How to distinguish cilantro from parsley
On store shelves you can find two similar bunches of greens: parsley and cilantro (aka coriander). They are easy to confuse during a quick examination, and this can lead to incidents when preparing dishes or traditional medicine.
Such a mistake can be potentially dangerous to health, since the effects of these herbs on the body are different. In this article we will tell you how to distinguish parsley from cilantro and what is the composition of these similar-looking plants.
Description of parsley and coriander
Fragrant parsley and tart coriander, which can be found on store shelves in winter and in garden beds in summer, have different chemical compositions and origins. To understand how one plant differs from another, consider their characteristics.
Characteristics of parsley
Curly parsley (Petroselinum crispum) is a herbaceous plant native to the rocky soils of southern Greece. The name “petroselinum” itself is translated from Greek as “growing on a stone.”
Botanical characteristics:
- family Umbelliferae, class Dicotyledons;
- growing season 2 years;
- plant height 30-100 cm;
- the root system is taprooted, the root has a spindle-shaped thickening;
- stem erect;
- leaves are twice pinnately dissected, triangular in shape, dark green with a shiny surface;
- the flowers are greenish-yellow, collected in inflorescences in complex umbels at the tops of the stems;
- fruits are oblong-ovoid;
- The flowering period is from June to July, the fruiting period is in August.
The shoots of the first year of the growing season produce a larger harvest of greenery, the shoots of the second year are more prolific in terms of seeds.
Chemical composition of seeds:
- essential oils (up to 7%) containing apiol, furocoumarin, bergapten and apiin;
- nutrients – fats (up to 22%), proteins, carbohydrates;
- vitamins A, E, C, groups B and H;
- mineral components - potassium, calcium, magnesium, sodium, phosphorus and iron.
Parsley seeds are used to obtain essential oil, and also as a raw material for the production of technical oil, in cooking - as a seasoning for baking bread. In medicine, shoots and seeds are used as components of diuretic preparations; a number of drugs used for flatulence, neuralgia and dysmenorrhea are obtained from them.
Chemical composition of fresh greens:
- nutrients - proteins, fats, carbohydrates;
- vitamins – A, E, K, C, H, group B;
- essential oil (up to 0.3%);
- biologically active substances – flavonoids and phytoncides;
- minerals - potassium, calcium, iron, magnesium, phosphorus, sodium, zinc, copper, manganese and selenium.
Fresh and dried greens are used in cooking as a seasoning for meat, fish dishes, soups and salads. Umbrellas and dried leaves are added to canned dishes.
Juice is obtained from fresh shoots, which is used in folk medicine as a prophylactic agent that improves the functions of the adrenal cortex and thyroid gland. In traditional medicine, dietary supplements and drugs that have a diuretic effect are made from parsley.
Parsley preparations support the tone of the smooth muscles of the uterus, intestines and bladder.
Medicines and dishes with parsley are contraindicated during pregnancy due to the increased risk of uterine bleeding due to placental abruption and uterine contraction, which can cause serious harm to the body and lead to miscarriage.
This is interesting:
We distinguish hot fruits easily and simply - cayenne pepper and chili.
Characteristics of coriander
Coriander (Coriandrum sativum) is a herbaceous plant native to ancient Rome. The name of the plant comes from the Mycenaean Greek “κoρις”, meaning the word “bug”, since the immature leaves have a specific odor similar to that emitted by bedbugs when in danger.
Cilantro is the name given to coriander greens collected before the seeds ripen. The word “cilantro” comes from the Georgian language; this seasoning is widely used in Georgian national dishes.
Botanical characteristics:
- family Umbelliferae, class Dicotyledons;
- growing season 1 year;
- plant height 40-70 cm;
- the root is tap-shaped, spindle-shaped;
- the stem is bare, straight, with branches in the upper part;
- the shape of the leaves varies depending on the position on the stem - the basal leaves have a broad-lobed, tripartite, coarsely dissected leaf plate, in the lower part of the stem there are leaves with a short petiole that are twice pinnately divided, in the middle and upper parts of the stem the leaves are sessile, pinnately dissected with linear lobes;
- the flowers are white or pink, collected in an inflorescence of a complex umbrella at the tops of the peduncles;
- fruits are non-disintegrating ovoid-spherical ovoid-shaped fruits;
- The flowering period is from June to the end of July, the fruit ripening period is from August to September.
Coriander is cultivated everywhere, including in the central regions of Yakutia. Distributed not only in the temperate and subtropical climate zone of Eurasia, but also in America, Australia and New Zealand.
Chemical composition of seeds:
- essential oil (up to 1.6%) containing linalool, geraniol, borneol, geranyl acetate and other volatile components;
- nutrients – proteins, fats (up to 28%), carbohydrates;
- vitamins B1, B2, C, PP;
- mineral components – calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, sodium, potassium, iron, manganese, copper, selenium, zinc;
- biologically active substances - sterols, tannins, organic acids, rutin.
The fruits are used in cooking as a seasoning for meat and fish dishes, Borodino bread, and canned preparations. In medicine, the seeds are used to obtain drugs that have choleretic, expectorant, carminative, antihemorrhoidal, laxative, appetite stimulant and wound-healing properties.
Essential oil from coriander seeds is used in perfumery and in the manufacture of cosmetics. Fatty oil is used in soap making.
