Easy-to-care gooseberry variety “Yarovaya” - ideal for the most delicious preparations
Spring gooseberry is one of the most popular varieties among gardeners in Russia and the CIS countries. It produces a harvest with high taste characteristics of berries and has simple agricultural technology.
In this article you will find a detailed description of the variety, its advantages and disadvantages, technology and cultivation features depending on the region.
What kind of gooseberry is this?
A number of key advantages and relative unpretentiousness have brought the variety into the range of promising ones.
Brief history of origin and distribution
Yarovaya gooseberry was bred by sectional scientist A.G. Voluznev at the Belarusian Research Institute of Horticulture and Potato Growing.
The Columbus variety was used as the mother base. Its seeds were processed using the open pollination method and a berry with new varietal qualities was obtained.
Characteristics and description of bushes
Spring gooseberry is classified as medium in height - the bush reaches 1.5 m and consists of smooth, erect shoots. The crown shape is slightly spreading. The branches are moderately covered with double or single thin thorns. Dark green leaves are round in shape with jagged edges.
An adult plant requires support or garter to a trellis.
Temperature resistance
The variety is characterized by increased winter hardiness. It easily tolerates frosts down to -30...-35°C. Under more severe conditions, the root system suffers and the buds die, which will affect the harvest of the next season.
Particular attention is paid to young bushes, for which at -4°C the likelihood of frost damage increases. Their pre-winter preparation necessarily includes insulating the root zone with a thick layer of mulch.
If the bush freezes, the recovery period will take 4-5 years.
Moisture and drought resistance
The Yarovaya variety can withstand prolonged heat and drought. The greatest need for moisture occurs during flowering and the beginning of fruit ripening. Systematic irrigation at this time will increase the yield by 20-25%.
Constant excessive watering or close groundwater leads to the death of roots.
Resistance to diseases and pests
The variety is not susceptible to powdery mildew, one of the most common crop diseases. In unfavorable phytosanitary conditions on the site, it is affected by pests and pathogenic organisms.
Characteristics and description of fruits
Yields are high - up to 6 kg per bush. Most of it is formed on shoots that are 3-6 years old. Under the right growing conditions, stable fruiting lasts at least 20 years.
Increased yield and masses of berries timely watering and good lighting promotes. In the shaded area, the fruits become smaller and their number decreases.
The fruiting period begins at the end of June - beginning of July. The berries are lemon-yellow in color, with thin skin and a sweet and sour taste. The shape is oblong, there is almost no edge, the average weight of the fruit is 3-4 g.
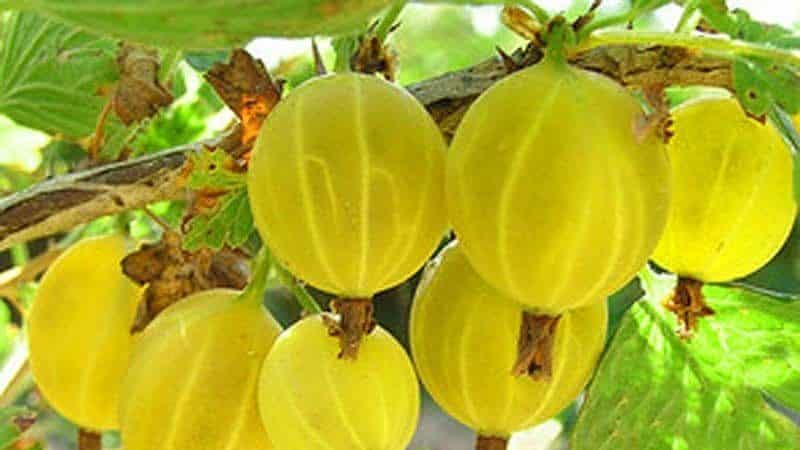

Important! Overripe gooseberries bake in the sun and take on a watery and empty taste.
Areas of their application
The Yarovaya variety belongs to the category of universal use. The berries are processed into jam, compotes and various desserts.Freshly harvested crops are stored in the refrigerator, scattered in containers in a thin layer.
If transportation is necessary, unripe gooseberries are collected.
Advantages and disadvantages of the variety
The variety has many advantages:
- early maturation;
- high yield rates;
- long fruiting;
- drought and frost resistance;
- transportability, berries retain their presentation for a long time;
- resistance to powdery mildew.
During the cultivation process, some shortcomings were discovered:
- high probability of infection with fungal diseases;
- the berries quickly ripen and the pulp acquires a mealy texture;
- sharp thorns interfere with harvesting and care.
Growing technology
The rules for growing gooseberries come down to determining a suitable site, planting time and further care.
Optimal conditions
Choosing a planting location is one of the primary conditions for trouble-free cultivation and the development of varietal capabilities.
