How to plant an apple tree in the fall and how to do it correctly
Grafting is an effective way to increase fruiting, rejuvenate, and improve the taste characteristics of apple tree crops. Beginning gardeners are often afraid to graft trees, considering this procedure to be complicated and accessible only to professionals. In fact, if the timing is correctly chosen and the instructions are followed, new branches can easily and quickly take root in apple trees.
The optimal time for grafting is considered to be spring, when the trees are just beginning to flow sap, and before winter frosts the new cuttings have time to get stronger and take root. If the work could not be completed during this period, it is successfully carried out in the fall.
Why graft an apple tree?
Vaccination is not included in the list of mandatory procedures when growing apple trees. Many gardeners have maintained apple orchards for decades without grafting any of the trees. However, sooner or later such a need arises.
Some start vaccinate still young trees, achieving improved quality of plantings. Nurseries often sell already grafted seedlings.

Vaccination has different purposes:
- Rejuvenation. Over time, the yield of trees decreases, the fruits become smaller, and their taste becomes worse. In some cases, plants stop bearing fruit altogether. They correct the situation by removing old branches and grafting new ones onto them. cuttings. This way the tree will receive a strong, developed base and young fruit-bearing branches.
- Cultivation of wild animals. If the apple tree was grown from a seed, most likely it will be wild with small and sour fruits. The advantages of such plants are high frost resistance and endurance. To maintain resistance to negative environmental factors and improve the quality of the fruit, branches of cultivated trees are grafted onto the game.
- Space saving. In small areas there is not enough space for landings a large number of trees. To grow more varieties, branches from different apple trees are grafted onto one plant.
- Growing non-registered varieties. If you want to cultivate a variety that is not suitable for the local climate, it is grafted onto zoned apple tree varieties.
- Rescue of trees damaged by rodents or frost. New shoots are grafted in place of damaged branches.
- The desire to experiment or decorate the garden with unusual trees. A tree on which apples of different colors, shapes and sizes hang looks original. The apple tree is suitable for grafting some other stone fruit plants - this combination is amazing.
When is it better to plant: spring or autumn
The best time for vaccination is spring. At this time, sap flow begins, tissue growth is activated, so the scion easily grows together with the tissues of the rootstock. In addition, there is enough time left before winter for the plants to take root, grow stronger and easily withstand frosts.
Spring vaccination is performed in all regions of Russia. Only the exact timing of the work depends on the climate.
Although spring is considered the optimal period for such work, you can graft an apple tree almost all year round. Even in winter this is done at home.
Attention! Spring is a more suitable time for vaccination, but this procedure is also carried out in the fall.
If the procedure is performed correctly and the appropriate timing is chosen, the new branches can easily take root.
Advantages and disadvantages of autumn vaccination
Grafting an apple tree in the fall has the following advantages:
- Favorable weather conditions. In autumn it is no longer as hot as in summer, but it is not yet cold. It is comfortable to work in the garden at this time.
- Possibility to correct spring errors. If the grafts do not take root, you can add new branches to the tree in the fall.
- The ability to accurately assess the condition of the branches. After wintering, some shoots die and become frostbitten. In the spring this happens unnoticed, and the cuttings will not take root on them. In autumn it becomes clear which branches are strong enough and which are not.
Some gardeners refuse the autumn procedure due to its disadvantages:
- Some of the grafts will not have time to take root and will die after wintering.
- Buds will awaken and new shoots will begin to form only next spring.
- Tissue fusion occurs more slowly in autumn than in spring.
- Not all grafting methods are suitable for autumn.
Timing and features of autumn vaccination
The timing depends on the region and method of work. It is important to have time to graft the apple tree 2-3 weeks before the temperature drops below +15°C. The beginning of September is suitable for carrying out any work, including budding. In October, it is allowed to graft an apple tree using all methods except budding.
It is best to graft young 2-3 year old trees in the fall. Grafting old apple trees is possible, but the chances of successful tissue fusion are less.
Hot or rainy weather is not suitable for work. It is better to do this on cloudy but dry days, in the morning or evening.
