Mid-early gooseberry variety with high winter hardiness “Hinnonmaki Green”
Gooseberries have been and remain one of the most popular berries among plot owners. Gradually, old, unproductive varieties are being replaced by modern ones with improved agrotechnical characteristics and a more pronounced taste. Hinnonmaki Green is one of the representatives of the culture that is worth paying attention to both novice and experienced gardeners.
Features of the variety
Hinnonmaki Green is from Finland and zoned specifically for cold European climates.
History of origin and distribution
In the middle of the last century, before Finnish scientists the task was set to develop a new version of the crop, fundamentally different from others in its unpretentiousness and productivity. The work was crowned with success - the Hinnonmaki variety appeared.
Interesting! But scientists went further and continued crossing to obtain bushes with different berry colors and other varietal characteristics. The series includes the popular Hinnonmaki Red (Roth), Yellow, Gelb and Green. The latter is distinguished by green fruits.
Characteristics and description of bushes
This is a tall plant with a mid-early ripening period.. The usual height is 1-1.2 m, but in an ideal place and with quality care it can grow up to 2 m. The crown is spherical and compact, the branches are thorny, slightly spreading, but grow densely. The bark is dark brown, peeling off in scales.
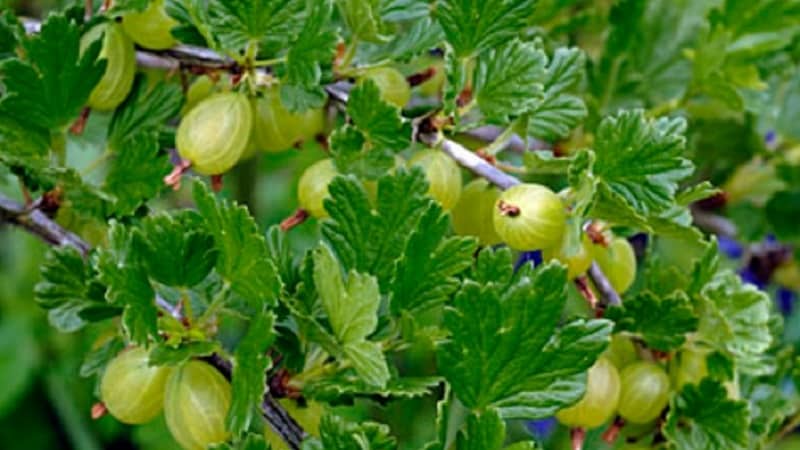

Dark green foliage with three to five lobes and slight pubescence. Pale yellow flowers appear in May from the axils of the leaves one at a time or in groups of 2-3.
Temperature resistance
Hinnonmaki Green has extremely high frost resistance. Since the harsh Northern European climate was taken into account when breeding, it easily tolerates cold temperatures down to -30°C. In more extreme conditions, bushes require complete shelter for the winter.
Moisture and drought resistance
Gooseberries tolerate periods of drought well and do not die without an influx of moisture.. Water is required during fruit formation and filling. If it is not enough, the bush will shed some of the ovaries. The remaining berries will be small and sour.
Resistance to diseases and pests
The variety exhibits high resistance to diseases and pests. Immunity against mildew and powdery mildew is more developed. It is affected by pests when they spread throughout the entire area.
Characteristics and description of fruits
The berries are large, drop-shaped, weighing 4 g. The color is green with an olive tint, with dark veins inside. The fruits are juicy with a delicate aroma and taste sweet and sour. Tasters give the variety a score of 4.7 points. The berries are prone to shedding, but the skin does not crack.
Gooseberry Hinnonmaki Green bears fruit in the third year after planting. The yield is stable, 4-7 kg per bush per season. Collection begins in the first half of July and continues until mid-August.
