Treatment of greenhouse cucumbers for diseases: photo and description
Novice gardeners think that greenhouse plants do not need protection from diseases and pests. However, this is not so - cucumbers in a greenhouse get sick just as often as in open ground. Moreover, infections spread much faster indoors. If one plant in a greenhouse is sick, the risk of infection of all plantings is higher.
In order not to lose your harvest due to diseases, you need to know how to prevent them. If the infection has already affected the plants, it is important to promptly identify the disease and promptly take therapeutic and protective measures.
Our article contains everything about diseases of cucumbers in a greenhouse and their treatment: photos, descriptions, symptoms, causes and methods of prevention.
Description and symptoms of cucumber diseases
To cure a disease, it is important to correctly identify it. There are viral, fungal and bacterial infections that affect plants. The fight against them has its own nuances.
Fungal
Plants become infected with fungal infections through soil, garden tools, planting material or from other affected crops. The development of such diseases begins from the site of the lesion and gradually spreads throughout the entire bush.
Fungal infections in most cases treatable. They most often affect plants in a greenhouse when the rules of care are violated or due to unfavorable weather conditions.
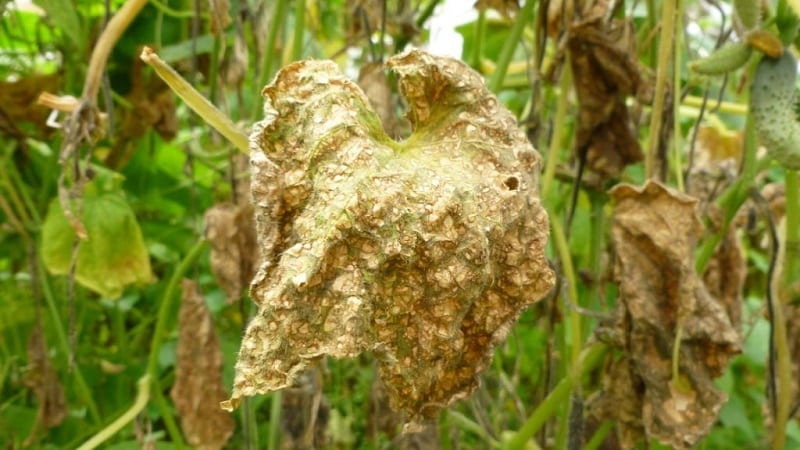

Types of fungal diseases:
- White rot. Most often it affects greenhouse cucumbers. The leaves and stems of plants become covered with a white, wet coating, which leads to their rotting. The fruits begin to rot, look frostbitten and have a pungent putrid odor. Gradually the plants die.
- Gray rot. “Velvet” light gray spots appear on the ground part of the bush. They quickly spread throughout the entire plant and healthy plantings.
- Root rot. The fungus attacks the roots and root collar of plants. Because of this, the leaves turn yellow and dry out. The root part rots and becomes thinner, which leads to the stem breaking off.
- Ascochyta blight. The disease is also called black rot (pictured above). Brown spots appear on the inside of the leaves of affected cucumbers, which gradually turn black. In some cases, the fungus spreads to the leaves.
- Powdery mildew. A fungal disease that quickly spreads throughout all plantings. Its symptoms are white plaques on the leaves that lead to wilting.
- Downy mildew. Dull light yellow spots appear on the leaves and stems of cucumbers, gradually merging with large areas of the lesion. This leads to the death of plants.
- Anthracnose. The leaf plates are covered with tubercles, which soon turn into holes. The fruits become limp and rotten cavities appear on them.
If there was an epidemic of fungal diseases in a greenhouse, then The pathogen will remain in the soil for several years. Experienced farmers recommend replacing the top layer of contaminated soil with new soil.
Bacterial
Bacteriosis also called “angular spotting” because the ground part of the affected cucumbers is covered with triangular or polygonal dark spots.
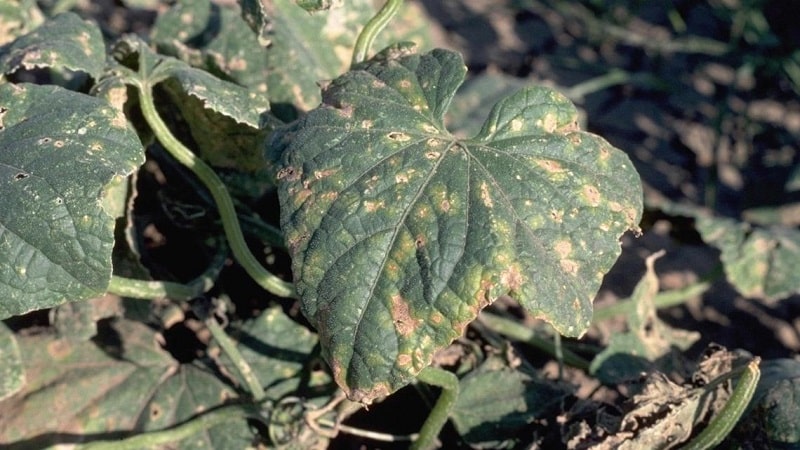

With such a disease dry voids form inside the fruit. The rest of the cucumber often begins to rot.