Required materials and tools
For vaccination you will need some tools:
- Secateurs for trimmings thin branches.
- A sharp garden knife or saw for cutting thick branches and giving the cuts the desired shape.
- Garden tape for wrapping cuts. It can be replaced with film, tape or electrical tape.
- Garden varnish for covering cuts. Some gardeners use whitewash or other disinfectants.
- Screwdriver. It is used to make splits in thick branches.
- Budding knife. This is a tool with a rounded blade and a sharp plastic end on the opposite side for peeling away bark.
Rootstock selection and preparation
For grafting, zoned varieties are chosen. Trees must be strong, robust and hardy. It is important that there are no growths, compactions, deformations, changes in the color of leaves, cracks in the bark and other signs of disease and pests.
The branch itself (or trunk) to which the shoot will be grafted must be perfectly smooth, without bending or growths.
Attention! To maximize the plant's hardiness, it is grafted onto wild plants.
The best rootstock for apple branches is an apple tree. Here the chances of survival are equal to 100%. However, other plants are also suitable for grafting:
- Rowan. The apple tree takes root better on the red-fruited variety than on the black-fruited one. It should be taken into account that when grafted onto rowan, apples often become smaller and taste more sour.
- Hawthorn and viburnum. Apple tree branches are grafted onto these shrubs to increase their winter hardiness. But the fruits will become smaller and taste less sweet.
- Quince. It is used as a rootstock for apple trees, but the chances of survival will be low. This proximity leads to crushing of the fruit.
- Pear. It takes root well when grafted onto an apple tree. Apple rootstocks do not take root as well on pears.
2 days before grafting the rootstock watered and feed. Use fertilizers containing nitrogen.
Scion
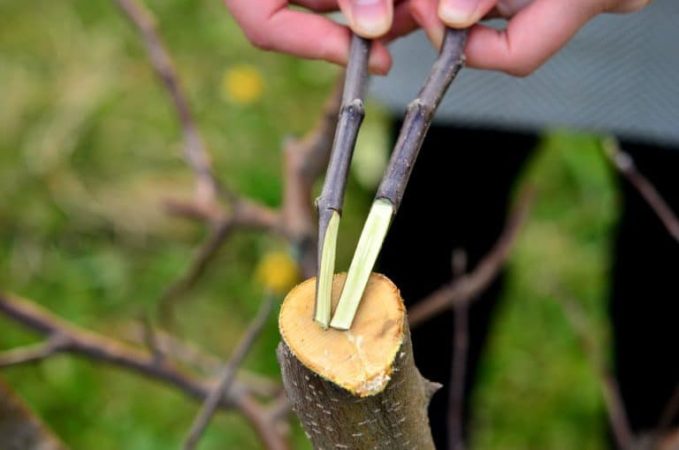
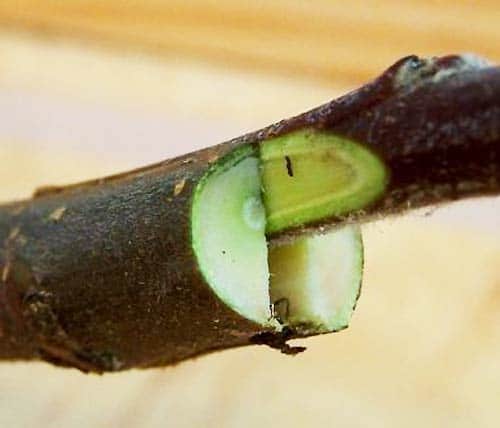
As a scion, they take a shoot or bud of a plant that has already bear fruit: an apple tree or another suitable crop. It is important that the branch is smooth, without growths, bends, deformations, cracks in the bark, stains and other signs of infection by diseases and pests.
There should be at least 2 living buds on the scion. It is better to use the central part for grafting.
Advice! To ensure a neat cut, the tool is sharpened before use.
The scion is cut in one quick, even movement to avoid the formation of jagged edges; the cuttings are cut at an angle of 45°. The bud is cut out along with part of the bark and wood.