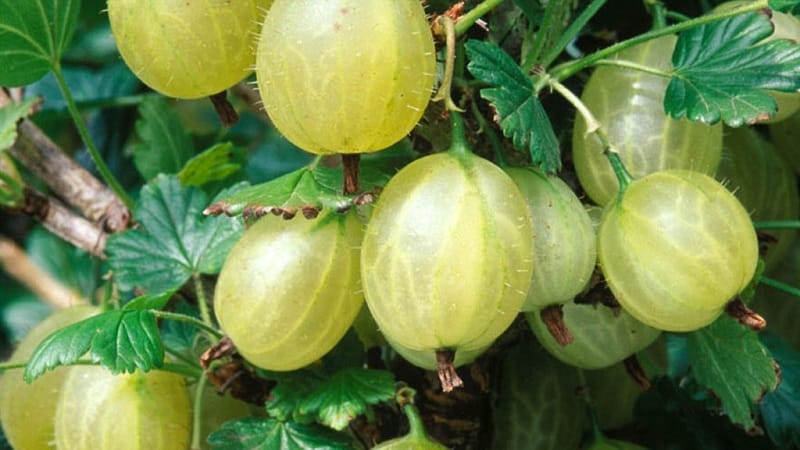

Application area
Berries are picked with stems to extend shelf life. To preserve their presentation, they are scattered on a tray in a thin layer and stored in the refrigerator or basement. The latter option requires a temperature no higher than +3°C. Under such conditions, the crop does not spoil for up to 60 days. If you use closed containers, the shelf life is extended to 3 months.
Gooseberries are consumed fresh and used for fillings for pies and fruit desserts. The fruits are also used to make juices and wine.
Other gooseberry varieties:
Mid-early green gooseberry variety "Malachite"
Advantages and disadvantages compared to other varieties and hybrids
The variety was appreciated by professionals and amateurs for a number of advantages.:
- distinctive frost resistance;
- does not require constant attention in terms of watering and fertilizing;
- productivity is above average;
- berries with high taste characteristics;
- accepted on standard;
- resistance to many diseases characteristic of the culture.
The disadvantages include a large number of thorns and shedding of ripe berries.
Growing technology
The correct choice of seedling and adherence to agricultural technology when planting give a good start to the successful development of the bush.
Optimal conditions
A plot is prepared for gooseberries that meets the following conditions::
 Constant illumination throughout the day. In a dark place, the bush begins to hurt, the yield and quality of the fruit decreases.
Constant illumination throughout the day. In a dark place, the bush begins to hurt, the yield and quality of the fruit decreases.- There is protection from northern winds.
- The site is a plain or hill with a low groundwater threshold. Soggy soils and spring floods will lead to the death of the bush.
Gooseberries should not be planted next to or after raspberries and currants.. The land in this place is already depleted, and the diseases and pests of the crops are the same.
Landing dates and rules
In regions with harsh, long winters, gooseberries are planted only in spring. Usually this time falls in the middle - end of April, when the snow has melted and the surface layer of the earth has warmed up and become saturated with moisture.
In temperate and warm climate zones planted in autumn and spring. In each case, it is taken into account that the minimum suitable temperature for survival is +4...+6°C. For work, choose a cloudy, windless day.
Selection of seedlings
When purchasing, pay attention to the condition of the root system and shoots. Choose a high-quality seedling 2-3 years old with flexible branches without damage. The buds and bark are alive, without spots, and there are at least three basal shoots.
The bush in the container is removed and inspected. Healthy roots are white, without signs of dryness, tightly intertwined in an earthen ball.
Preparing the site
2-3 weeks before landing, prepare the site according to the instructions:
- pull out weeds with roots;
- per 1 sq. m scatter a bucket of humus and 30 g of phosphorus-potassium fertilizer;
- dig to a depth of 30-35 cm;
- make holes 60 cm deep and 40-50 cm in diameter;
- drainage made of crushed stone or expanded clay is placed at the bottom;
- The hole is half filled with earth and watered.
The variety prefers soil with medium acidity (pH 5.5-5.6). The clayey soil is loosened with sand, and black soil is added to the sandy soil.
Landing technology
Before planting, the seedling is kept for 30-40 minutes in water or Kornevin solution. Further:
- a mound is formed in the middle of the hole, a bush is placed with a slight slope and the roots are straightened;
- cover with earth so that the neck goes 5-7 cm below the surface level;
- compacted to avoid the formation of voids;
- make a roller around the bush from the remains of the soil;
- watered.
Further care
Gooseberries do not need constant attention. All the main measures come down to rare fertilizing and watering, pruning and treatment for the purpose of prevention infections and pests.
 At first, water once a week if there is no rain. In total, moisture is charged three times per season.:
At first, water once a week if there is no rain. In total, moisture is charged three times per season.:
- in the phase of flowering and ovary formation;
- at the beginning of fruit ripening;
- in preparation for winter.
Water is poured under a bush to the root zone.
Important! Avoid contact with leaves, otherwise drops and sun will cause burns.
When the soil dries out, loosen it, mulch if desired.
If the area was initially well supplied with nutrients, auxiliary feeding is required only for 2-3 years. In the spring, water with a solution of nitrogen-containing fertilizer, mulch with a mixture of half a bucket of humus and 0.5 liters of ash.
