How to determine the starch content in potatoes
Why is it better to mash one potato and fry another? It's all about starch - its quantity influences culinary choices. For this reason, some potato varieties are not used for frying at all, while others are not used for industrial processing.
About properties potato starch, what its content depends on and what it influences, how to determine its quantity - you will find out in the article.
Properties and Features
Part of the glucose produced during photosynthesis in plant organisms is converted into polysaccharides, which are called starch. These substances are stored as reserve nutrition in the tubers and fruits of some crops. The content of raw potato tubers is usually up to 30%.
The structural features of the polymer chain provide potato starch with unique properties:
- low gelatinization temperature - about 60°C;
- high degree of swelling;
- lack of foam when dissolving;
- preservation of white color during long-term storage.

Receipt
The potatoes are crushed, which releases the polysaccharides from the cells. Then the product is washed, dried and starch is obtained in the form of a white powder without taste or odor.
Application
Potato starch is widely used in the food industry as a thickener and component of sausages and confectionery products. It is used to make glue, compositions for paper production and textile processing.
In the production of medicines it is used as a filler or disintegrant.
Benefits and harms
Starch is a valuable carbohydrate. Under the influence of digestive enzymes, the substance decomposes to glucose, which, oxidizing to carbon dioxide and water, provides the body with energy.
The product has enveloping properties, so starchy dishes are recommended for exacerbation of peptic ulcer disease.
Although starch is considered a complex carbohydrate, its glycemic index is quite high and equal to 95. The thermally processed substance in the body is quickly almost completely converted into glucose. Two hours after eating 100 g of starch, your blood sugar level will be the same as after eating 95 g of pure glucose.
The main harm lies in this feature of the substance.
Abuse of products with potato starch leads to:
- overweight;
- increased blood sugar levels;
- disruptions in the gastrointestinal tract (constipation, flatulence, belching).
What determines the starch content in potatoes?
The amount of polysaccharides is not constant and varies by 5-7% depending on varietal characteristics, weather conditions, agricultural technology, yield and tuber size.
Varietal features
Early varieties contain the least amount of starch, since during the short growing season the compound does not have time to accumulate in the tubers.
Late-ripening varieties, as a rule, are harvested unripe, and the starch content in such potatoes is also low.
Mid-season potatoes lead in the amount of starch. The duration of summer in most Russian regions is optimal for the accumulation of the maximum amount of polysaccharides in tubers of such varieties.
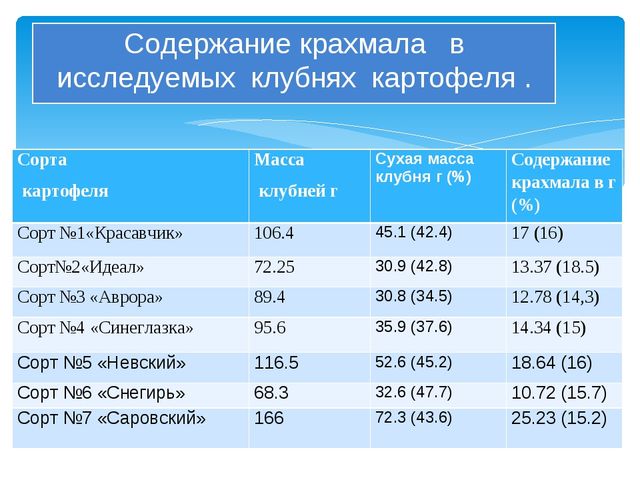
Weather
In dry, hot and sunny weather, more starch is formed, since the processes of photosynthesis and the formation of nutrients are most intense.
Potatoes grown in northern regions tend to be less starchy. This is due to later planting and early harvesting, and lower temperatures.
Agricultural technology
On light loamy soils, tubers accumulate more starch due to proper air exchange and humidity.
And the abuse of nitrogen fertilizers increases the growing season of plants and leads to a decrease in the amount of starch.
