What is the effect of nitrate on wheat and how is it used for fertilizer?
Ammonium nitrate is used in agriculture as a fertilizer. Its main element is nitrogen, which is needed by almost all agricultural crops, including wheat. Fertilizing with saltpeter has a beneficial effect on the growth of the vegetative mass of the plant, increasing the amount of protein and gluten content. Read about all aspects of the substance’s influence on wheat and its use in growing cereals in the article.
What is saltpeter
Ammonium nitrate is a fertilizer belonging to the class of mineral substances, obtained by neutralizing nitric acid with ammonia. When it gets on the soil surface, the fertilizer quickly decomposes, releasing nitrogen in large quantities.
Other names for ammonium nitrate are ammonium nitrate, ammonium nitrate and ammonium salt of nitric acid.
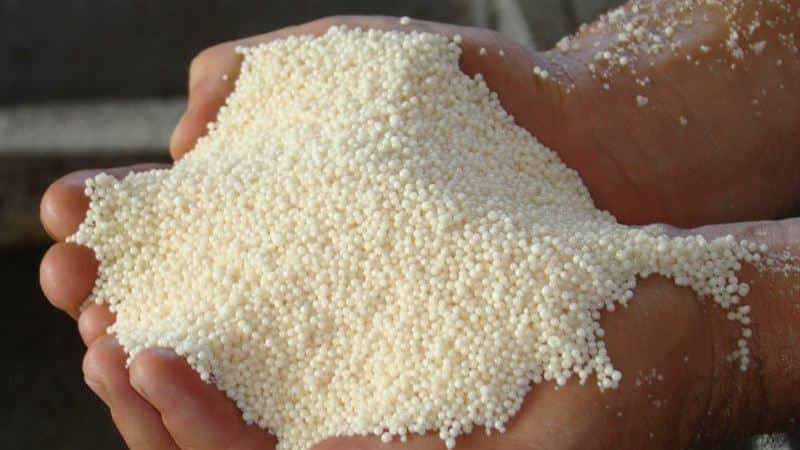

Composition and properties
The fertilizer is produced in the form of a white powder or granules with a slight yellowish tint.. To create saltpeter, nitric acid concentrate and ammonia are used. The chemical formula of ammonium nitrate is NH4NO3.
Very often, sulfur is added to fertilizer with saltpeter. It is not included in the chemical formula of the substance, but only helps to better absorb nitrogen.
Ammonium nitrate is an ideal fertilizer during the growth period of wheat. In spring, plants are capable of absorbing large amounts of nitrogen.
Nitrate is an acidic fertilizer. It will not acidify soil with normal pH.But in acidic soils it is necessary to additionally add calcium carbonate (aka calcium carbonate) and lime flour.
On alkaline or buffer lands, the agrochemical is used in its pure form.
Ammonium nitrate has a neutral reaction, thereby creating ideal conditions for nitrogen nutrition in the zone of its application, where the bulk of the plant's roots are located.
Calcium-ammonium nitrate contains calcium and magnesium carbonates, which are responsible for increasing the efficiency of fertilizing not only on acidic, but also on alkaline soils, as well as on soils of light texture (sandy, sandy loam) and saline soils. Positive results can be seen after adding calcium ammonium nitrate to soil deficient in magnesium. Regular use of this fertilizer does not lead to acidification of the soil.
Important! To feed winter wheat, it is necessary to apply nitrate with phosphorus and potassium - this will significantly increase the crop yield.
