How and with what to treat garlic before planting for the winter: rules for preparing planting material and useful tips
Farmers who invest effort and money in preparing garlic in the fall receive an early and rich harvest. The advantages of winter garlic (planted in the fall) are disease resistance, high yield, and long-term storage.
From spring Winter garlic is distinguished by a uniform arrangement of small cloves around the stem in the head. They have an even number - 6-10 pieces, a thicker shell, a pronounced burning taste and are great for food and pickles.
We will reveal the secrets of a bountiful harvest and tell you how to treat garlic before planting for the winter.
Preparing the land for autumn planting of garlic
The first stage is choosing a site for planting and preparing the soil in the fall. Planting activities begin in early September. When choosing a place for a bed of garlic, make sure that it is well lit and not in a draft.
So that when the snow melts, water does not accumulate in the garden bed and the garlic does not rot, we place the plantings on a hill. Notice where the snow falls first on your site, where the highest place is, and try to plant there.
If potatoes, carrots, turnips, onions or radishes previously grew in the selected bed, this place is not suitable for planting garlic, because their pests are the same. It is better if these are beds after tomatoes, zucchini, legumes, and cucumbers.
 The soil should be loose and light, so we’ll first dig up the bed to the depth of a spade and fertilize it.If there is a lack of time, we buy ready-made fertilizers, but they are easy to prepare yourself. For example, let's feed with the following mixture: 45 g of classic mineral fertilizer - nitrophoska and 45 g of superphosphate, 250 g of dolomite flour, add this to a bucket of humus and fertilize the bed for the crop (calculated per square meter).
The soil should be loose and light, so we’ll first dig up the bed to the depth of a spade and fertilize it.If there is a lack of time, we buy ready-made fertilizers, but they are easy to prepare yourself. For example, let's feed with the following mixture: 45 g of classic mineral fertilizer - nitrophoska and 45 g of superphosphate, 250 g of dolomite flour, add this to a bucket of humus and fertilize the bed for the crop (calculated per square meter).
Advice. Sprinkle wood ash between the rows of garlic to repel pests. The distance between rows is 25 cm.
Be sure to determine the acidity of the soil. If nettles, coltsfoot, and clover grow, these are signs of soil with normal acidity. We noticed plantain or ivy - high acidity. Garlic bears fruit well in soil with normal acidity, so if the levels are elevated, treat the soil with chalk or dolomite flour.
Garlic is planted to a depth of 12 cm, then covered with peat or sawdust, or, in extreme cases, dry leaves or pine needles.
The third stage is soil disinfection. This can be done in several ways:
- 5 g of manganese per 10 liters of water;
- 40 g of copper sulfate per 10 liters of water;
- 1 g manganese, 1 g boric acid, 1 g copper sulfate per 1 liter of water.
After this, pour in tinctures of calendula and yarrow, cover with film and remove it only before planting.
Selection and preparation of seed material

