Why is it necessary to plant cucumbers and how to do it correctly
Growing cucumbers involves the use of important agricultural techniques. Stepchildren is one of them. The procedure is necessary to obtain a healthy plant and a bountiful harvest. Not all gardeners, even experienced ones, carry out pinching. For beginners, removing excess shoots causes certain difficulties without the proper knowledge and skills.
What is stepsoning
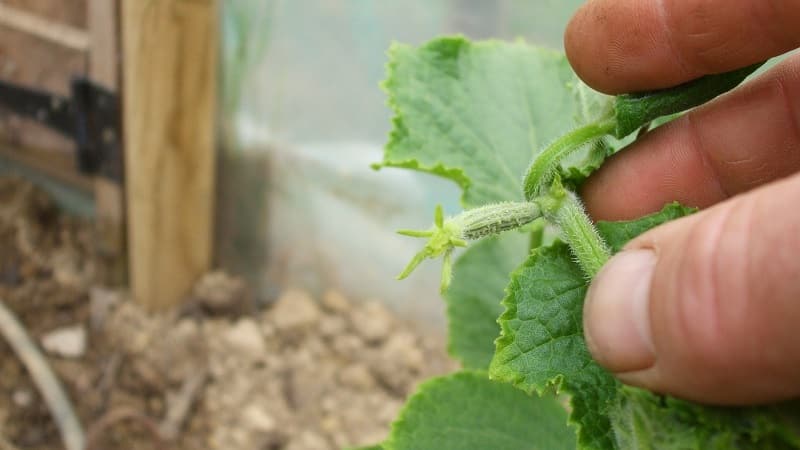
Stepsonning – this is the removal of side shoots growing from the leaf axil (the place between the leaf and the stem). It is necessary for the formation of healthy vines, full flowering and fruit formation. Stepchildren take away juices and nutrients, preventing the formation of flowers, much less fruits. In addition, pinching cultivates an overgrown plant.
Reference. Proper formation of a bush using pinching increases its level of illumination, redistributes nutrients and minerals, which has a beneficial effect on yield.
Why pick cucumbers?
Cucumbers are climbing plants. Without proper care, plantings become very thick, which limits the flow of sunlight and stops the growth and development of the crop. Besides, in dense plantings, air circulation deteriorates, which leads to leaf rot and increases the risk of disease development.

Stepped beds are easier to care for, they are easier to harvest due to better visibility.Such plantings can bear fruit until late autumn, and the fruits ripen much earlier.
Reference. Cucumbers in an open garden can do without pinching, but greenhouse plantings must be thinned out.
When to do it
The timing of pinching largely depends on the time of planting and place of cultivation. (greenhouse or open ground), soil condition, and planting method - direct or seedlings. General recommendations for pinching time come down to the stages of crop growth.
It is recommended to do the first pinching when the plant has reached 15-20 cm in height. The main branch is determined - the most powerful shoot, and all side shoots are removed by pinching or complete removal from the leaf axil. It is recommended to remove more powerful shoots using pruning shears. The last pinching is carried out before the end of July, depending on the climate.
Features of pinching cucumbers
Depending on the growing method, the characteristics of pinching are determined.: different requirements are due to differences in methods of cultivating plantings. The correct scheme is chosen based not only on the growing method, but also on the characteristics of the plants themselves.
In the greenhouse
Compact varieties that are not prone to abundant growth and do not require frequent pinching are suitable for greenhouses.

Pinching is carried out according to bush management schemes - in one or more stems. Topping carried out in several stages.
Read also:
In the open ground
Growing cucumbers in open ground is not popular among vegetable growers. Bushes growing on the ground do not shoot. Plants that need support are subjected to the procedure.Patterns of pinching also differ depending on the type of cucumber - self-pollinating or insect-pollinated.
On the trellis
Stepping on a trellis carried out after at least 4-5 internodes are formed (distance from sheet to sheet). Depending on the management scheme of the bush, pinching up to 3-4 leaves is carried out. Further pinching is carried out according to the chosen scheme.
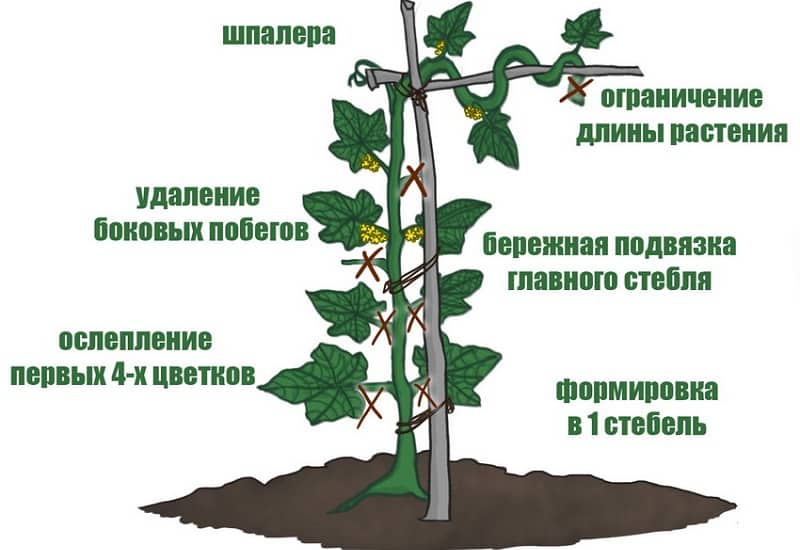
What is needed for the procedure
Most often, pinching is done by hand, but some prefer to work with a disinfected tool.
Used for pinching:
- sharp scissors;
- pruner;
- small knife.
When pinching with your hands, it is better to work with gloves.
How to properly pick cucumbers
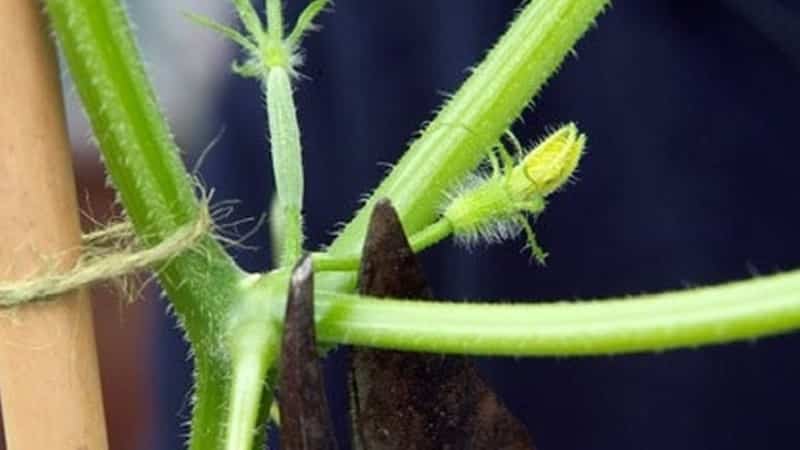
It is important to carry out the pinching procedure correctly so as not to harm the plant.. It is advisable not to allow the stepsons to grow more than 15-20 cm, otherwise it will be difficult to determine which branch is the main one and which is the secondary one: it is easy for an inexperienced gardener to confuse them. The optimal length for pinching is no more than 4-6 cm.
Step-by-step instruction
The general scheme is as follows:
- The leaf with the stepson is pulled in the direction opposite to pinching or cutting.
- The shoot is broken off as close to the stem as possible, being careful not to damage the skin of the leaf or stem.
- When working with a tool, the stepson is cut as low as possible.

