High-yielding honeysuckle variety Sibiryachka
Sibiryachka honeysuckle is an early edible variety. It has gained popularity due to its ease of care and high taste of the fruit. Siberian is also used to decorate the site, as it has good decorative properties.
From the article you will learn about the origin of this variety, its pros and cons, cultivation characteristics and disease resistance.
Description of the honeysuckle variety
This variety has become a real find for gardeners due to its versatility. It combines decorative and fruit-bearing properties.
The bright appearance perfectly complements the garden plot. The berries are used for culinary and medicinal purposes.
Origin and development, history of breeding
The variety was bred by employees of the Bakcharsky stronghold of northern gardening, which is located in the Tomsk region. It was obtained in 1972 by crossing Kamchatka honeysuckle and Turchaninov honeysuckle. The Siberian was added to the State Register in 2000.
Characteristics, description of appearance, taste
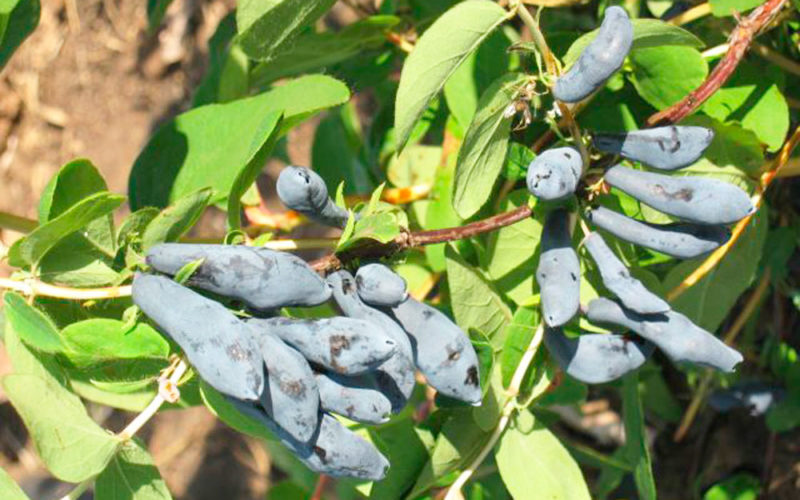

The bushes are of medium height - approximately 160 cm. The crown is spherical, of medium density. The skeletal branches are brownish-brown in color, the side shoots are spread wide to the sides. Young branches are red.
The apical bud is oval in shape. The leaves are medium-sized with a heart-shaped or rounded base, light green.
Inflorescences are reduced, two-flowered. This variety of honeysuckle produces medium-sized, pale yellow flowers. Their petals are half-closed.
The fruits are quite large, aromatic and sweet, and have a dark purple color. Their length varies from 2 to 2.5 cm. The shape is teardrop-shaped and elongated. The pulp is tender and juicy.
Experts highly appreciate the taste. The tasting rating of the berries is 4.9 out of 5 points.
Features of the use of this variety
The variety is grown both as an ornamental plant and for harvest.
Berries are used in fresh and processed forms. Juices, compotes, jams, preserves, etc. are prepared from them.
Productivity and fruiting
Siberian honeysuckle bears fruit for the first time in the second or third year after planting. The berries ripen at the same time, so the harvest is carried out once.
In the first year of fruiting, 500 g of fruits are collected from the bush. At the age of ten, the crop produces about 3.5 kg of berries per bush. The highest yield occurs in the 14th year after planting. At this time, the plant produces about 4.5 kg of fruit. On average, 3.7-4 kg are collected from each bush.
Ripening period
Honeysuckle Sibiryachka is an early variety. Berries mature in early or mid June.
Resistance to diseases and pests
Pests rarely affects this variety. Also, Siberian practically does not get sick. Fungal infections are possible only with excessive watering.
Resistance to cold and drought
This is a frost-resistant variety that can withstand temperatures down to -50 degrees. Flowers are not harmed by returning spring frosts down to -7°C.
The variety also tolerates drought well.
For which regions is it best suited and what are the climate requirements?
Siberian is suitable for cultivation throughout Russia. The variety is frost and drought resistant. Gives bountiful harvests in different climatic zones.
The main advantages and disadvantages of the variety
The main advantages of Siberian honeysuckle:
- stable annual fruiting;
- precociousness;
- high yields;
- good taste;
- large-fruited;
- high resistance to frost.