What kind of seeds you plant is also important. You can select and prepare the soil perfectly, and the planting material will be pumped up. Then don’t expect a harvest.
We pay attention to the following subtleties:
- We choose planting material that is large and dry, without damage, in a word, healthy. Please note that the cloves should have scales;
- When separating the cloves, be careful not to damage the bottom part. The end of the clove should be dry and uniformly gray in color.
Processing garlic before planting
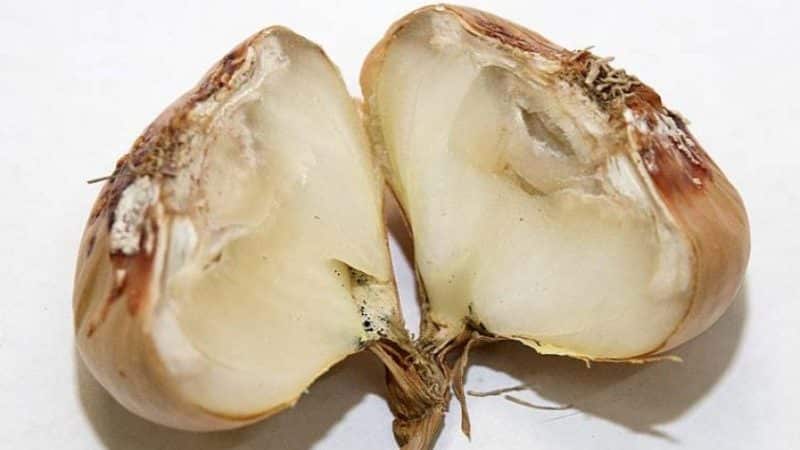
Before planting, processing of planting material is required. Garlic, despite the fact that it itself perfectly removes various viruses and bacteria, is very susceptible to various diseases. These are, for example, neck or bacterial rot, downy mildew or downy mildew, garlic rust or garlic fusarium.
Look at the photo to see what the diseases look like.
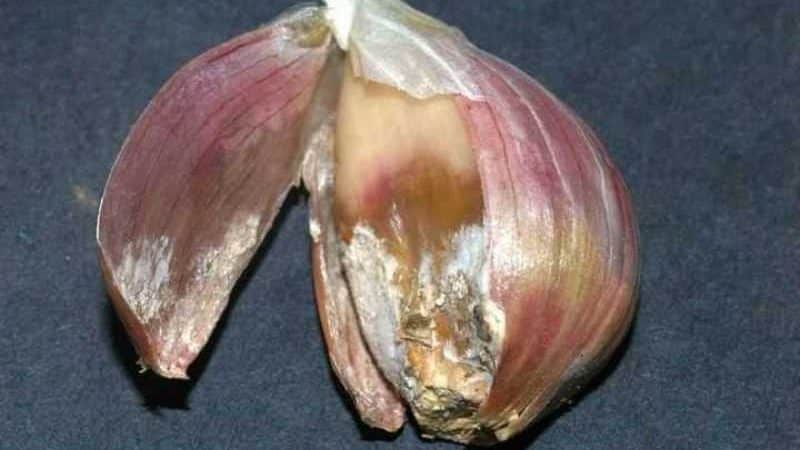
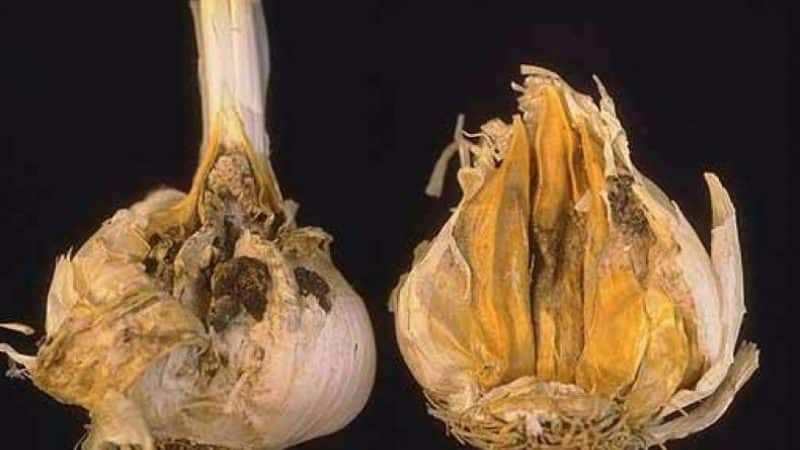

We get rid of potential pathogens before planting by properly processing the planting material.
For example, garlic bacteriosis affects plants not only during growth, but also during storage. Bacterial rot manifests itself as brown sores on the cloves or transparency of the clove. Garlic is susceptible to disease if it is not ripe or is poorly dried before storage, or perhaps stored in a damp place. With this disease, it is not enough to process only the garlic; you also need to cultivate the soil.

How to process garlic
Let's take a closer look at what and how garlic is processed.
Brine
Solution: 2 tablespoons of salt per 1 liter of water.
Soaking time: half an hour.
Copper sulfate
Solution: 10 g of vitriol in 1 liter of water.
Soaking time: 3-4 hours.
Potassium permangantsovka
Solution: a couple of manganese crystals per 5 liters of water.
Soaking time: overnight or 3-4 hours.
Ash liquor