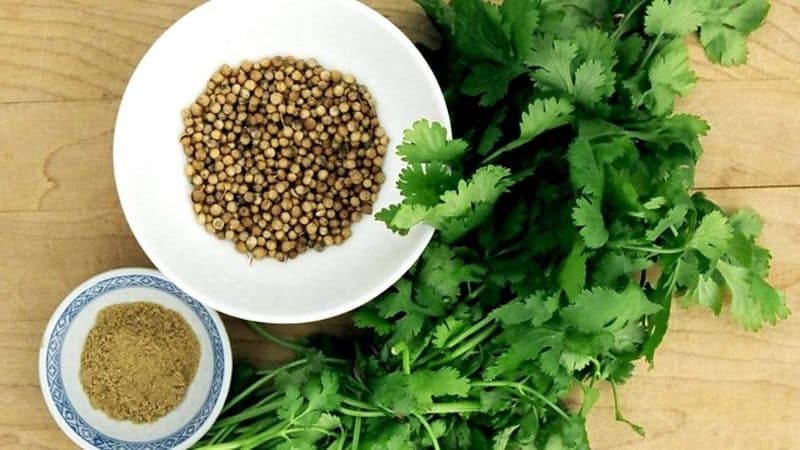

Chemical composition of cilantro:
- nutrients;
- vitamin A, groups B, C, E, K, PP;
- aldehyde trans-tricedenol-2, which gives the plant an unpleasant “bug” smell;
- biologically active substances – choline, carotenes, rutin;
- minerals - calcium, iron, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, sodium, zinc, copper, manganese, selenium.
Greens are used as a seasoning for meat dishes, soups and salads. Young leaves are eaten, before the shoot of the stem begins to form. In folk medicine, cilantro juice and decoction are used to improve vision, for nervous disorders, indigestion and high cholesterol levels.
Comparative characteristics of parsley and coriander
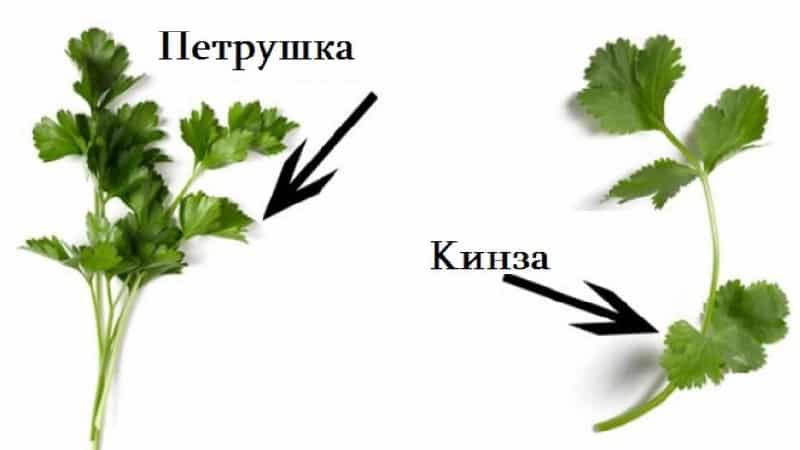
The plants belong to the same Apiaceae family, but to different genera. The differences between cilantro and parsley are shown in the table.
| Distinctive feature | Parsley | Cilantro |
| Leaf Shape | Double pinnately dissected | Trifid, coarsely dissected and doubly pinnately divided |
| Smell | Pleasant, spicy | Unpleasant, pungent "bug" |
| Use during pregnancy | Forbidden | Allowed in limited quantities |
| Daily consumption rate | 50 g, exceeding the norm can lead to poisoning, hallucinations and convulsions | 105 g, exceeding the norm leads to sleep disturbances, weakened memory, and hormonal imbalances in women |
| Content of vitamins (except A, group B, E, K and C, which are contained in both plants) | Contains biotin - vitamin H | Contains niacin - vitamin PP, choline - B4 |
| Flower color | Greenish yellow | White or pink |
| Stems height | Up to 100 cm | Up to 70 cm |
| Plant lifespan | 2 years | 1 year |
In the photo you can see the difference in the appearance of these two herbaceous plants, but the most telling sign by which you can distinguish coriander and parsley is the smell. If a bunch of greens smells like bugs, you're holding cilantro, not parsley.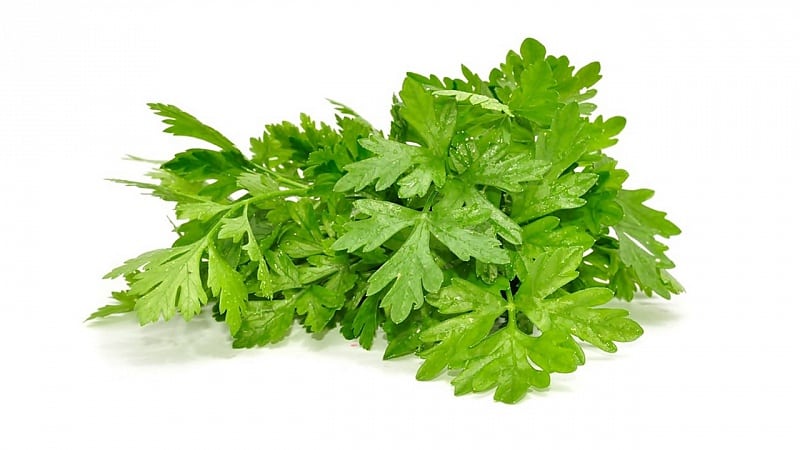
The seeds of these plants are even easier to distinguish. In coriander they are in the form of small yellow-brown round peas, and in parsley they are pear-shaped with easily separated segments.
Read also:
How to make parsley ice for the face: beauty and health of the skin.
Conclusion
Coriander and parsley are not the same thing, but completely different plants. The greens of these plants can be distinguished by their smell and appearance.These types have different chemical compositions, so their areas of application are different.
Cilantro is not used in traditional medicine, but folk recipes with this plant are known. Parsley is used in traditional medicine as a raw material for preparations and medicinal preparations. Both plants are used in the culinary and cosmetic industries.