What to do if potatoes rot in the ground and why this happens
Potato diseases, especially various types of rot, are the scourge of many gardeners. It is very difficult to recognize the development of the disease in the early stages, and sowing into contaminated soil is fraught with damage to the tubers. How to treat potatoes against mold, why does it rot in the ground and what needs to be done if it is infected? Read on for answers to these and other questions.
Types of potato rot
Mold on potatoes is a rot caused by fungal and bacterial infections.. The fight against them is difficult due to the abundant damage to the soil and the complexity of its cultivation. Also, the development of rot is facilitated by violations of the rules of crop rotation and agricultural technology - watering and fertilizing regimes.
Wet
Wet rot of potatoes is caused by the activity of several types of bacteria. They penetrate into the tuber due to mechanical and fungal skin lesions.
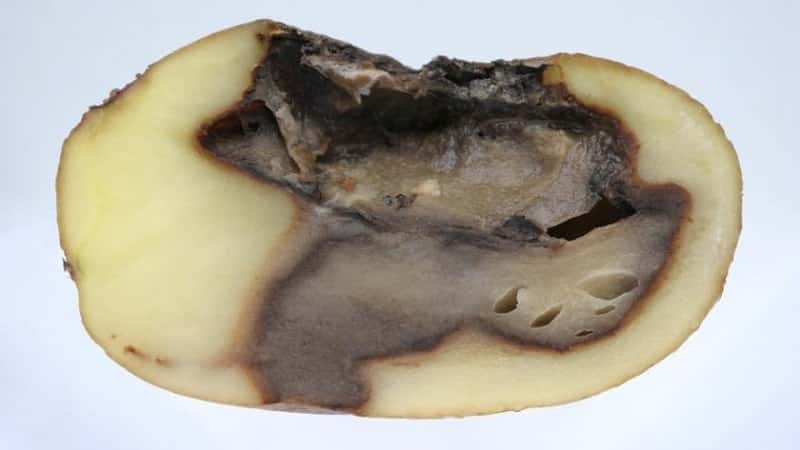
The disease in its early stages begins in the ground or during harvest, however, with excessive watering or during the rainy season, it develops to a late stage in the soil, infecting it with bacterial spores. Another cause of the disease is the lack of hilling of tubers and their “suffocation.” Rot grows best in those tubers that were exposed to sub-zero temperatures during storage.
At the last stage of development, the disease is difficult to confuse with others. The inside of the tuber softens to a liquid state and acquires a pronounced unpleasant odor. At the initial stages, the peel is not touched, but at later stages the softening and liquefaction of the tuber reaches it. Dark, wet areas appear on the affected tubers. When squeezed onto the surface, an internal liquid starch mass is released through cracks.
To combat wet rot, it is necessary to follow the rules for storing seed material.:
- plant only whole tubers;
- do not expose the seed to hypothermia;
- store in dry, ventilated areas and disinfected boxes;
- treat seed tubers with drugs against fungi and bacteria (“Glyokladin”, “Microcide”).
The disease cannot be cured. If rotten potatoes are found in the ground, all tubers within a radius of 20-30 cm are destroyed.
Interesting things on the site:
How to deal with scab on potatoes and cure the soil
What is potato late blight: description and treatment methods
Dry
Fusarium, or dry rot of potatoes, is a disease of fungal origin. The pathogen spreads very quickly from tuber to tuber and can destroy up to a quarter of the entire crop. Infection with dry rot provokes the addition of a secondary infection.
