Honeysuckle honeysuckle (fragrant vine): description, methods of propagation, nuances of care
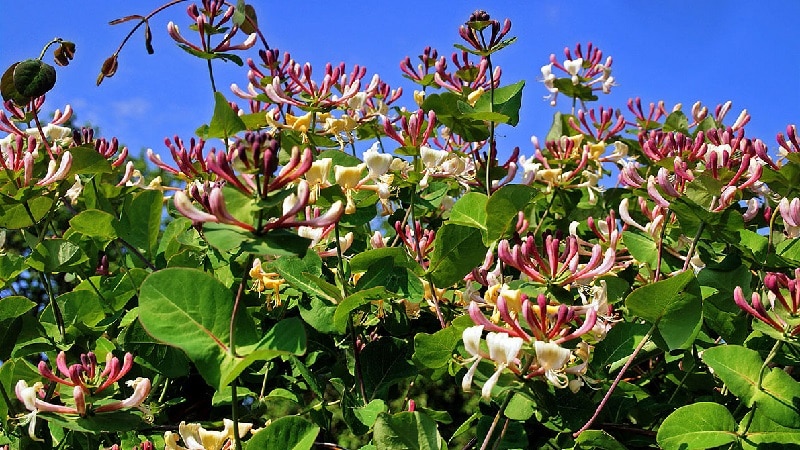
Honeysuckle is also called goat leaf, Italian honeysuckle. The culture belongs to the multi-flowered plants of the Caprifoliaceae family, widespread in Europe, and the South-East of Great Britain is considered its homeland. Honeysuckle is distinguished by its unusual shape of red, cream and yellow flowers with prominent stamens and a pleasant aroma.
Description of honeysuckle honeysuckle
Honeysuckle Honeysuckle is a flowering shrub reaching 8 m in height. The leaf shape is ovoid or ellipsoid. The surface of the leaf plate is glossy, green, the back is matte, bluish-gray. The bluish-green color lasts until late autumn. The lower leaves are located on short stems.
The flowers are colored in red, cream and yellow shades, gather at the ends of the branches in three inflorescences. The length of the flower is 5 cm. The fruits are round, coral in color.
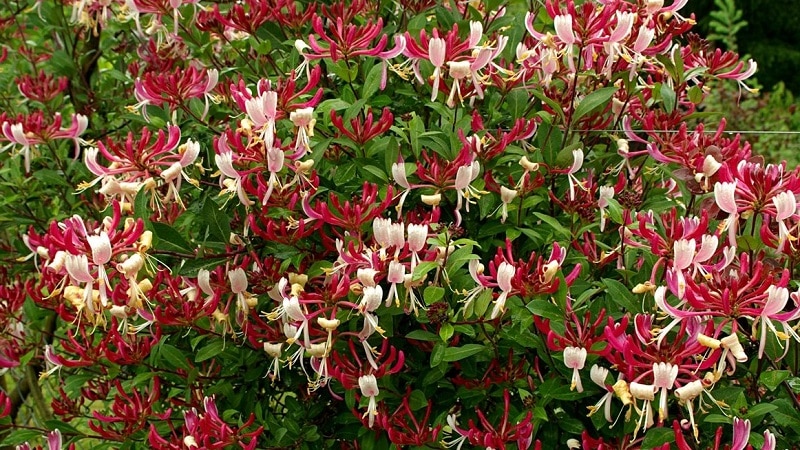

The bush enters the flowering period in early summer. The flowers exude a pleasant aroma that intensifies in the evening. Honeysuckle flowers differ from other types of honeysuckle by protruding stamens, which are collected in bunches of 5-6 pieces. The flowering period is short - only 3 weeks. Each flower lives for 3 days and fades. The enchanting aroma of honeysuckle attracts bees. They literally swarm around the bushes.
Branches grow up to 2 m in one season. The lifespan of the plant reaches 30 years. The crop is frost-resistant; damaged branches quickly recover after pruning.
There are four varieties of honeysuckle honeysuckle:
- Belgica is a flowering shrub with broad green leaves and dense clusters of purple and pink flowers. The berries ripen in autumn and are bright red in color.
- Harleguin attracts attention with colorful pink flowers with a light edge.
- Munster is characterized by soft pink flowers and white edges.
- Grahm Thomas features tube-shaped flowers and white-yellow petals.