Important! To grow tasty potatoes, you need a balance of mineral fertilizers - nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium (NPK). For better results, use balanced brands of NPK fertilizers, for example, “Nitroammofoska” - 18-18-18.
Productivity and tuber size
The higher the potato yield, the less starch in the tubers.
Small and medium-sized potatoes contain more sugary substances than large ones.
What is the difference between high and low starch potatoes?
Depending on the percentage of starch, varieties are distinguished:
- low starch - contain 10-13%, used for salads and soups, since when boiled the potatoes remain whole and do not crumble;
- medium starchy - with 13-16% starch, ideal for frying, the slices have a pleasant taste and texture and at the same time retain their shape;
- high starch - tubers with 16-18%, easily boiled, indispensable for making purees, baking, boiling;
- technical - contain over 20% polysaccharides; due to their high nutritional value, they are used as feed in animal husbandry, in the production of alcohol and starch.
How to determine quantity
When buying potatoes, it is not always possible to find out their variety.
You can determine whether there is starch in potatoes in the amount necessary for preparing the intended dish at home.
Attention! To determine, you need scales and measuring containers with an error of no more than 5 ml.
The method is based on the dependence of the density of the raw tuber on its starch content.
How to determine the density of potatoes:
- Peel and weigh the potatoes. Write down the mass, it will be needed for calculations.
- Fill a measuring cup with 1000 ml of water according to the mark (V1).
- Place the weighed tuber in the water and measure the level after the potato is immersed (V2).
- According to Archimedes' law, the volume of the body is equal to the volume of the displaced liquid: tuber volume = V2-V1
- Calculate the density in g/cm3: divide the mass of the tuber by its volume.
Using the table below, determine the starch content (A):
| g/cm3 | A, % | g/cm3 | A, % | g/cm3 | A, % |
| 1,080 | 13,9 | 1,107 | 19,7 | 1,134 | 25,5 |
| 1,081 | 14,1 | 1,108 | 19,9 | 1,135 | 25,7 |
| 1,082 | 14,3 | 1,109 | 20,1 | 1,136 | 25,9 |
| 1,083 | 14,5 | 1,110 | 20,3 | 1,137 | 26,1 |
| 1,084 | 14,7 | 1,111 | 20,5 | 1,138 | 26,3 |
| 1,085 | 14,9 | 1,112 | 20,7 | 1,139 | 26,5 |
| 1,086 | 15,1 | 1,113 | 20,9 | 1,140 | 26,7 |
| 1,087 | 15,4 | 1,114 | 21,1 | 1,141 | 27,0 |
| 1,088 | 15,6 | 1,115 | 21,4 | 1,142 | 27,2 |
| 1,089 | 15,8 | 1,116 | 21,6 | 1,143 | 27,4 |
| 1,090 | 16,0 | 1,117 | 21,8 | 1,144 | 27,6 |
| 1,091 | 16,2 | 1,118 | 22,0 | 1,145 | 27,6 |
| 1,092 | 16,4 | 1,119 | 22,2 | 1,146 | 28,0 |
| 1,093 | 16,6 | 1,120 | 22,5 | 1,147 | 28,3 |
| 1,094 | 16,9 | 1,121 | 22,7 | 1,148 | 28,5 |
| 1,095 | 17,1 | 1,122 | 22,9 | 1,149 | 28,7 |
| 1,096 | 17,3 | 1,123 | 23,1 | 1,150 | 28,9 |
| 1,097 | 17,5 | 1,124 | 23,3 | 1,151 | 29,1 |
| 1,098 | 17,7 | 1,125 | 23,5 | 1,152 | 29,3 |
| 1,099 | 17,9 | 1,126 | 23,7 | 1,153 | 29,6 |
| 1,100 | 18,2 | 1,127 | 24,0 | 1,154 | 29,8 |
| 1,101 | 18,4 | 1,128 | 24,2 | 1,155 | 30,0 |
| 1,102 | 18,6 | 1,129 | 24,4 | 1,156 | 30,2 |
| 1,103 | 18,8 | 1,130 | 24,6 | 1,157 | 30,4 |
| 1,104 | 19,0 | 1,131 | 24,8 | 1,158 | 30,6 |
| 1,105 | 19,2 | 1,132 | 25,0 | 1,159 | 30,6 |
| 1,106 | 19,4 | 1,133 | 25,2 |
Express method for determining starch
There is a not so accurate, but quite objective method. Cut the potatoes and quickly rub the halves together:
- if liquid is released, then the tubers contain a little starch and will not boil;
- if the halves stick together, the starch content is high: such potatoes will become crumbly when cooked.