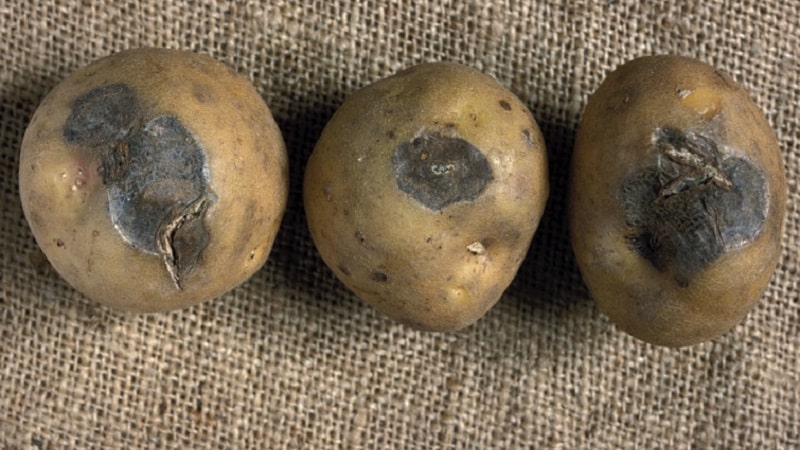

The main causes of potato infection include mechanical damage to seed and growing tubers during hilling, damage by insect pests, waterlogging, excessive manure content in the soil.
Not only potatoes are infected, but also other nightshades. - tomatoes, eggplants, peppers, as well as garden strawberries and wild strawberries.
The tips of the leaves of the affected plant lighten and become whitish as the disease progresses.. A characteristic pink coating appears on the stems.Brown spots first form on the tubers, which gradually increase in size; the affected areas dry out and form voids with a white coating inside.
The disease cannot be cured. Measures to prevent contamination of seed and soil include:
- compliance with the rules of crop rotation and agricultural technology;
- regular inspection of plantings for damage to stems and foliage;
- use only whole undamaged potatoes for sowing;
- removal of infected bushes along with tops and tubers by burning.
In no case Do not put affected stems in the compost heap.
Fomoznaya
Phoma rot (button rot, button disease, Phoma, potato gangrene) is a disease caused by several types of fungi. Phoma is considered one of the most dangerous fungal diseases of potatoes.. The infection spreads by airborne droplets in rainy, cool weather. The spores settle on the stems or fall with drops of water into the soil.
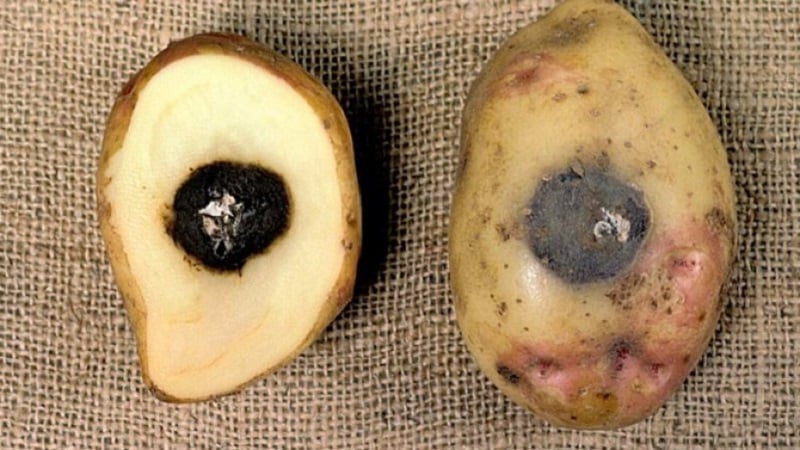

Plants affected by button rot die, the tubers do not have time to ripen. Foci of infection very quickly develop into an epidemic and affect up to 100% of plantings. In terms of danger, fomoz is second only to late blight.
The first signs of potato gangrene appear during the flowering period. Dark oblong spots appear on the leaf petioles at the base, which gradually cover the entire stem. The affected tops quickly die, falling off and contaminating the soil.
Round, depressed spots first appear on developed tubers., similar to button marks. On the section, under the dark spot, a translucent strip is visible containing waste products of the fungus. Further, cavities with a gray fungal coating form in the tubers.As a result, the tuber dries out almost completely, leaving only dead tissue.
It is impossible to fight the disease. All efforts are directed towards preventing infection and suppressing the source of the disease:
- compliance with the rules of crop rotation and agricultural technology;
- use of resistant potato varieties - Lazurit, Rosinka;
- compliance with the rules for storing seed;
- its treatment with fungicidal preparations “Ditan M-45”, “Rovral Aquaflo”;
- inspection of potato bushes and removal of affected plants entirely by burning.