Reproduction methods
Honeysuckle honeysuckle is most often propagated in two ways - by seeds and cuttings. The first is considered the most cost-effective and low-cost, the second guarantees abundant flowering. A plant planted with seeds quickly adapts to the landing place and increases green mass. Reproduction by layering and dividing the bush is used less frequently.
Growing the fragrant honeysuckle vine honeysuckle from seeds
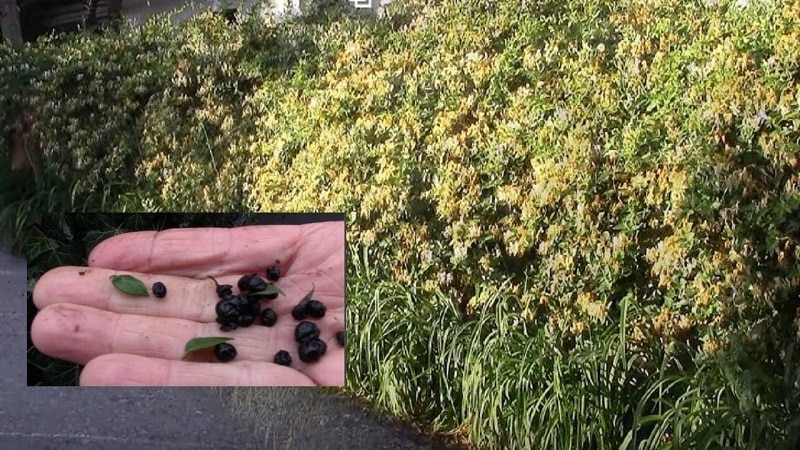
Propagation by seeds is a lengthy process if you prepare them yourself. It's easier to buy at a gardening store. The material is collected manually after flowering - at the end of July. Large, overripe fruits are suitable for this.

In practice, two methods of obtaining seeds are used:
- The berries are ground through a sieve and filled with water. The pulp is discarded, and the seeds are washed with tap water and dried on a napkin.
- The fruits are placed between two layers of paper towel and crushed with a masher or spoon. The seeds, along with the pulp, are dried in the open air and used for planting.
Planting material in bags is sold in the form of berries or seeds. When purchasing ready-made seeds, it is important to check the expiration date and information about the botanical name of the species and variety.
Seeds for sowing in the year of collection are stored at room temperature in a dark place.. Next year they stratify - mix with wet sand and store in the refrigerator at +2...+5°C. The germination rate of stratified seeds is 70% and lasts for 2 years.
Sowing is carried out in March - April. This guarantees high germination and allows the plant to gain strength before the onset of cold weather. The seeds are pre-disinfected in a solution of potassium permanganate. Exposure time - 24 hours.
Any container is suitable for planting. The soil mixture is taken from a gardening store or prepared independently from peat, river sand, turf and humus in equal proportions. The soil is spilled with a dark solution of potassium permanganate or heated in the oven at a temperature of +100...+110°C. The containers are filled with the prepared substrate, but not compacted.

