Which types of potatoes are better for frying: red or white?
Fried potatoes leave few people indifferent, but not every variety of vegetable is suitable for preparing this dish. Let's talk about the main characteristics that distinguish red potatoes from white ones, and find out which one is more suitable for boiling and which one is more suitable for frying.
What properties do potato varieties differ in?
According to nutritionists and breeders, tubers with skins of different colors differ from each other not only in appearance, but also in chemical composition, as well as technological properties.
Crumbly or dense
Potatoes are usually divided into four types depending on the density of the pulp:
- A - non-cooked, salad type, with minimal starch content;
- B - a slightly boiled variety, used primarily for making chips;
- C - highly boiled, medium-starchy, ideal for deep-frying;
- D - the most starchy, used for purees and casseroles.
There is a direct relationship between the relative density of potatoes and their dry matter content. However, not only the amount of starch in tubers is important, but also the ratio of protein and starch in them. So, if there is 8 times more starch than protein, the vegetable will not boil. If the difference reaches 16 times or more, the potatoes quickly boil over, since they lack adhesives.
Reference. In industrial production, to determine the relative density of tubers, so-called Parov starch scales are used, the operating principle of which is based on Archimedes' law.

Starch content
Starch makes up 70-80% of all tuber dry matter. There are two main categories for this indicator:
- Mealy potatoes with a high starch content (16-22% by weight of the tuber). The pulp is dry and flaky; when cooked, it acquires a granular texture.
- “Waxy” varieties feel watery when exposed to heat; they hold their shape well when heated.
Reference! Late-ripening varieties are the starchiest, since over a longer growing season they accumulate more sugars than early-ripening ones.
The amount of starch is an unstable indicator, depending on growing conditions, storage duration, tuber size and other factors. Therefore, fluctuations within 5% are permissible for the same variety.
- young, freshly dug potatoes will be waxier than fully mature ones;
- small and large tubers contain less starch than medium-sized ones;
- During storage, hydrolytic decomposition of starch to sugars occurs.
Reference! When starchy potato varieties are cooked, intercellular connections are weakened, which is why the tuber loses its structural unity. A similar splitting reaction also occurs in waxy potatoes, but at higher temperatures. The difference is almost 12°C.
Taste qualities
The taste of a product is determined by such an objective indicator as its chemical composition. However, the perception of taste is subjective and depends on the characteristics of the national cuisine, individual preferences and even the arguments of commercial advertising.
The taste of potatoes is affected by starch and sugars (glucose and lactose), protein, fatty acids, mineral elements, the so-called “dry protein” - nitrogenous compounds, etc.
The presence of fatty acids in tubers - glutamic and aspartic - during cooking contribute to the formation of volatile compounds that affect taste buds. Another group of substances responsible for taste are nucleotides, the so-called breakdown products of nucleic acids. The more there are, the richer the potato bouquet.
The chemical composition largely depends on agricultural technology:
- The absence of mineral supplements during potato growing has a beneficial effect on taste. Ideally, if only humus and ash were added to the soil, such a crop is recommended for dietary and baby food.
- Watery pulp is often due to excess nitrogen and lack of potassium. Excessive feeding with nitric acid salts or slurry, although it increases yield, but leads to the accumulation of nitrates in tubers. Such potatoes often have an off-odor, and their flesh quickly turns black.
Certain changes in taste are associated with improper storage:
- at low temperatures (from 0 to +1°C), starch turns into sugar, and potatoes acquire an unpleasant sweetish taste;
- bitterness occurs if the tubers have been exposed to light for a long time and have turned green, as a result of which a glycoalkaloid, solanine, accumulates in them.
In small quantities, solanine is safe and gives potatoes their characteristic flavor. If the concentration of the substance is only 50-100 mg per 1 kg of vegetable, potatoes are perceived as tasty. You can reduce the amount of glycoalkoloids by simply peeling and boiling the tubers.
Attention! Signs of solanine poisoning occur when a person consumes 400 mg of the substance at a time. In addition to potatoes, it is found in all nightshade crops, including tomatoes and eggplants.
What is special about white potato varieties?

There is an opinion that potatoes with white skin contain more starch and boil quickly. This stereotype has a historical background: for a long time foreign “red-skinned” varieties were unknown in Russia; they came into wide use only in the 1990s.
Foreign consumers, due to culinary traditions, prefer poorly cooked potatoes. Our compatriots, on the contrary, have always appreciated hearty, starchy potatoes. As a result, imported red and pink varieties are still perceived as “waxy”, while the more familiar white varieties are still perceived as “floury” (starchy).
However, selection has erased the clear differences between potatoes with different shades of skin. Taste and technological qualities are individual for specific varieties.
They are distinguished by high and increased starchiness Lorch with an indicator of 15-20%, Temp - 16-22% and some others. Also among the “white-skinned” there are low-starch varieties: Impala – 10-14%, Luck – 12-14%, Karatop – 12-14%.
The color of the pulp is more indicative. Thus, a yellow tint indicates the presence of carotene, that is, vitamin A, in the tubers: the more saturated it is, the higher the content of the substance. For example, in 100 g of raw potatoes with white flesh there are 14-53 mg of carotenoids, with cream and light yellow flesh - 150-400 mg, and in Peruvian potatoes with dark yellow flesh - 1700-2000 mg.
As a rule, yellow potato varieties are not very boiled, moderately sweet and pleasant to the taste. One of them - Gala - is suitable for dietary nutrition due to its low starch content - only 10.2 - 13.2%.
What is special about red potato varieties?