Ring
Ring rot is a bacterial infection. She develops slowly, affecting up to 40-45% of the crop. The tubers become infected first, and then the entire plant. You can track it only by observing the growth of the above-ground part of the bush.
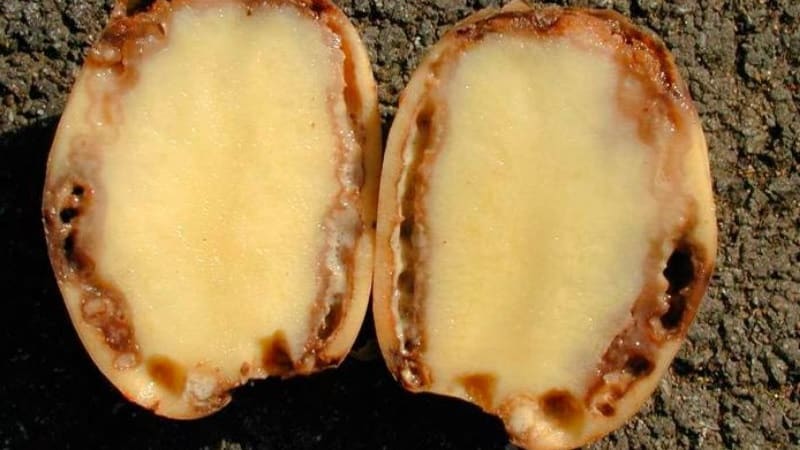
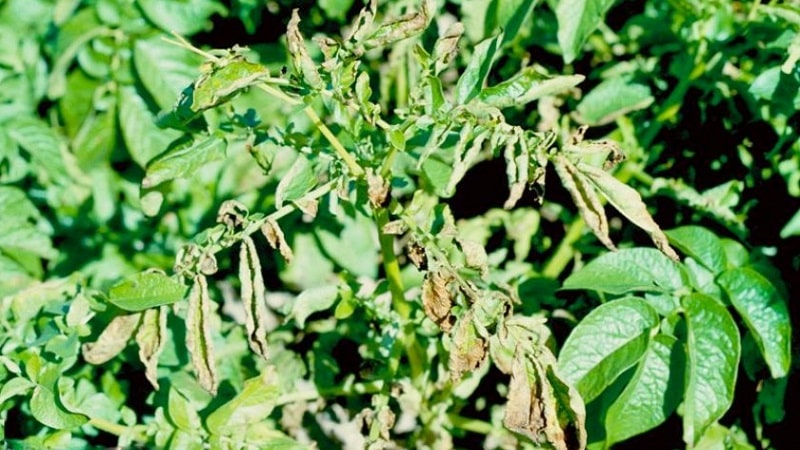
The first signs appear during the flowering period. The bushes wither and fall to the ground, which is considered a characteristic sign of ring rot. Small brown spots appear on the tips of the leaves. The leaves themselves become whitish and speckled. The lower ones curl up. When the disease develops at an early stage of bush growth, they become shorter compared to healthy ones.
On a section of diseased tubers, already at an early stage, yellowing and softening along the vascular ring are noted. As the disease progresses, the entire vascular system of the tuber is destroyed, turning into a single mucous mass.
The disease progresses at high humidity and temperatures above +20°C. In dry, hot weather, development slows down to a complete stop. Bacteria do not linger in the soil, which makes it easier to combat them. The source of infection of healthy tubers are exclusively affected ones.
The following measures are used to prevent the disease::
- the use of resistant varieties - Merrimack, President, Teton, Friso, Furor;
- compliance with the rules for storing seed potatoes;
- identification and removal of diseased plants;
- compliance with the rules of crop rotation and agricultural technology;
- sprouting potatoes before planting;
- treatment of seed storage areas, for example, with a slightly pink solution of potassium permanganate.