How to properly plant an apple tree in the fall in different ways
There are several ways to graft apple trees. Below are step-by-step instructions for the most popular ones.
Budding

Budding is the grafting of a kidney. In autumn, a sleeping eye is used. It should be elastic, without peeling, deformation or damage.
Budding is carried out from mid-August to early September. For beginners, it may seem difficult to follow, but if you follow the instructions step by step, the method gives the highest survival rates.
How to graft a bud onto an apple tree in a T-shaped cut:
- The scion bud is grafted in place of the bud on the rootstock. The selected area is wiped with a damp cloth to remove dust and dirt.
- A T-shaped cut is made on the rootstock bark. The vertical notch should reach 3 cm, and the horizontal notch should reach 1.5 cm.
- The scion bud is cut from a one-year-old branch. The width of the scion should be 1.5 cm, and the length should be 3 cm. The knife is held almost parallel to the bud.
- The bark flaps on the rootstock are pushed apart. The graft bud is inserted into the resulting window.The valves are closed, and the peephole should be located in the center of the cut and look out.
- The junction of the rootstock and scion is wrapped with film or garden tape, without touching the eye.
Copulation
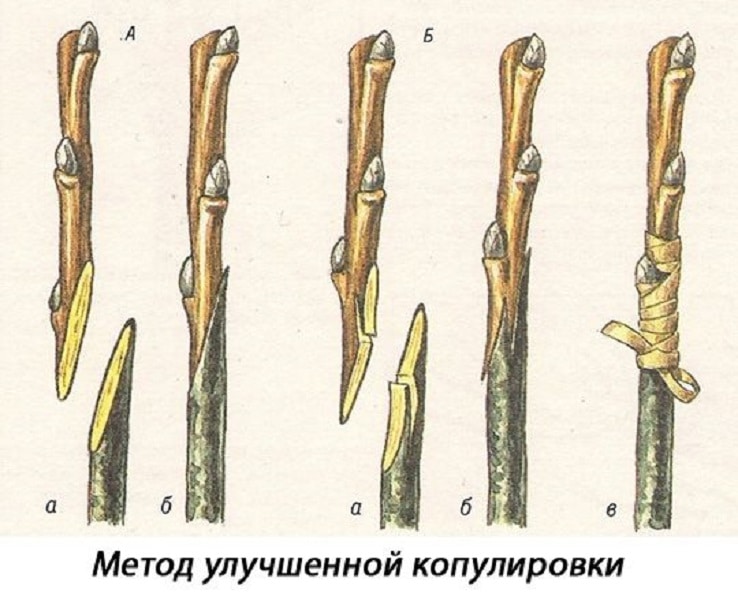
The method is used when the diameters of the rootstock and scion are the same. It involves connecting branches and tightly wrapping them. The method is simple to implement, but does not always give good survival rate.
Copying instructions:
- An even oblique cut 3-4 cm long is made on the rootstock. To make it smooth, they work with a sharp tool and move towards themselves.
- The lower end of the scion is cut obliquely. It must match the rootstock. The scion should have 3-4 buds, its length should be from 10 cm.
- The scion cut is pressed against the rootstock cut with rubbing movements so that the cambial layers coincide. It is important that there are no free areas left.
- The junction is tightly wrapped with electrical tape or film. All open sections of the cuts (for example, in the upper part of the scion) are coated with garden varnish.
An improved copulation method is used, which increases the chances of survival:
- Identical oblique cuts 3-4 cm long are made on the scion and rootstock. It is important not to touch the cut parts with your hands and work with gloves.
- 1/3 of the length departs from the bottom of the cut of the rootstock. Make a notch 1 cm deep.
- On the scion, 1/3 is removed from the top of the cut and a notch is made 1 cm deep.
- The scion and rootstock are connected by inserting the resulting tongues at the notches into each other, like puzzles.
- Make a winding at the junction of the scion and rootstock.