Possible schemes
There are several pinching schemes for forming bushes.
The universal scheme is suitable for both self-pollinating varieties, and for varieties with insect pollination:
- After 4-5 leaves appear, all lower lateral ovaries and stepsons are removed.
- After the formation of the 8th leaf, all side shoots are removed, except one - the top one.
- The next pinching is carried out after 10-11 leaves on the main shoot.Remove all stepsons on the main and side shoots, leaving two side shoots at the tops.
- When the main branch reaches a length of 50-60 cm, break off the top for more competent formation of the remaining side shoots. Small stepsons on all branches are removed.
The scheme for forming a bush into one stem is suitable for plants with insect pollination. This arrangement makes it easier for pollinators to access flowers:
- All side shoots, flowers and ovaries are removed up to the fifth leaf.
- At the level of 6-9 leaves, one ovary is left per internode.
- From the 10th leaf, all stepsons and fruits are left untouched.
Formation into several stems is necessary for varieties whose fruits tied precisely on the lateral branches:
- After the formation of 5-6 true leaves, all stepsons, flowers and ovaries are removed, leaving only one upper stepson - it will later become the second main branch.
- Up to 9-10 leaves are left, one fruit per internode. The main branches are directed in different directions along different supports.
- Further pinching is carried out as the lateral branches grow.
Another scheme is to maintain a bush with two stems. It is almost no different from the multi-stem scheme, except that the stepsons are removed completely after the formation of the second main branch.

Do all cucumbers need to be pinched?
Not all varieties need pinching. To save yourself from this procedure, plant varieties that grow not in vines, but in bushes. Also, hybrids that do not form lateral branches do not need pinching.
The most popular hybrids are:
- Regina Plus F1;
- True friends F1;
- Bouquet F1.
Bunch varieties include:
Varieties and hybrids that do not require pinching:
- Snowstorm;
- Gribovchkanka;
- Sarov F1.
Advice from experienced summer residents
Even experienced gardeners will benefit from advice "colleagues":
 It is recommended to plant not only the side shoots, but also the tendrils - they are not needed at the level of 6-7 real leaves.
It is recommended to plant not only the side shoots, but also the tendrils - they are not needed at the level of 6-7 real leaves.- The procedure can be carried out by hand, but it is easiest to do the cutting with sharp scissors or garden pruners - this will avoid unnecessary injuries to the plant.
- You should not feel sorry for the stepsons on which ovaries have already formed - they will only take away nutrients from the main ovary and slow down ripening.
- For long-term fruiting, the stepsons are removed along the entire length of the main branch, the crown of which remains intact.
- You should not delay the first planting - early removal of excess shoots will have a beneficial effect on the formation of the root system, which will subsequently feed the entire plant.
- It is better not to remove stepsons whose length has already exceeded 20-25 cm - this will not bring any benefit to the plant. Such a stepson can be left and launched as a side branch.
- For pinching with tools, it is recommended to have separate scissors or pruners. If diseased or old leaves or branches were previously removed with a tool, an infection may be introduced to the wound site. If it is not possible to use a special tool, it is advisable to disinfect the scissors before the procedure by calcining them over a fire or soaking them in a slightly pink solution of potassium permanganate.
Conclusion
Stepping is a painstaking process, and often difficult for a beginning gardener. At first, it is better to enlist the support of more experienced farming colleagues in order to understand the principle and learn to distinguish the stepson from the main branch, especially on young plants and with overgrown side shoots.