The effect of nitrate on wheat
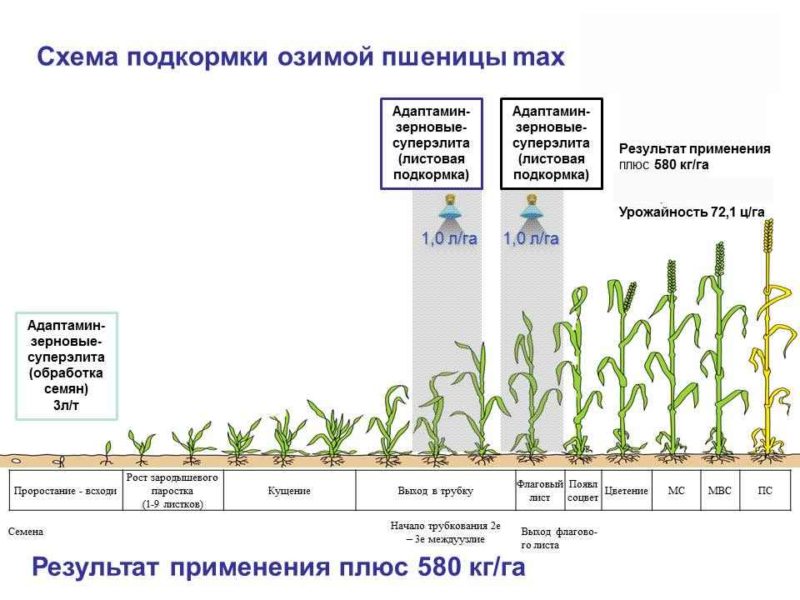
Ammonium nitrate can be used on all types of soils and for all agricultural crops, including cereal grains.
For winter
Ammonium nitrate can act as the main fertilizer or feeding during the growing season.
On soils susceptible to oxidation, its use in winter wheat crops reduces the negative effect of applying acidic fertilizers.
Reference. Ammonium nitrate does not cake during long storage periods.
For spring
The main part of nitrate is needed by spring wheat during flowering, tube setting, and heading. Nitrogen fertilizers should be applied during fall plowing and during spring sowing in rows.
Is it necessary to feed wheat with saltpeter in spring, summer and autumn?

It is better to fertilize wheat under plowing. Afterwards, it is recommended to carry out root and foliar feeding on all types of soil.
Fertilizing of spring and winter wheat is carried out in the fall. For the first, ammonium nitrate is added at the end of October or beginning of November. For the second, nutrients are added at the end of August and beginning of September.
Important! If autumn fertilizing for spring wheat has not been done, it should be done in the spring, with the onset of the first warmth.
When is it necessary to fertilize wheat with saltpeter?
Ammonium nitrate is one of the safest types of fertilizers. But a good harvest and preservation of the fertile properties of the top layer of soil can only be guaranteed if the terms and rules of fertilizing are observed.
Timing for fertilizing
It is most effective to apply fertilizer in a high dose once before sowing.
Fertilizer technology
The method of using the agrochemical is simple. It is applied to the soil layer where the bulk of the roots are located.
For cereals, ammonium nitrate is added to pre-sowing cultivation. In the spring, after the restoration of the growing season, fertilizing is carried out on frozen soil.
After soil diagnostics, if necessary, fertilize the root zones with lime-ammonium nitrate in the bushing phase.
This is interesting:
How is potassium nitrate useful for cucumbers during the fruiting period?
Calcium nitrate against blossom end rot.
What is good about nitrogen fertilization of winter wheat and how is it applied.
Dosage
Norm for fertilizing 1 hectare of soil:
- 200-350 kg of ammonium nitrate in the fall for winter wheat;
- 200-300 kg in spring for spring wheat.
What other substances does wheat need?
In addition to nitrogen, cereals need to be fed with other nutrients: phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium and sulfur.The choice of substances depends on the type and condition of the soil.
Symptoms of their deficiency:
- Phosphorus deficiency can be detected in wheat by external signs. If the leaf turns reddish-purple, it means the plant lacks phosphorus.
- Potassium deficiency – necrosis of old leaves, marginal chlorosis.
- The need for calcium is yellowing and deformation of young leaves.
- With a lack of magnesium, small yellow spots appear on the leaves.
- With a sulfur deficiency, the leaves of the cereal turn yellow.
- Insufficient amount of chlorine – leaf spotting.
- Interveinal chlorosis is a sign of iron deficiency.
- With copper deficiency, the tops of young leaves wither, curl, and die.
- With a lack of zinc, wheat appears yellow and brown necrotic spots, which quickly increase in size towards the top and base of the leaf.
- Wheat needs nitrogen throughout the growing season. But its excess can also have a bad effect on culture. The correct regime and dosage of application will help grow a healthy and strong plant.
Read also:
Fertilizers for winter wheat: what to feed in the fall
Conclusion
Ammonium nitrate is a simple and cheap mineral fertilizer. In agriculture, it is used for all crops with small nuances, which, if observed, can significantly increase productivity.