosen depending on the region, variety and growing method.
Basic patterns: in one stem, on shoots of the second or third order. This simple procedure does not have a general approach; the best option is determined experimentally.