This the disease cannot be treated and quickly attacks healthy plants. To save unaffected plantings, diseased specimens are removed by the roots from the beds and destroyed.
Viral
Viral diseases are considered the most dangerous: they cannot be treated. Therefore, prevention plays an important role.
Attention! Viral infections are most often spread by insects.
Viral diseases of cucumbers:
- Green mosaic. The leaf blade of affected plants becomes covered with light green spots, wrinkles and withers. Lumpy colored formations appear on the fruits. The plant stops forming ovaries and inflorescences.
- White mosaic. The leaves are covered with sharp-angled white and yellow spots. The fruits acquire a striped white-yellow color.
- Viral necrosis of cucumber. The greenery of the plant turns purple and becomes covered with brown spots. Inflorescences and lashes die off, but new ones are not formed. This leads to the death of culture.

Difference between diseases and problems due to pests
Plants change their appearance not only because of diseases. Gardeners often confuse traces of pests with diseases:
- Spider mite. The pest sucks sap from plants, causing the leaves to dry out. The bushes are covered with cobwebs.
- Aphid. Leaves and stems become pale and limp. The ovaries fall off, but new ones are not formed. Small light green midges are found on the back of the leaf blade and stems.
- Greenhouse whitefly. Insect caterpillars suck the juices from the plant, which leads to its death. The insect feels good in conditions of high humidity.Whiteflies can be recognized by the presence of caterpillars and butterflies that resemble moths.
Causes of disease development
What to do if cucumbers disappear in the greenhouse? Most often, plants in greenhouses and greenhouses get sick due to errors in agricultural technology. Unfavorable weather conditions are less common.
Why do cucumbers get sick in a greenhouse?:
 contaminated soil - diseases occur if plants that previously grew in the greenhouse were infected or the soil was not disinfected before planting;
contaminated soil - diseases occur if plants that previously grew in the greenhouse were infected or the soil was not disinfected before planting;- contaminated fertilizers - compost, humus and manure may contain pathogens;
- infection on materials - pathogens often enter plants from garden tools or planting material;
- violation of watering rules - the development of fungal diseases is promoted by both high and low humidity, condensation in the room;
- incorrect pinching - if you water the cucumbers immediately after pinching, it will be easier for fungal spores to penetrate into the “wounds”;
- lack of micronutrients - the immunity of cucumbers decreases, and they become more susceptible to diseases;
- Pests spread viral infections.
Methods for treating cucumber diseases
Before treating cucumbers for diseases in a greenhouse, you should choose the appropriate type of product:
- Folk. They assume the use of household (often food) products. This option is safe.
- Chemical. Special remedies for plant diseases, sold in gardening stores, are considered the most effective. Their disadvantage is that such drugs can accumulate in the fruits.
- Biological. Can be purchased in special stores. Safer than chemical ones.
- Pharmacy. Some drugs are suitable not only for treating people, but also for combating plant diseases. They are considered effective and safe.
Viral diseases are not treatable. To save the plantings, infected plants are completely removed.
For fungal infection Only the affected parts of the plant are removed. The rest of the bush can be saved by treating it with antifungal drugs.
Chemical
Experienced gardeners recommend using chemicals when home recipes no longer help. Such products reduce the ecological purity of cucumbers, but save the harvest.
The most effective chemicals:
 "Quadris". Belongs to the group of strobilurins. Effective against downy and ordinary powdery mildew, spotting, rot, etc. Completely kills fungal diseases. Harmful to people - work with it only in protective masks.
"Quadris". Belongs to the group of strobilurins. Effective against downy and ordinary powdery mildew, spotting, rot, etc. Completely kills fungal diseases. Harmful to people - work with it only in protective masks.- "Ridomil Gold". One of the most effective antifungal drugs. Contains components that work inside and out.
- "Thanos". Effective against rot and downy mildew. It is considered the most effective way to combat Alternaria. Forms a film on the ground part of the bush that is not washed off with water. The drug penetrates the fungus and provokes irreversible changes in it. The infection does not develop resistance to this drug.
These drugs help against fungal diseases. They are aboutespecially effective in the initial stages of disease development.
By such means spray plants no more than once a week. It is not recommended to use them after the ovaries form.
Note! Fungi often develop immunity to drugs that act inside the plant.Products that protect cucumbers from the outside are less likely to cause resistance.
Biological
Biological preparations are sold in gardening stores. They are effective in combating diseases of cucumbers and are safer than chemicals.