Making lye is quite simple. We take ash from burning pine and birch firewood, corn and sunflower stalks, rye straw and buckwheat straw. Lighting agents must not be used, as well as burning plastic, cellophane and garbage in the same fire. The ash must be clean.
Solution: sift the ash and fill it with water after rain, melted water or simply boiled water. Proportions: for 0.5 kg of ash we use 3 liters of water.
Then there are two ways:
- Leave for 3-5 days, shaking regularly, then remove everything that floats on top and pour into plastic bottles.
- Leave for 20-30 minutes, then heat, almost bringing to a boil (but do not boil!). Let it cool completely, remove all excess from above and bottle the remaining cloudy liquid.
Store for about six months. It cannot be used in concentrated form. Dilute with water in a ratio of 1:2.
We use it instead of saline solution to disinfect garlic before planting. Dilute the lye and soak the garlic in it for 1-2 hours.
Fungicide "Maxim"
The fungicide is not toxic to humans; it is the only product of its class approved for use in gardens and summer cottages. It is odorless and mixes easily with water. A red pigment is added to the suspension, which allows you to control the application process.
It is valid for 48 days after application, so you can treat it at any convenient time.
It is also used to treat planting crops. Please note that the disinfectant cannot be used on sprouted or already infected seeds that have cracks. It doesn't cure, it prevents disease.
"Maxim" is prepared in glass or plastic containers. The shelf life of the solution is one day after preparation.
Solution: 2 ml of the drug is mixed with 1 liter of water.
This is enough for 1 kg of garlic. The drug protects garlic from such forms of rot as bottom rot, black rot, gray rot and penicillium rot.
Fitosporin
Phytosporin is sold in powder, liquid and paste form. It is better to buy it in the form of a paste - it is both more convenient and economical to dilute. The powder is poorly soluble and cannot be stored; the liquid form is weaker in effect.
Solution: take a packet of paste (200 g) and dilute it in 400 ml of water.This is the so-called mother liquor. You can store it for a long time. When there are leftovers before winter, you can dilute them with water and water the compost pit or soil near trees and shrubs.
To soak garlic you will need 0.2 g of mother liquor and 250 g of water. Soak for 0.5-1 hour.
If phytosporin is in powder form, then take ½ teaspoon and dilute it in 1 liter of water and soak for 15 minutes.
"Fundazol"
“Fundazol” is a therapeutic and prophylactic drug, so the love of summer residents for it is fully justified. However, it is dangerous for humans, so it must be used in strict accordance with the instructions. Available in the form of a white powder with an odor.
Solution: 0.5 liters of water per 10 g of powder.
Soaking time: for a day.
Tar
Birch tar is the most natural and safe remedy for humans and all living things. It is used to get rid of rot and onion flies.
Solution: add 1 teaspoon of tar to 1 liter of water.
Soaking time: literally half an hour before planting.
Can be repeated after garlic sprouts. Water not the seedlings themselves, but between the rows. The irrigation solution is prepared from 10 liters of water, 1 tbsp. l. tar and 30 g of soap. After two weeks, repeat the treatment.
Disembarkation dates and rules

Before winter, garlic begins to be planted 2-3 weeks before frost, so that before the frost its root system is already developing, but there are no shoots yet.
You can navigate by temperature: when the average is +10...+12 °C, planting begins.
Approximately in the middle zone this is the end of September - beginning of October. The further south you go, the later they start, and vice versa.
Key points to pay attention to when planting:
- bed width – 1 m;
- the distance between planted garlic cloves is at least 10 cm;
- distance between rows – 20 cm;
- garlic planting depth in autumn – from 8 to 12 cm;
- the cloves are planted bottom down;
- after planting, the ground is covered with peat, leaves, spruce branches, etc.
Useful tips
Some advice from experienced summer residents:
- when buying garlic for planting, you may buy the wrong variety, so it is better to take planting material from friends on recommendation or develop your own over time;

- do not plant garlic without scales; if they peel off on their own, such a clove is more susceptible to rotting;
- do not plant garlic immediately after digging and preparing the bed for planting - let the soil settle a little and the fertilizers take root;
- pay attention to the time of planting: do not plant too early so that the garlic does not have time to sprout, because when cold weather sets in, the planted garlic will die;
- in the spring, during the formation of the head of garlic, remove the arrows so that they do not take all the strength.
Conclusion
Each summer resident has his own rules and advice. Varieties, land, water and much more differ. Understanding the optimal growing technology comes with experience and your own observations. Some believe that garlic will succeed if planted before the Intercession, others are sure that productivity does not depend on this. Some people cover their beds not with mulch, but with polyethylene or roofing felt.
How to treat crops is a matter of your personal choice. Manufacturers now offer a wide selection of disinfectants. Try several types of solutions on slices at once, and then, when harvesting, you will conclude what is applicable specifically to your type of land.
Be sure to write down the varieties you plant, carefully monitor their germination, recording the results.By analyzing yields and records, you will become an experienced agronomist, and your yield will increase year after year.