Rubber
Rubber rot appeared on the territory of Russia relatively recently compared to other species. She affects seed germination and plant productivity, as well as the safety of tubers. The disease is of fungal origin and has two forms - tuberous and sprout.
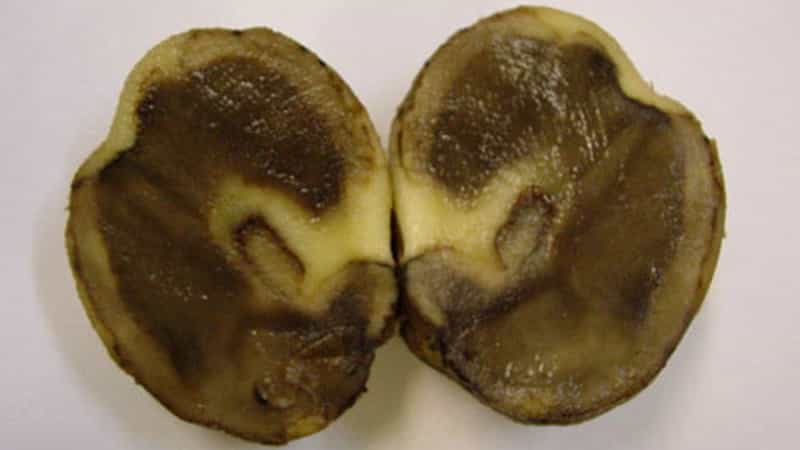
The pathogen penetrates into tubers through eyes, lenticels and mechanical damage, obtained during sowing, processing or caused by insect pests.
The tubers are covered with irregular brown spots with a black border around the entire perimeter. To the touch, the spots are dense, elastic, similar to rubber. On a cut, the affected tissue first turns pink, after which it turns brown and black. When pressed, the cut tubers release brown contents with a fishy odor.
Rubber rot develops at high soil moisture and in acidic soil at temperatures above +20°C. The source of infection is infected seed tubers, soil residues and fungal spores in the soil.
Control measures:
- compliance with crop rotation;
- improvement of planting material;
- carrying out deep plowing of the soil;
- loosening during heavy rains;
- compliance with the storage regime for seed material.
Important! There are no varieties resistant to rubber rot.
The main reasons for potato rotting in the ground
Why do potatoes rot from the inside? The main reasons include:
- violations in agricultural technology - excessive watering, lack or, conversely, excessive loosening, irregular weeding;
- non-compliance with crop rotation rules - this applies to rot with fungal etiology;
- use of diseased seed.
What is the source of infection?
Source of fungal rot infection affected tubers and spores remaining in the soil, rot of bacterial origin - infected tubers. In both cases, an additional source may be diseased tops left in the soil or used as compost.

How to deal with potato rot
It is almost impossible to fight rot on diseased plants.. All control measures are limited to removing the diseased bush and preventing disease in those adjacent to it at a distance of at least 1 m.
Prevention measures
Preventative measures for all types of rot include:
- compliance with the rules of crop rotation and agricultural technology;
- proper storage and processing of seed material;
- the use of varieties resistant to one or another type of rot;
- regular inspection of bushes for disease.
For prevention, the land must be cultivated 50-100 g of copper sulfate per 10 liters of water or 100-200 g of Bordeaux mixture per 10 liters of water. An alternative option is copper-based fungicides, for example, “Ordan”, “HOM”.
Read also:
Is it possible to eat potatoes with white coating?
Eating potatoes if mold has appeared is extremely undesirable, even if the affected area is removed. Toxins secreted by one or another pathogen accumulate in diseased tubers.Eating such potatoes will cause gastrointestinal upset, general poisoning of the body and other consequences, including death.
Conclusion
Potato rot is a group of dangerous diseases that lead to the loss of a large part of the crop. It is useless to treat the affected bushes - they are immediately removed to avoid infection of neighboring plants. To prevent potatoes from becoming moldy, it is important to follow the rules of crop rotation, agricultural technology and prevention.