Areas along fences and fences are suitable for gooseberries, which will protect them from wind blowing.
Other requirements:
- lack of shadow;
- passage of groundwater at a level not exceeding 1.5 m;
- neutral or slightly acidic drained soil.
Landing dates and rules

Autumn is most suitable for planting crops. 3-4 weeks before the onset of frost, prepare the place. In this case, the adaptation of the plant to the climate of the area will be easier. In the spring, they are planted in March-April in order to have time before the sap begins to flow.
When purchasing planting material, they are guided by the following quality criteria:
- seedling age 2 years;
- 2-3 main shoots from 20 cm long;
- main roots - from 25 cm;
- no deformation or damage.
The planting holes are placed in such an order that there is a distance of at least 1-1.5 m between neighboring bushes, and 2 m between rows. The hole is made 2 times larger than the volume of the roots.
Important! Thickening of bushes will lead to a decrease in yield, insufficient air circulation, and an increased risk of disease development and the spread of pests.
Planting stages:
- The soil from the hole is mixed with compost or rotted manure, 2 tbsp is added. l. potassium sulfate and superphosphate.
- Trim dried roots.
- The branches are shortened by 1/3 of the length, but so that at least 5 buds remain. This will ensure active growth and tillering.
- The seedling is placed in the middle of the hole so that the root collar is 5-8 cm below the ground level.
- Cover with soil, compact and mulch with any organic matter.
Further care
Creating favorable conditions for growth immediately after planting will ensure rapid survival and adaptation of the bush. In autumn, seedlings are watered with warm water once if the weather is dry. During pre-winter preparation, they are insulated with sawdust, leaves or spruce branches.
In the spring, when the buds awaken, the entire growing season is watered as the soil dries out. In the phase of ovary formation, moisten 1-2 times a week - 10 liters of water per adult bush. After picking the berries, watering is continued, since at this time the buds are being laid for the next season. The surface layer of the earth is loosened shallowly so that a crust does not form.
Important! Water is poured only under the root on the tree trunk circle. Sunburns often form on wet leaves, and fungal spores are activated in cloudy weather.
Top dressing
Gooseberries do not require constant feeding; several times a year are enough.
Subsequence:
- In spring, pour 30 g of saltpeter in a solution.
- In summer - feed once during berry set with a mixture of 70 g of superphosphate and 30 g of potassium sulfate.
- The second time after harvesting, fertilize with a complex mineral composition according to the instructions.
Trimming
Pruning is done in April, before the buds awaken, and in the fall, before the first frost. In the first 3 years, the perennial branches of the gooseberry are shortened by half. This procedure sets the basis for a healthy bush crown. Dry and diseased shoots are cut off at the very base.
In the 4th year, the bush is thinned out to prevent thickening. According to the standard, the crown should consist of 15-20 branches, with 2-3 branches for each age.
Important! Correct and timely pruning has a positive effect on yield and reduces the risk of disease.
Possible problems, diseases, pests
Problems during cultivation are caused by diseases, the appearance of which cannot be ignored:
- Septoria - small brown spots turning into white. The leaves fall, the quantity and quality of berries decreases.
- Anthracnose - spreads in humid climates. Settles on the underside of foliage in the form of dark red spots. It quickly affects the entire green mass of the bush, then spreads to the shoots.
- Spherotheca (American powdery mildew) is a white coating on berries that gradually thickens. The harvest becomes unusable.
The Yarovaya variety is practically not susceptible to viral infections. For treating bushes process before flowering and after fruiting with fungicides. Among gardeners, Arcerid, Topaz, and Tiovit-Jet are trusted. For prevention and in the early stages of the disease, biological products “Fitoverm”, “Trichodermin”, “Fitosporin-M” help.
Pests that cause the most damage:
- Spider mite - settles on the underside of the leaf, entangles it in a web and feeds on the sap of the plant. Hot weather promotes spread.
- Yellow sawfly - winters under a bush, in the spring it flies to the bush, lays larvae and eats greenery.
- The moth is a butterfly that lays eggs in gooseberry flowers. Unripe berries turn red, indicating the presence of a caterpillar inside.
- Glasswort - overwinters in the bark of shoots. It eats the buds and then feeds on the core of the branches, which leads to their drying out and breakage.
The danger of pests is not only the destruction of the bush, but also the spread of pathogens. Autumn treatment with insecticides, including the tree trunk circle, will save you from them. “Aktara”, “Aktellik”, “Iskra-M”, “Karbofos” are suitable for gooseberries. If parasites appeared during the growing season, then spray only after picking the berries.