Description of different types of funds:
 Fungal. They are made on the basis of fungi that penetrate the mycelium of the infection, destroying it. Effective against rot, powdery mildew, verticillium. They have a short shelf life and require storage requirements. Such remedies include Trichodermin.
Fungal. They are made on the basis of fungi that penetrate the mycelium of the infection, destroying it. Effective against rot, powdery mildew, verticillium. They have a short shelf life and require storage requirements. Such remedies include Trichodermin.- Bacterial. Protects against diseases and pests. Used for watering and spraying. Natural antibiotics are released. Such drugs include “Baktofit” and “Fitosporin”.
- Plant extracts. Protect against diseases and pests, increase plant productivity. They are similar in action to folk remedies.
Biological preparations not only help fight diseases, but also strengthen plant immunity. Unlike chemical fungicides, they do not accumulate in cucumbers.
Pharmacy
Pharmaceutical products are used not only to treat people and animals, but also to combat plant diseases. Such agents have a pronounced antifungal and antimicrobial effect. They are considered quite effective:
- Iodine. A drug with a pronounced antifungal effect. Useful for the prevention and treatment of diseases, strengthening the immune system, and improving the quality of vegetation. To prepare the medicine, add 10 drops to 10 liters of water. Cucumbers are sprayed with this composition, spending up to 1 liter per m².
- Diamond Green (“green”) Effective against powdery and downy mildew. To prepare the drug, take half a bottle of “green stuff” per 10 liters of water.The above-ground part of the cucumbers is sprayed with the product.
 "Metronidazole". For every 10 liters of water, take 20 crushed tablets for adult plants and 10 tablets for seedlings. The resulting mixture is sprayed onto cucumbers immediately after preparation.
"Metronidazole". For every 10 liters of water, take 20 crushed tablets for adult plants and 10 tablets for seedlings. The resulting mixture is sprayed onto cucumbers immediately after preparation.- "Aspirin" helps against rot. To prepare the medicine, dissolve 2 crushed tablets in 10 liters of water. The drug is used for spraying.
- Potassium permangantsovka. Used to disinfect soil (dark pink solution) and planting material (light pink solution). For preventive purposes, adult plants are sprayed with a light pink solution of potassium permanganate during an epidemic.
- Hydrogen peroxide. Used to disinfect seeds. Planting material is soaked in liquid for a quarter of an hour.
- "Nystatin". Effective against all types of fungal diseases. For every 1 liter of water take 1 tablet. The product is sprayed on cucumbers for treatment and prevention during epidemics.
Folk
Folk remedies are considered the safest. They are good for the prevention and treatment of diseases in the early stages of development.
The most popular ones:
- Ash. A universal product that is used for feeding, treatment and pest control. Add a glass of ash and a bar of soap to a bucket of water, and spray the leaves with the resulting product once a week.
 Garlic solution. Helps against fungi. Add a head of chopped garlic to a liter jar of water. The mixture is infused for 2 weeks in a dark place. The composition is diluted in 10 liters of water.
Garlic solution. Helps against fungi. Add a head of chopped garlic to a liter jar of water. The mixture is infused for 2 weeks in a dark place. The composition is diluted in 10 liters of water.- Garlic, oil and soap. Two heads of garlic, 0.5 liters of vegetable oil and 60 g of liquid soap are mixed. The product is infused for two days and diluted with water. This amount is enough to prepare 20 liters of medicine.
- Serum. Has an antifungal effect. 1.5 liters of whey are poured into a bucket of water. The solution is used for spraying.
- Soda Ash with soap. To 10 liters of water add 40 g of soda and a piece of laundry soap.
Disease Prevention
When plants begin to get sick, even chemicals do not always help preserve the harvest. To prevent the development of infection, It is recommended to follow the rules of prevention:
 Compliance with crop rotation. Cucumbers are not planted in the same greenhouse for more than three years in a row. If you have to constantly plant a crop in the same greenhouse, then replace the top layer of soil.
Compliance with crop rotation. Cucumbers are not planted in the same greenhouse for more than three years in a row. If you have to constantly plant a crop in the same greenhouse, then replace the top layer of soil.- Disinfection. Disinfectant compounds are used to treat soil, planting material, containers for seedlings, and garden tools.
- Compliance with watering rules. The soil should not be overdried or waterlogged. Cucumbers are watered in the greenhouse 1-2 times a week.
- Compliance with the rules of stepsoning. Plants are planted in the morning or at sunset.
- Preventative treatments. Plants are sprayed with folk remedies during cold spells and epidemics.
- Insect protection. To do this, mosquito nets are placed on the greenhouse windows.
- No drafts. Cucumbers are afraid of drafts. In a greenhouse with this crop, only one window is opened.
Conclusion
Plant diseases are the most common cause of crop loss. They can overtake even an experienced gardener. Following the rules of prevention significantly reduces the likelihood of this problem occurring. If the cucumbers are still infected, choose the safest means for treating plants.