Main disadvantages:
- average transportability;
- difficult harvesting due to curved branches;
- slight crumbling during ripening.
What is the difference from other varieties and hybrids
The Sibiryachka variety is suitable for growing in difficult climatic conditions. At the same time, the taste of the berries is very high.
Agricultural technology
Agrotechnical measures come down to the correct choice of planting site, planting itself and care. Care consists of regular watering, fertilizing and periodic scraps.
Choosing a place in the garden and preparing holes
For planting honeysuckle, they try to choose the following areas:
- not blown by strong winds;
- most of them are illuminated by the sun.
In bushes planted in partial shade or shade, the shoots begin to lengthen, which is why few flower buds are formed.
Important. If the Sibiryachka variety is grown in windy areas, then in a strong wind all the ripe berries fall from the bush.
The depth and diameter of the holes should be approximately 40 cm. Add 1 bucket of organic fertilizer (compost, peat or humus) and 50 g of phosphorus and potassium fertilizers to each planting hole.
Preparing for landing
Siberian honeysuckle seedlings must not be pruned before planting. Because of this procedure, young plants do not take root well.
Also, before the procedure, some gardeners soak the roots of seedlings in a root formation stimulator for several hours. This contributes to faster survival and accelerated development of the root system.
Soil requirements
It is desirable that the soil be loamy and moderately moist. Acidic and swampy soils reduce crop yields.
Dates, scheme and rules of planting
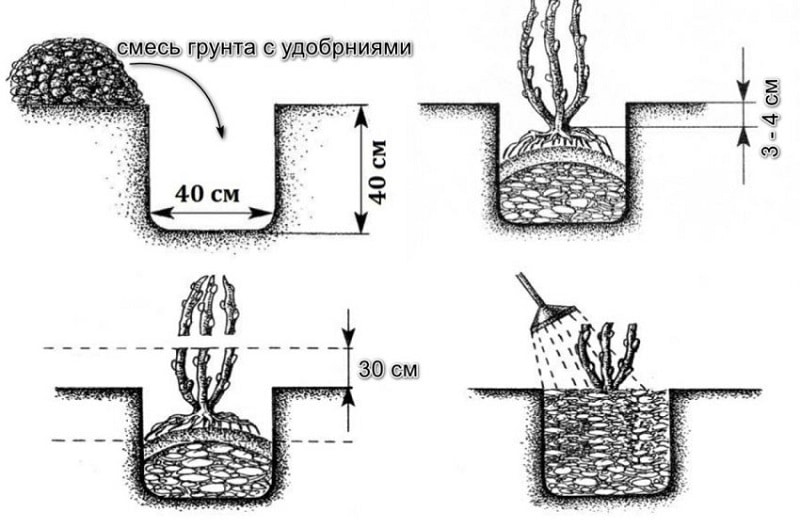
The optimal time for planting is considered to be autumn, about 3 weeks before the arrival of frost.
Boarding procedure:
- Immediately before planting, pour a bucket of water into the planting hole and wait until it is completely absorbed.
- A mound of soil is formed in the center of the hole and a seedling is placed on it.
- The roots are carefully spread over the mound.
- The hole is filled in and the earth is compacted.
- After planting, the tree trunk circle is watered with a bucket of water and mulched. Peat or humus is used for mulch.
Attention. The distance between individual bushes should be 2-3 m.
Features of cultivation
Young seedlings will quickly take root in a new place. The main thing is to provide them with proper care.
Nuances of care
Watering is carried out regularly. As soon as the soil around the trunk dries 20 cm deep, the plant is watered with a bucket of water. It is advisable to spray the bush with additional water. The next day after watering or rain, the tree trunk circle is loosened. This is required so that oxygen gets to the root system.
It is also important to feed honeysuckle on time. Fertilizers are applied for the first time during planting. This is enough for the first 2 years.
After 2 years, they begin to regularly feed the crop:
- in the spring add 1 tbsp. l. urea for 1 bucket of water for each bush;
- in summer, pour a bucket of organic fertilizer into the tree trunk circle;
- in the fall, feed with ash (1 liter jar per plant).