During autumn processing scattered under a bush 2 tbsp. l. superphosphate and dig up with the formation turned over.
Trimming
Pruning is aimed at rejuvenation and increasing productivity. It also prevents infections and improves the ventilation of branches. The work is carried out in the spring before the buds open or in the fall two months before frost. Remove:
- long shoots extending beyond the crown, leaving 5-7 buds;
- broken, diseased and damaged ones are cut out at the root;
- old branches.
The wounds must be lubricated with garden varnish.. Leave 5-6 young shoots so that they grow evenly throughout the bush in all directions.
Possible problems, diseases, pests
Disease outbreaks and insect pests are promoted by improper care or its complete absence. Such problems include too shady place, excess moisture, unsanitized cuts when pruning.
Possible fungal pathogens include: anthracnose, gray rot, rust goblet, white spotting. If signs are detected, diseased shoots are urgently cut out and burned. Before or after flowering and fruiting, they are sprayed with Topaz, HOM, Ridomil, and Skor.
Pests appear more often aphids, spider mites, sawflies, moths.At an early stage, treatment with a soap solution or onion decoction helps. In case of serious damage, insecticides “Karbofos”, “Aktara”, “Inta-Vir” are used.
Wintering
For a safe winter, gooseberries are watered abundantly and the root zone is mulched. any organic material. To be on the safe side in light snowy weather, they are additionally covered with straw.
In the middle zone, shelter is not required if Frosts below -30°C are not expected. In more severe conditions, snow is thrown over the bush and the root zone is trampled.
Reproduction
Vegetative methods are used for propagation. This way, varietal characteristics are preserved without loss of quality. Methods:
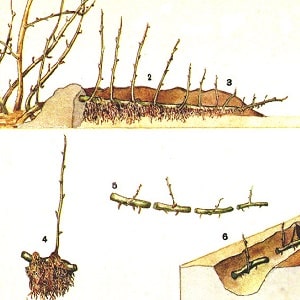 By layering - rooting of the shoot. In the spring, a healthy lower branch is selected, pinned to the ground with a staple and covered with earth, leaving 3-4 buds on the surface. It is watered all summer; it should not be allowed to dry out for a long time. In the fall, they are cut off from the mother bush and planted in a permanent place.
By layering - rooting of the shoot. In the spring, a healthy lower branch is selected, pinned to the ground with a staple and covered with earth, leaving 3-4 buds on the surface. It is watered all summer; it should not be allowed to dry out for a long time. In the fall, they are cut off from the mother bush and planted in a permanent place.- Division - the method is simple and fast. An adult bush is divided into parts so that each has 2-3 shoots, and planted as usual.
- Cuttings. An adult branch is cut into pieces 15-20 cm long with 3-4 buds on each. The cuttings are buried two-thirds into a box with soil, watered and covered with film to create a greenhouse. Ventilate and moisten periodically. When sprouts with several leaves appear, they are transplanted into holes.
Features of cultivation depending on the region
The variety easily adapts to cold climates, therefore suitable for the middle zone, Non-Black Earth Region and Siberia. For areas with constant frost, the difference is in winter preparation. The crown is wrapped with covering material, burlap, and the roots are insulated with a thick layer of spruce branches.
In the southern regions the variety is easy to cultivate, as it easily tolerates heat and drought.
Pollinator varieties
The variety Hinnonmaki Green belongs to the self-fertile type. It is pollinated by bees and bumblebees.
Reviews from summer residents
Gardeners have long tried the variety and speak neutrally or positively about it.
 Galina, Moscow region.: “This season I harvested the Hinnonmaki Green bush for the first time. The berries are completely green, not the largest, but I like the taste. If this continues, I will purchase other varieties for the collection.".
Galina, Moscow region.: “This season I harvested the Hinnonmaki Green bush for the first time. The berries are completely green, not the largest, but I like the taste. If this continues, I will purchase other varieties for the collection.".
Victor, Ryazan: “Finnish Hinnonmaki Green turned out to not have the highest yield, and there are a lot of thorns. The taste is honey-tinged; the berries are among the first to ripen and are eaten quickly. The bush is slightly taller than a meter, it has been growing for 6 years, I made a support immediately upon planting.”.
Conclusion
Gooseberry Hinnonmaki Green meets modern requirements. Due to its unpretentiousness and endurance, it is cultivated in most climatic zones. Care comes down to periodic watering, fertilizing and crown formation. Prevention of diseases and pests, vegetative propagation is required.