Varieties with high starch content

Table varieties containing a lot of starch are popular. Below are reviews of some of them.
Elizabeth
The variety is mid-early, recommended for cultivation in the Northern, Northwestern, Volga-Vyatka, and Far Eastern regions.
The tuber is round, white. The peel is smooth, with small uncolored eyes. The pulp is white and does not darken when cut.
Potato weight is from 80 to 140 g, starch content is up to 18.4%.
Aurora
Mid-season potatoes, suitable for cultivation in the Northern, Central, Volga-Vyatka, Middle Volga, Far Eastern regions.
The tuber is oval, with small eyes, weighing 90-120 g. The peel is smooth, with a reddish tint. The pulp is creamy, the taste is excellent. The content of starchy substances is up to 17.5%.
Zhuravinka
Recommended for cultivation in the Central region. Medium late ripening.
The tubers are round, with red, rough skin. The pulp is light yellow. The weight of one potato is from 90 to 140 g, starch contains up to 19.6%.
Bashkir
An early ripening variety, grown mainly in the Urals. The tubers are oval-round, with a smooth red skin, eyes of medium depth. The pulp is white, dense. Starch content up to 19.8%.
Medium starchy varieties
These varieties are used mainly for frying.
Sineglazka 2016
The variety is mid-season, recommended for cultivation in the Central region.
The tubers are oval, with eyes of medium depth. The peel is bluish, the flesh is white. Tuber weight is 70-190 g. Starch contains 11-14%.
Rowanushka
Medium early, grown in the Northern, Northwestern, Central and Middle Volga regions.
Potatoes are round, with small eyes. The skin is smooth and red. The pulp is creamy. Starch content up to 16%.
Red Lady
Early ripening variety for the North Caucasus and Middle Volga regions.
The tubers are oval, elongated, with very small eyes. The skin is red, the flesh is light yellow. Starch content 13-16%. The mass of the tuber ranges from 100 to 140 g.
Lapis lazuli
Mid-early variety, recommended for the Central Black Earth region. Potatoes are round in shape, with smooth yellow skin. The pulp is white. Tuber weight 90-120 g. Starch 13.5-16.5%.
Which potato has the least starch?
Here are some examples of popular varieties with low starch content.
Leader
Grown in the North-West region, ripening dates are early, harvesting begins 45 days after emergence.
The tubers are round, with small eyes. The peel is smooth, yellow. The pulp is white.
The starch content in potatoes is up to 12%.
Nevsky
Mid-early, suitable for cultivation in all regions.
The tubers are light beige, with white flesh. The eyes are small and pink. Tuber weight 90-130 g, starch content 10-12%.
Slav
Variety mid-season, for the Central Black Earth region.
The tubers are elongated, with small eyes. The skin is reddish, the flesh is creamy. The weight of commercial potatoes is 90-180 g, the starch content is 11-13%.
Zhukovsky early
Recommended for all regions, super early.
The tubers are pink, with white flesh. The eyes are red and small. The weight of the tubers is about 100 g, the starch content is 10-12%.
Conclusion
Starch is glucose converted into polysaccharides, stored as reserve nutrition in various parts of plants. The compound belongs to complex carbohydrates and has a high glycemic index.
Potatoes contain starch up to 30%, in table varieties - no more than 18%. The amount of starch depends on the variety, growing conditions, and weather. The more it is, the more the potatoes will boil during the cooking process. It’s easy to check the contents at home - this way you’ll find out which dishes the purchased or grown potatoes are suitable for.