Into the cleft

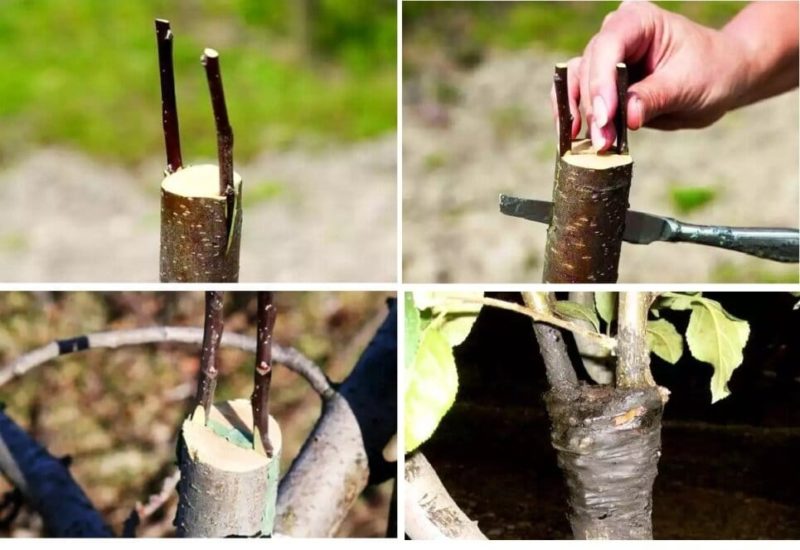
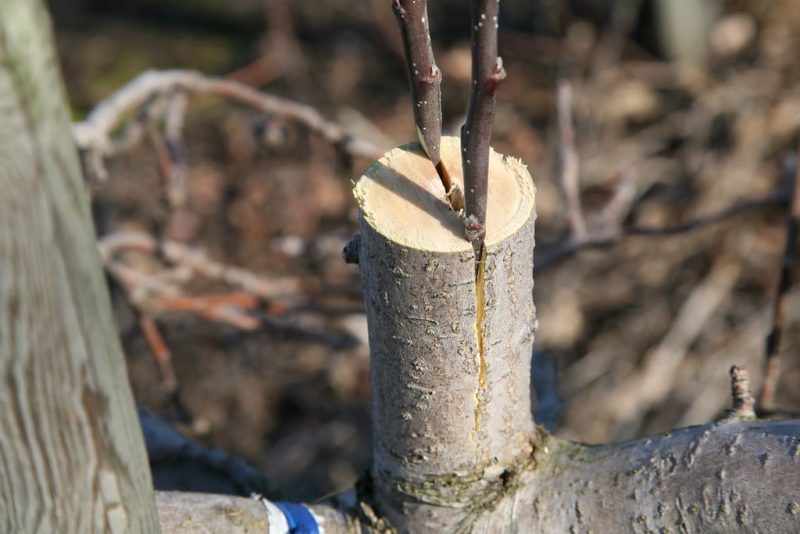
This is the easiest way. It is suitable even in cases where the rootstock has a significantly larger diameter than the scion (for example, when grafting branches into the trunk). In this case, several rootstocks are fixed on one scion.
How to graft an apple tree into a cleft:
- The scion is cut at a right angle. Its role is played by both the branch and the trunk. In the second case, the grafting is done no lower than at a height of 15 cm from the ground.
- The scion cut is cleaned of debris and dust with the raised side of the glove. A split is made in the center. For thin scions, the depth of the split should not exceed 3 of its diameters. For thick rootstocks, the depth is 5–8 cm. To prevent the split from closing on such rootstocks, a spacer, for example, a screwdriver, is inserted into it.
- The lower part of the scion is sharpened with a flat wedge on both sides. Its length should be equal to the depth of the split.
- The scion wedge is inserted into the split of the rootstock.
- The junction is wrapped with garden tape or electrical tape. Open areas of the cut are covered with garden varnish.