soil water with clean water at room temperature and place the seeds on the surface, without deepening, every 10 cm. On top - 0.5-1 cm of soil or a mixture of sand and soil. The container is covered with film or glass and placed on the windowsill on the south side of the house. The optimal air temperature for rapid germination is +20°C. Water the soil 2 times a week, using a sieve so as not to wash out the seeds.
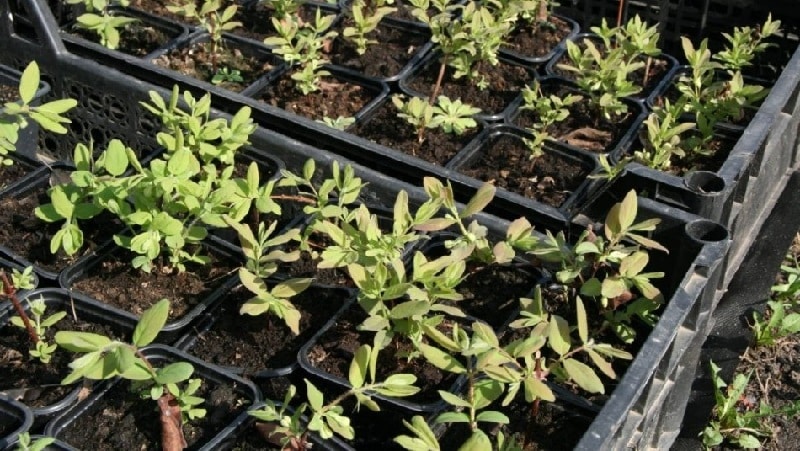
The first shoots will appear 30-35 days after sowing. Stratified material germinates 6-7 days earlier. When sowing densely, seedlings are planted in other containers, maintaining a distance of 5-10 cm.
Seedlings are transferred to open ground in late May - early June.
Interesting things on the site:
Honeysuckle Hekrota - description and characteristics
Cuttings
It is customary to plant honeysuckle cuttings in the spring, summer and in autumn. They are usually harvested in the fall, choosing strong shoots 10-15 cm long.Each of them should have 4-5 eyes. The cuttings are planted in loose and moist soil, leaving one bud on the surface. The soil is mulched with straw or dry leaves.
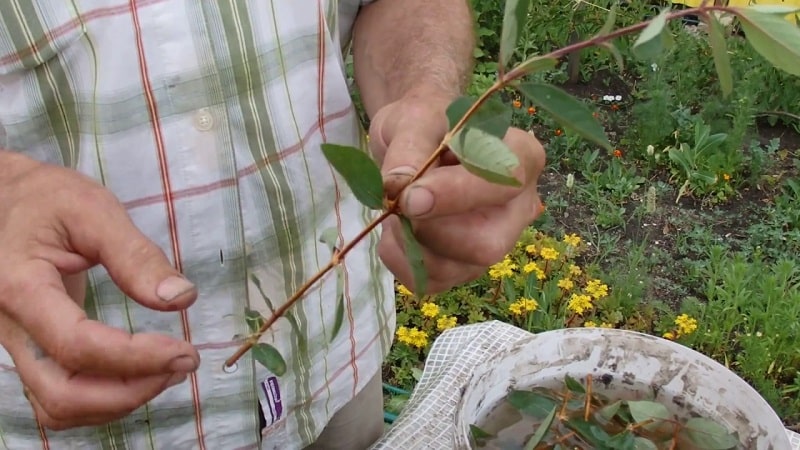

Summer harvesting of cuttings is carried out after flowering. At the end of July, cuttings with two internodes are selected and the lower leaves are torn off. Planting material is placed in a greenhouse or a place protected from direct sunlight. The cuttings are immersed in the ground to a depth of 2-3 cm every 15-25 cm. Each of them is covered with a plastic bottle until new leaves appear. The kidneys are moisturized 2-3 times every day. In the winter, the soil is mulched with peat, and in the spring it is planted in open ground.
Reproduction allowed honeysuckle cuttings from semi-ripe wood. Material at least 10 cm long is harvested in July–August. Harvesting cuttings of mature wood 20 cm long is carried out in the spring.
Reference. Botanists have determined a high percentage of germination when using cuttings.
Liana does not respond well to transplantation, so it is recommended immediately determine landing place. The bush will turn out more magnificent if you leave 2-3 buds or more on the shoot. They produce young shoots and, with proper care, create a hedge.
The trench planting method allows you to get a hedge or so-called vertical gardening. The culture loves illuminated areas and blooms profusely. In shaded areas, the vine forms strong shoots, but produces few flowers.
By layering
This is one of the easiest ways to propagate honeysuckle.. For rooting, layerings taken from mature strong bushes with a large number of young shoots are used.
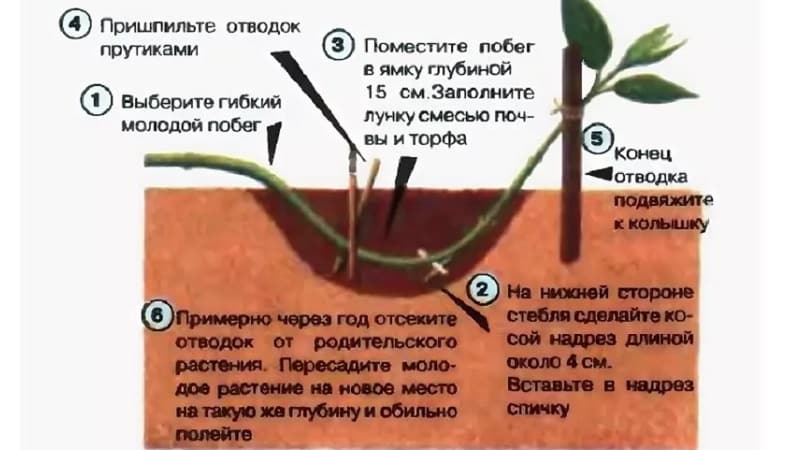
A shoot is selected from the bottom of the bush, bent to the ground and pinned. Part of the shoot is sprinkled with soil and watered.If you do this in the spring, by autumn a new shoot with roots will grow. It can be separated and planted in a new place or the transplant can be postponed until spring.
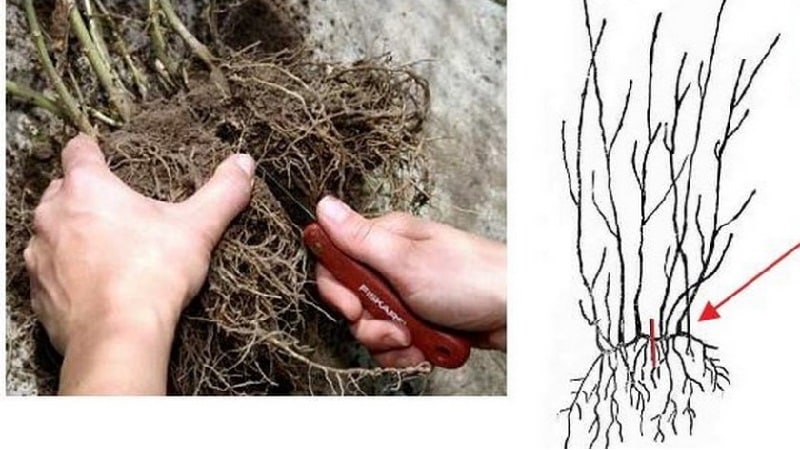
Dividing the bush
This method is suitable for all shrubs. The base of the bush is dug up, and part of the root system with branches is separated with a sharp shovel. The cut is sprinkled with coal, dried and planted in the prepared area. They also practice completely digging up a bush and then dividing it into parts.