Wintering
Before frost begins, collect fallen leaves and remove weeds. The tree trunk soil is loosened with a couple of handfuls of ash and mulched with compost or sawdust. If frosts below -35°C are not predicted for the coming winter, then insulation is not required.
Reproduction
Gooseberry reproduce seeds and vegetatively. The first method is used to breed new varieties. Ordinary gardeners propagate using shoots and dividing the bush.
Layerings
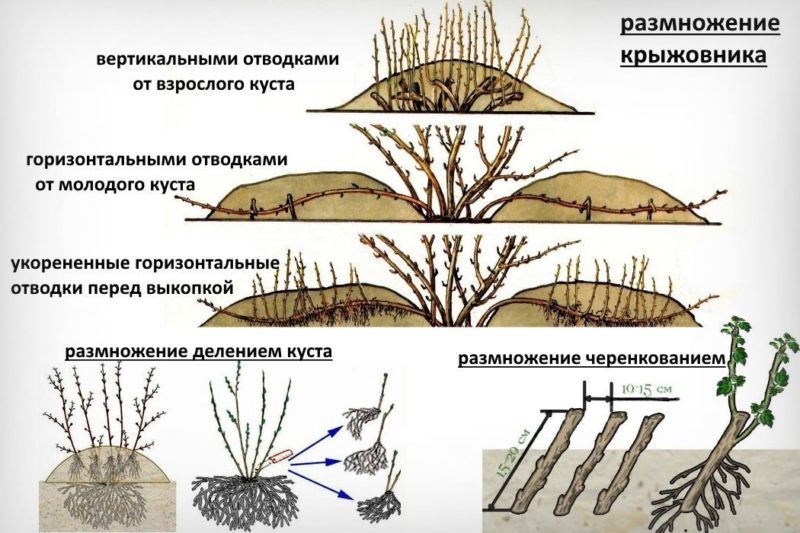
Horizontal - in early spring, one of the strongest shoots is bent to the warmed ground and fixed. They do not cover it with earth. By the beginning of summer, sprouts will appear, they are spudded with nutritious soil. In the fall, part of the branch is cut off from the bush, the seedlings are divided according to the number of rhizomes and planted in a permanent place.
Vertical - in autumn the shoot is shortened by 1/3 of its length. In the spring, new branches will emerge from the base. When they reach 15 cm in length, they are covered with fertile substrate.In October, the shoots are cut off along with the formed roots and replanted.
Cuttings
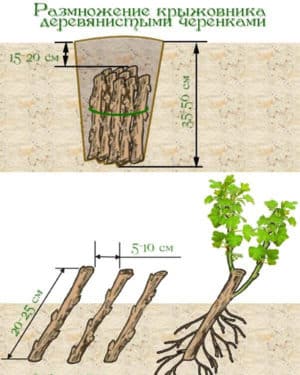
For this method, young branches are used. They are cut and divided into parts 8-10 cm long, so that each has 2 internodes. Root in a box with nutrient soil. Water and spray periodically until roots and new shoots appear. In autumn, the cuttings are ready for planting.
Dividing the bush

The bush is divided before the start of sap flow or after the end of the growing season. The dug up gooseberries are cut into pieces with sharp pruners or a knife so that each has a root and 2-3 new shoots. Planted in the traditional way.
Features of growing this variety depending on the region
Spring gooseberries are ideal for growing in the European part of Russia, the North-West region, the Volga region and the south of the country. The temperate climate provides optimal conditions for the growth of the crop.
In Altai, the Far East and Siberia, the variety requires shelter for the winter. In the southern regions, gooseberries need more frequent watering.
Pollinator varieties
The Yarovaya variety is self-fertile and does not need proximity to pollinators. But in practice, it has been noticed that when pollen from other types of gooseberries gets in, the yield increases.
Reviews from summer residents
Most owners of the variety are satisfied with the purchased variety; the advantages include taste and resistance to diseases.
Svetlana, Minsk: “I decided to find a sweet gooseberry variety. The seller advised Yarovaya, I believed it and for good reason. Already in the first spring I was pleased with a large number of berries. At the end of June I harvested the first harvest of sweet yellow berries.”
Dmitry, Nikolaev: “I am satisfied with the variety in terms of taste and yield, the berries are beautiful. Ripens a week earlier than other species. In 10 years powdery mildew I never noticed."
Leonid, Rostov-on-Don: “The variety justifies the title of early. The taste is good, there is little acid, the berries are medium to large in size. The branches were covered with them, so I had to make a support. Every season we make a lot of jam. We haven’t had to deal with pests or diseases yet.”
Conclusion
The Yarovaya variety takes root in all horticultural regions. Its popularity is explained by its early ripening, tasty berries and winter hardiness. Agricultural technology comes down to periodic watering, fertilizing, pruning, and preventing pests and diseases.