The bright color of the peel is achieved due to the high content of anthocyanins in the tubers. These substances are extremely beneficial as they have antioxidant properties and help the body resist the harmful effects of ultraviolet radiation and free radicals. In addition, anthocyanins increase the elasticity of vessel walls, accelerate collagen synthesis, and strengthen the retina.
The first imported varieties of red potatoes brought to Russia contained starch smaller than the usual light-skinned tubers. Some of the nicknames have remained so to this day: the pink variety of Russian selection Zhukovsky early with 10-12% starch, the Dutch Red Scarlett with 10-15%. They are distinguished by their wateriness and stability of shape during heat treatment.
Rich starch red varieties Symphony - 14-19%, Crimean Rose - 16-18%, Condor - about 18%, Rocco - 19.7%, Zdabytak - 19.2 - 25.4%.
Which potatoes are suitable for frying?
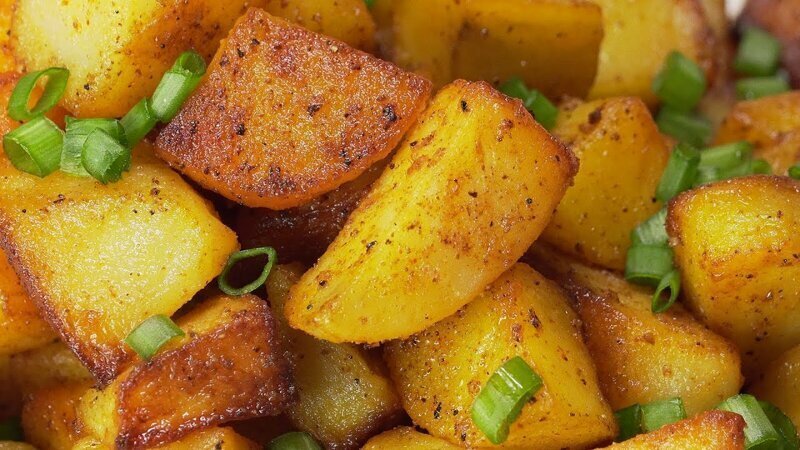

Some chefs argue that the varieties that contain the least starch are suitable for frying: the pieces should retain their shape when they are mercilessly mixed in a frying pan. Others are convinced that starch molecules help the formation of a golden brown crust, and the dense pulp prevents the oil from absorbing too deeply.
The reason for the disagreement lies in the different frying methods. French fries require starchy (flour) varieties. If the potatoes are cooked in a frying pan with a small amount of oil added, they should hold their shape well, i.e. in this case, “waxy” tubers are welcome. To prevent the slices from crumbling, they must contain enough sticky substance - pectin.
Reference. Potatoes with low water content are suitable for deep frying.The moisture in the boiling oil quickly evaporates, leaving a crispy crust on the surface and well-steamed flesh inside.
What type of potatoes are suitable for boiling and mashing
Potatoes are boiled for different purposes: for making soups, salads and purees.
In salads and soups, varieties are used whose starch content does not exceed 15%. Such potatoes have thin skin and watery pulp, after cooking the tubers retain their shape.
A starch content of 16% and above is a necessary condition for puree that melts in your mouth. Starch actively absorbs moisture, so to prevent the dish from tasting too dry, add a lot of milk and butter. This increases the calorie content of the dish significantly, but makes the puree especially tasty.
Tips and tricks
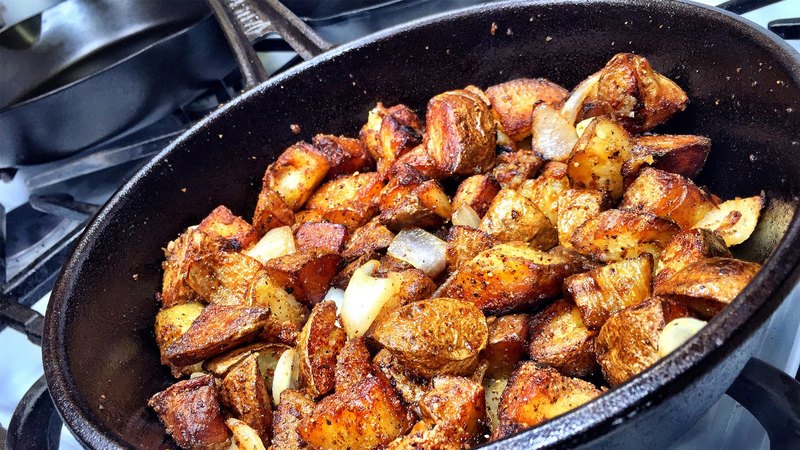

The less dry matter there is in potatoes, the more resistant it is to high temperatures. In cooking, this means that non-starchy potatoes hold their shape better, the slices do not fall apart when stirred, and the pulp absorbs less moisture. These varieties are suitable for salads, soups and frying in a pan. Varieties with bright red skin have the listed properties.
Vegetables with a high starch content have proven themselves well for making mashed potatoes and deep-fried potatoes, as well as for baking.
Conclusion
Selecting potatoes for different culinary purposes is not as simple as it seems at first glance. The rule that says red varieties are used for frying and white varieties for purees and casseroles does not always work. The starchiness of both is the same. Taste qualities and technological properties also change depending on the growing and storage conditions of the crop.