For the bark
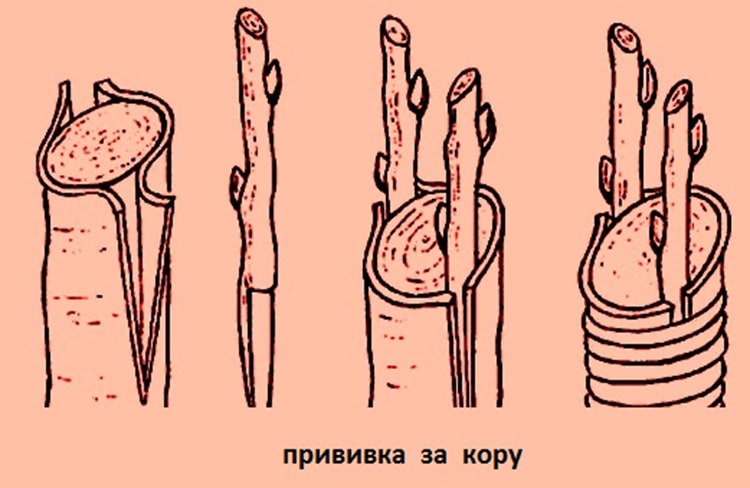
Apple tree branches are grafted onto the bark when growing them onto the stump of an old tree. Both a stump and a cut of a thick skeletal branch are suitable. Several rootstocks are usually taken for one scion.
Bark grafting technology:
- If the cuttings are grafted onto a stump, it is cut down at a height of 50–100 cm from the ground. In this case, 3-4 skeletal branches are left to provide the plant with juice. If the graft is made on a skeletal branch, when cutting it down, leave a twig at least 10–15 cm long.
- The cut area is sanded and cleared of debris and dust. Along the edges of the scion, from the cut down, longitudinal sections 5 cm long are made along the bark to the wood. The number of such cuts is made according to the number of cuttings.
- The scion is cut at an angle. The length of the cut should be equal to 4 diameters of the cutting.
- The bark flaps are moved apart, the scion is inserted into the resulting pocket so that its cut fits tightly to the wood of the rootstock and is 2-3 mm above the boundaries of the cut of the rootstock. The bark side of the cutting should face outward.
- The bark flaps on the scion are closed as much as possible. A tight winding is made at the junctions of the elements.
- All open areas of the cuts are covered with garden varnish.
Features of the procedure depending on the region
Autumn pruning Suitable for central and southern regions. In Siberia and the Urals, trees are grafted in summer or spring, since frosts come early, and in the fall the branches simply do not have time to take root.
In the Moscow region and other cities of central Russia, vaccination work will be completed by the end of September. In the south they can last until early November.
Further care
In order for the grafts to take root, it is important to properly care for the plant:
- 2 weeks after the procedure, check whether the graft has taken root and whether the wound has healed. If this does not happen, the cutting is removed, and the wound is covered with garden varnish and left until spring.
- All shoots that form below the grafting site are removed. Otherwise, they will draw juices onto themselves.
- Fresh grafting protects from direct sunlight. In hot weather they are shaded.
- A week after grafting the branches onto the apple tree, the tree is watered generously with water at room temperature. Fertilizers (rotted manure, humus) are applied to the tree trunk circle and mulched.
- If several shoots appear on an established cutting, leave the strongest one and cut off the rest. It is better to leave shoots at the top of the branch.
- When the grafts grow back, they are tied to a support for the first 3 years, since at this time the place of tissue fusion is not reliable enough.
- For the winter, plants are insulated by tying them with fabric or insulation. The tree trunk circle is mulched.
Advice from experienced gardeners

Experienced gardeners know several secrets of grafting:
- The cut areas should not be touched with hands.It is important to work with gloves, and disinfect the tool before use.
- If electrical tape is used for winding, it is wrapped with the sticky side out. Otherwise, when removing it, the fusion site will be damaged.
- Instead of garden varnish, lime is often used.
- The winding during autumn grafting is removed next spring.
Conclusion
Although spring is considered the best time for vaccination, autumn is also suitable for the procedure. In this case, it is important to choose the appropriate timing and prepare the plant for winter. This will increase the chances of new shoots surviving.
An apple tree is grafted in the fall in different ways, but budding is excluded in October. It is important to follow the instructions and follow the basic rules.