Step-by-step instructions for beginning gardeners: how to properly plant tomatoes in a greenhouse and why this is necessary
To increase the yield of tomatoes, you need to properly form the bushes. This way the plant will direct its forces to laying and ripening fruits. The main technique is stepsoning. Let's look at how to properly plant tomatoes in a greenhouse and look at common mistakes.
What is stepsoning and why is it needed?
Stepping and pinching is the formation of tomato bushes by removing unnecessary lateral shoots, the so-called stepsons, and the top. This technique increases productivity, accelerates fruit ripening, and facilitates care.
When and how often to carry out
The first pinching is carried out at the beginning of the formation of the first inflorescence. Tomatoes need to be regularly inspected and excess shoots removed when they have not yet grown more than 5 cm in length.
Greenhouse tomatoes stepchildren are planted once every 6-7 days, ground ones - once every 10-14 days. It is necessary to remove unnecessary shoots constantly, even after the fruits begin to ripen.
It is recommended to carry out pinching in the morning.
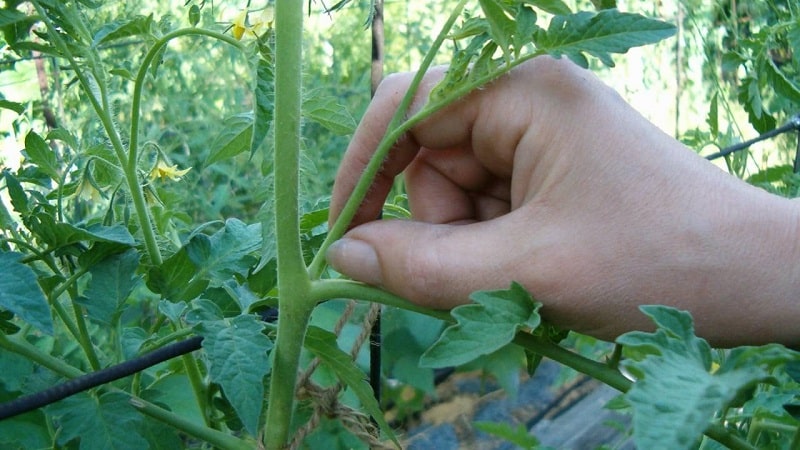

What are stepsons of tomatoes?
The stepson is a new shoot that the tomato throws out from the axil of the leaf. You can distinguish a stepson from a fruit cluster by the following characteristics:
- the stepson grows from the leaf axil, the flower raceme branches off from the stem;
- Even a small stepson has leaves; a flower raceme does not have leaves.
If doubts arise due to lack of experience, the lateral process is left for a day, after which the difference will become more obvious.
General rules
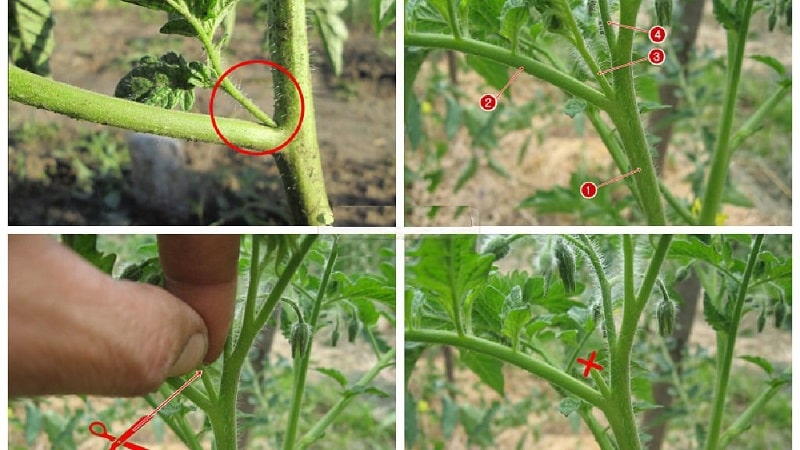
To prevent pinching from causing harm to tomatoes, you need to follow simple rules:
- Excess branches are torn off and broken off or pinch, but in no case cut.
- The event is held in the morning. In the first half of the day, the growing season is more active, and wounds caused by removing shoots will heal faster.
- When cutting or breaking off branches, be careful so that the juice does not get on your hands. This will help avoid the spread of diseases, if any, to other bushes.
- Do not allow stepchildren to grow more than 5 cm in length. Removing large shoots is a big stress for plants.
- No more than three stepsons are removed from one bush at a time. If there are a lot of shoots, pinching is carried out for 5-6 days, first removing large shoots, then moving on to smaller ones.
- Leave a shoot about 1-2 cm long when separating the stepson from the bush. This prevents the growth of new shoots in the same place.
- The removed shoots are removed from the site. Rotting plant debris can become a source of disease.

