What is foliar feeding of wheat and what fertilizers can be used for these purposes
To obtain a good wheat harvest, mineral fertilizers are necessary. The root system takes the necessary elements from the soil, which is why it is so important to fertilize it. But lack of moisture, low temperature and other unfavorable conditions reduce the ability of the roots to receive the necessary nutrition. In these cases, the leaf feeding method of wheat helps.
What is foliar feeding?
During the entire growing season, wheat needs nutrients. The soil does not contain enough of the necessary elements, so it is important to supply them from outside. Foliar feeding is carried out by spraying. Fertilizers are supplied through the leaves and not through the roots, which is why this method is also called foliar. Absorption occurs faster, but there are limitations. Elements such as magnesium, potassium and nitrogen are absorbed faster, while sulfur and phosphorus are absorbed more slowly. This method of fertilization reduces the possibility of nitrogen removal during leaching and denitrification.
Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages of the method:
- saving wilting plants;
- feeding under unfavorable conditions;
- a quick way to absorb fertilizers.
Flaws:
- Sick plants should not be processed;
- in too hot or cold weather, fertilizing is ineffective;
- It needs to be done often, so it takes more time.
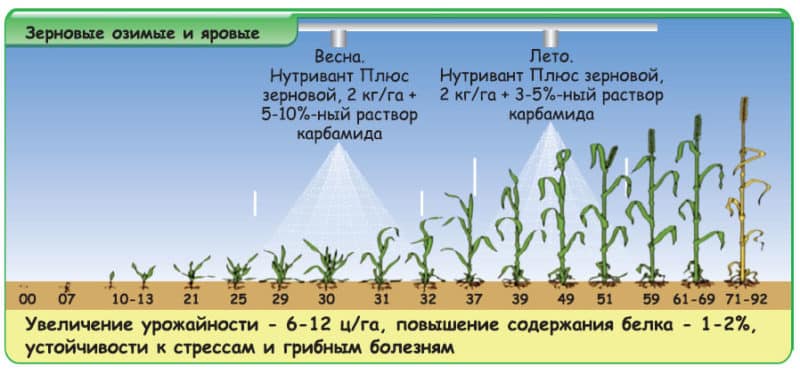
When does feeding begin?
For proper growth and increased yield, it is important to know exactly when to add minerals. fertilizers. At different stages of the growing season, wheat requires different dosages of additives.
Foliar feeding in autumn
During emergence, nitrogen, potassium and phosphorus are needed. If there is a lack of phosphorus, the harvest will be smaller, and it is impossible to compensate for its deficiency at later stages. Potassium is absorbed by the plant before flowering, so it is important that it be contained in the soil before sowing. The content of nitrogen fertilizers should be minimal so as not to reduce resistance to cold and not expose the wheat to diseases and pests.
Foliar feeding in spring

After 6-7 months, active growth of wheat begins. At this stage, the plant needs zinc, magnesium, manganese; Also, the content of sulfur, nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium requires constant monitoring.
Urea is best suited as a fertilizer. Due to its rapid penetration and good absorption along with sulfur and magnesium, it is most often chosen for growing wheat. Urea may be applied together with fungicides and insecticides.
Potassium nitrate is sometimes used; it helps to increase the amount of yield after three treatments. Also during the growth stage, the plant needs ammonium nitrate. Urea is also used; it can increase the protein and gluten content of grains.
Important! The main thing is not to forget that foliar feeding is not the main way a plant obtains fertilizer. The main thing remains the receipt of elements by the root system from the soil.
How to feed wheat
For wheat, in addition to nitrogen, potassium and phosphorus, the presence of the following elements is important:
- sulfur - affects gluten, improving its composition;
- manganese - affects metabolism, participates in water absorption, reduces soil acidity;
- iron - prevents leaves from turning yellow, improves photosynthesis, where this element is needed;
- copper - participates in the metabolism of proteins and carbohydrates;
- zinc - affects productivity, increases the number of grains in ears;
- calcium - reduces soil acidity and disease incidence, increases disease resistance;
- magnesium - participates in the metabolic and respiratory processes of wheat.
Organic fertilizers improve the composition of the soil. Urea (also known as urea, a nitrogen-containing agent) increases wheat growth, density, and increases the amount of protein in the grain.
Correct dosage of fertilizers
When diluting irrigation compositions, the age, variety of plants, and weather conditions are taken into account.
Important! At different stages of the wheat growing season, different nutritional elements are needed.
Nitrogen fertilizers