Caring for young honeysuckle honeysuckle
Honeysuckle Honeysuckle easy to care for, even a novice gardener can cope with its cultivation. For normal growth and development, the vine needs support. Bushes are often planted next to gazebos, walls, fences, and garages. Any vertical surface is suitable so that the vine has the opportunity to cling to it and grow. Honeysuckle usually reaches 4-5 m in height. It takes her about 5 years to do this.
The shoots have small roots. With them the vine clings to the rough surface. Without support, the branches grow horizontally.
Bushes water as the soil dries out. Honeysuckle loves moisture, so during drought the frequency of watering is increased. Consumption per bush is 10 liters of water.
The first fertilizing is applied 2-3 weeks after planting.. To do this, pour 10 liters of mullein infusion (1:10) mixed with 200 g of wood ash under each bush. Also upon landing the soil is mixed with manure and peat. In this case, the plant will have enough nutrients for 3-4 months. In the second half of summer, ash (200 g) and superphosphate (25 g per 10 liters of water) are used for fertilizing. Nitrogen fertilizers are not used, because they provoke a rapid increase in green mass.
To prevent fungal infections In the spring, the bushes are sprayed with copper sulfate, Bordeaux mixture, and Ridomil solution.
When grown in regions with harsh winters, honeysuckle is covered tarpaulin or agrofibre, folded in 2-3 layers. The soil is mulched with sawdust, straw or dry leaves.

Bush pruning
Timely pruning helps to form a beautiful vine. It is important to choose a strong and high support made of wood, metal or mesh. Honeysuckle branches are guided by hand. They grow quickly and need distribution to create a beautiful and well-groomed appearance.
When the honeysuckle reaches the desired height, the tops are cut off. This stimulates the development of side shoots. The lower leaves of honeysuckle fall off. To hide bare branches, tall flowers or low-growing conifers are planted nearby.
Reference. In the spring, sanitary pruning is performed, removing frozen branches.
Conclusion
Honeysuckle honeysuckle (fragrant vine) - not to be confused with edible honeysuckle - blooms with amazingly beautiful yellow, red or cream flowers and bears inedible red fruits. Honeysuckle is unpretentious in care and needs timely watering, organic and mineral fertilizing, pruning and prevention of fungal infections. The liana is used to create hedges and decorate the local area.