Features of the formation of different varieties of tomatoes
All varieties of tomatoes can be divided into groups according to the growth characteristics of the bush: indeterminate, determinate, semi-determinate. The approach to formation is different for each group of varieties.
Semi-determinant
Semi-determinate tomatoes (semi-detached) grow up to 1.5 m in height. Such plants are formed into two stems: the strongest stepson is left above the first flower cluster.
As it grows, 2-3 fruit clusters are left on such a side stem, and 3-4 clusters on the main stem.
Indeterminate
A feature of indeterminate tomatoes (indets) is the unlimited growth of the stem in height; the length of the stem can reach 2-4 m. When the required height is reached, the growth point at the top of the bush is pinched.
Seedling of indets is a mandatory measure, otherwise the bushes will quickly grow to the detriment of fruiting. They are formed into one stem.
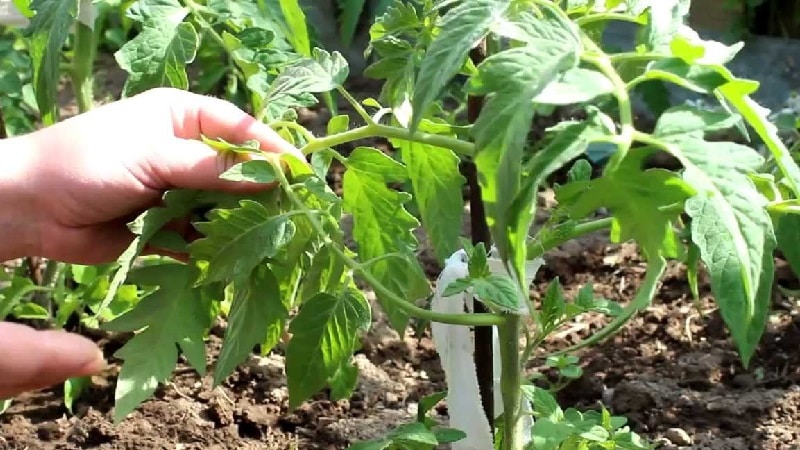

Determinant
Determinate tomatoes (children) stop growing in height with the appearance of an inflorescence at the top of the stem. The harvest of such a bush is limited to previously formed clusters.
To increase the number of fruits, use a formation scheme of 2-3 stems. 1-2 of the most powerful stepsons are left, usually they are located under the first inflorescence.
The subtleties of forming tomatoes in a greenhouse
The peculiarities of the formation of tomato bushes in closed ground arise from the limited size of the space.
To make fuller use of the greenhouse space, they mainly grow indeterminate varieties. They use a single stem formation scheme and always tie it up, otherwise the stem will not withstand the weight of the fruit.
To obtain abundant harvests in the greenhouse with determinant bushes they are formed into 2-3 stems, leaving shoots under the first and second flower clusters.
Non-growing tomato varieties for growing in a greenhouse
Non-stepping varieties are characterized by a low bush, up to 70 cm, and the absence or very small number of stepsons. Resistant to diseases, tolerate changes in temperature and humidity well.
All non-sowing tomatoes are early or ultra-early, therefore, by growing these varieties in a greenhouse, you can get a bountiful harvest by mid-July. The fruits are smooth, weighing 80-100 g.
Here are some varieties suitable for growing in a greenhouse:
- Oak - ultra-early, the fruits are round, with fleshy pulp, weighing 50-100 g;
- Siberian pirouette — produces elongated tomatoes, which are very good for canning;
- Countryman — high-yielding early variety; The peculiarity of the variety is that it can be grown without seedlings - the seeds can be planted directly in greenhouse soil.
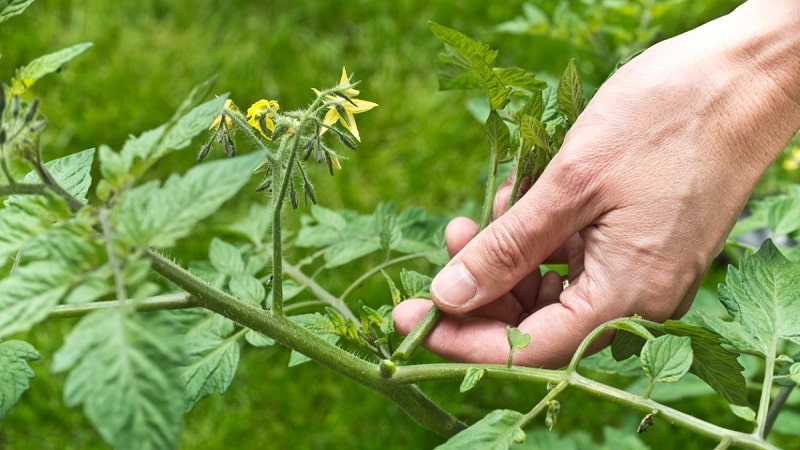