When applied during the growing season, these products enhance plant growth, their density, and increase the amount of grain. The most expedient of nitrogen fertilizers use urea - it increases the amount of protein in grains. It is also important to evenly distribute the amount of fertilizer throughout the growth period:
- Before sowing, treat the soil with ammonium nitrate - 30 kg per 1 ha.
- In the tillering phase - 35-40 kg/ha.
- Tubing - 65-75 kg per 1 ha.
- The remainder is calculated up to the norm and added during flowering.
Potassium and phosphorus
They help the plant ripen faster and improve its taste. Phosphorus affects the synthesis of nucleic acids and nitrogen digestibility. Superphosphates are the choice. Phosphorus oxide leads to the fact that the fruiting period begins earlier, the crop ages more slowly, the grain becomes of better quality, and the absorption of elements improves.
Potassium
Increases the nutritional value of cereals. Potassium must be added before sowing.Potassium chloride and potassium salt are used as fertilizer at a rate of 50-60 kg/ha.
Calcium
Necessary to reduce soil acidity, which is especially important for the growth of winter wheat. It also improves the quality of photosynthesis and promotes the accumulation of carbohydrates. The most commonly used are calcium carbonate, chalk, limestone, and calcium nitrate at a rate of 3-5 c/ha.
Magnesium
Enrichment of plants with magnesium is carried out in the form of treatment with magnesium sulfate. It normalizes protein-carbohydrate metabolism. Distributed at the rate of 15 kg/ha.
Sulfur
The element is necessary for the absorption of nitrogen and also regulates protein metabolism. Magnesium sulfate (S - 13%) and superphosphate (S - 24%) are used for this. The quantity depends on the quality of the soil.
Reference. Another important point is organic fertilizers. Chicken droppings, humus, manure are used - 25-30 t/ha, wood ash - 3-5 t/ha.
Technology of applying foliar fertilizing
Carry out by spraying in compliance with important conditions:
- Slow drying is necessary, so it is advisable to do it on cloudy days or in the evening.
- Spray all leaves equally at all levels of the stem.
- More than twice a season.
- Selection of a sprayer - the drops should not be too small or, conversely, a strong jet should not be made.
- The water in which fertilizers are diluted must be soft or settled.
- It is important to dissolve fertilizers.
Factors that help the absorption of fertilizers:
| Factor | Characteristic |
| Agrotechnical | Soil acidity, soil preparation, protective measures for plant health. |
| Plant age | Young leaves absorb minerals better. |
| Climate | Sufficient soil moisture and low temperature to prevent leaf scorch. |
| Element Ability | Each element has a different rate of penetration into the leaves. |
| Compound with urea | Urea helps the penetration and absorption of elements. |
| Spray method | Fine droplet spraying with the necessary set of elements. |
Features of the fertilizer

When fertilizing winter and spring wheat varieties Different amounts of mineral fertilizers are needed per 1 hectare of land.
Winter wheat
Winter wheat is more demanding on soil composition.
At the beginning of growth, 45 kg/ha of preparations are required. At the heading stage - 30 kg/ha. At the ripening stage - 15 kg/ha.
Nitrogen is used in amide form (urea). Apply 3-4 times a year.
Spraying with potassium is not cost-effective, since it is slowly absorbed through the foliage.
Spring wheat
Since the root system of wheat is not as developed as that of other grains, the use of fertilizer under the leaf is of great importance for it.
Most of the nutrients are consumed in the first half of the growing season (before flowering):
- 82–90% nitrogen;
- 82–100% phosphorus;
- 100% potassium.
Spring grain crops experience the greatest need for nitrogen during the tillering and booting phases. During this time, they absorb up to 40% of the nitrogen consumed during the growing season.
The critical period for phosphorus and potassium is the initial period of growth. If there is a deficiency, the yield decreases by 20-30%.
Conclusion
The main mistake when carrying out fertilizing is exceeding the permissible concentration of substances in the solution. Instead of fertilizer, this can lead to the death of the entire crop. Leaf feeding is an effective method, especially when combined with root feeding. If you approach the procedure wisely, you can expect a good harvest.