What is the procedure
The formation of bushes is the regulation of the growth of leaves and stems. To direct the plant’s forces to generate fruits, it is recommended to leave no more than three stems and eight flower clusters on one plant.
Advice. To obtain an earlier harvest, leave no more than three fruit clusters on the bushes and pinch the tops. In this case, the fruit begins to ripen and growth stops.
Formation of tomato bushes in a greenhouse: stages of work
The formation of tomato bushes consists of several stages:
- Step-sonning - removal of excess shoots, limiting the growth of green mass and allowing the selected shape to be maintained in one, two or three stems.
- Pinching the top, which stops the growth of the bush and directs the plant’s forces to ripening the fruits.
- Trimming lower wilting leaves after fruit formation to protect against fungal diseases.
The first pinching is carried out 2-2.5 weeks after planting the seedlings. You should adhere to the general rules of stepsoning:
- Inspect the tomato bushes and mark all the stepsons for removal to form them into one stem. In a two-stem scheme, leave one of the most powerful shoots located under the first brush; shoots from the second stem must be removed according to the same rules as on the main one.
- Stepchildren are removed by carefully breaking them off from the bush.To prevent branches from growing back in the same place, leave a small shoot 1-2 cm long.
- All removed shoots are collected in a container and taken out of the greenhouse.
Stepping is repeated step by step once every 6-7 days.
Pinching Instructions
The tops of tomatoes are pinched at the end of July - beginning of August, when the required number of inflorescences have formed on the bush.
Carefully pinch off the stem above the last inflorescence that appears, leaving 1-2 leaves on top. Tall varieties are pinched all season long.
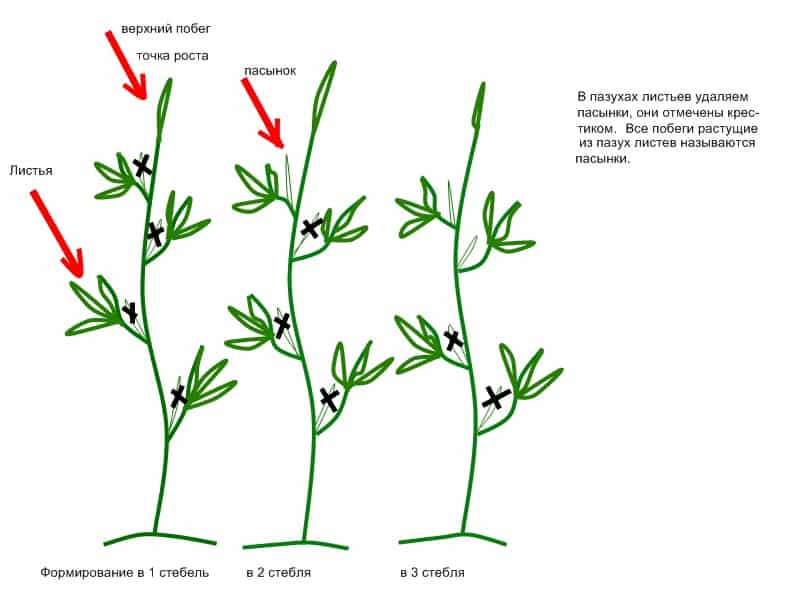
Form into one stem
Three formation patterns are common: one, two and three stems.
When growing in one stem, all shoots are removed, leaving one stem. The bush develops quickly, large fruits are formed. In this case, it is necessary to tie up the plants, otherwise the stem will break under the weight of the harvest.
Formation of a bush into two or more stems
When forming into two stems, the main stem and one most viable stepson are left, which is located immediately under the first brush.
The three-stem design involves maintaining two stepsons in addition to the main stem. Below the first hearth cluster, two strong shoots are left. This scheme is extremely rarely used in greenhouse conditions.
Common mistakes when pinching
What should not be done when planting, so as not to harm the plants:
- Stepsoning is rare and irregular. This requires plants to spend a lot of money on recovery. In addition, time and nutrients have already been spent on the growth of the tops, and not on the ovaries.
- Remove fruiting shoots instead of stepsons. If the shoot comes directly from the stem and inflorescences form on it, then this is a fruitful branch.
- Use dirty garden tools. Before pinching and after processing each bush, they need to be disinfected, for example, with a 1% solution of potassium permanganate or bleach. Therefore, experienced gardeners pluck off excess shoots by hand - this is faster and more efficient.
- Carry out pinching in the evening or in cloudy, damp weather. At this time, the growing season slows down. Wounds resulting from the removal of shoots will take longer to heal, and the risk of contracting diseases will increase.

Conclusion
Pinching helps direct nutrients to the formation of inflorescences and fruits, reduces ripening time, reduces the risk of infections and makes plant care easier. Caring vegetable growers regularly remove stepsons no more than 5 cm long, maintaining the chosen shape of the bushes. And tomatoes delight with an abundance of large, sweet fruits.