The crop is prone to thickening, so it is important to trim:
- For the first 6-8 years, only sanitary pruning is performed. Only cut off weak, dried, damaged branches, as well as those that grow inside the bush or downwards.
- A few years after the start of fruiting, thickened plants begin to be thinned out. Most of the old branches over 8 years old are cut out. Replacement shoots will appear from their stumps. This pruning is performed once every 3 years.
- By about 20 years, the bush practically stops producing crops. In this case, anti-aging pruning is carried out. In the fall, all skeletal branches are cut off, leaving 15 cm stumps. Next season, young shoots will begin to grow on them. The bush will recover in a year. This procedure helps to extend the fruiting period by about 5-10 years.
Pollinators
The Sibiryachka variety is sterile, so pollinators are required to obtain a harvest. For pollination, choose any Siberian, Altai or Kamchatka variety of honeysuckle, for example, Kamchadalka or Enchantress. A bush of another variety is planted 2-3 m from Sibiryachka.
Disease and pest control
The Siberian is almost not susceptible to diseases and attacks pests, but still it happens sometimes. Among the most common parasites and diseases are:
- Honeysuckle aphid. When she appears the leaves on the bush curl and quickly turn yellow or become covered with dark spots. This pest slows down the development of the bush, and in some cases causes the death of the plant. To combat aphids, the drugs “Rogora”, “Aktellik”, “Confidor” or “Aktara” are used.
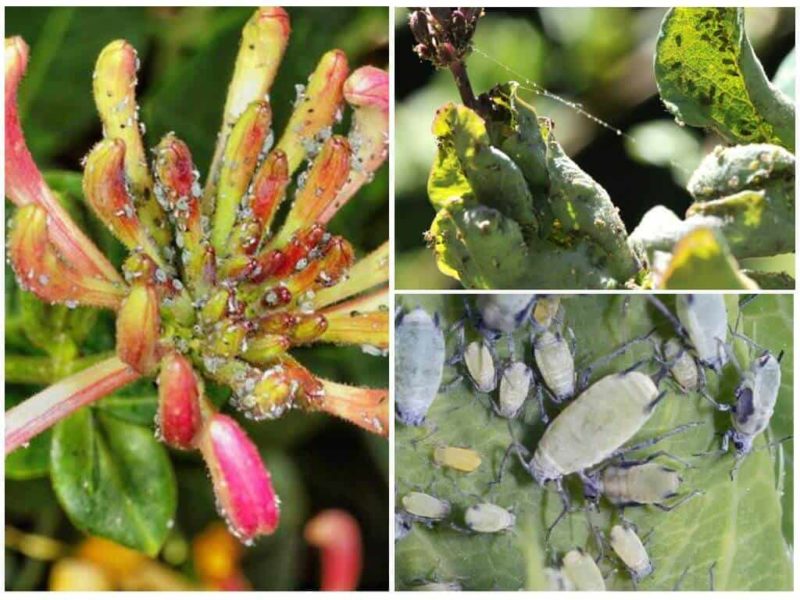

- Honeysuckle mite. The presence of the parasite is signaled by brown, shapeless spots on the leaves, as well as the appearance of gray fungi. Affected leaves fall off. To eliminate the pest, use the drug “Aktellik”, “Mavrika” or “Rotor”.
- Fungal diseases (ramularia, cercospora, powdery mildew). Most often they occur when the soil is waterlogged.For treatment, the bushes are sprayed with a solution of the drug “Topaz” or “Fundazol”.
Preparing for winter
The Siberian fish tolerates frost well, so it does not require special preparation for the winter season. The bushes are only mulched with peat or humus before the arrival of frost.
Reproduction

More often reproduce honeysuckle by cuttings or dividing the bush
Dividing the bush
In early spring or autumn, young bushes (3-5 years old) are dug up and divided along skeletal branches that have their own roots. After this they are seated.
Propagation by cuttings
At the beginning of July, the strongest annual shoots are selected and cut off, including old wood. They are kept in a root formation stimulator, after which they are planted in a moist and loose substrate consisting of compost, peat and sand. The plants are covered with film to create a greenhouse. The film is removed every day for ventilation. By autumn, the seedling will be ready for planting in a permanent place.
Harvesting

Harvesting is carried out at technical ripeness. It occurs a month after the end of flowering.
How and when to collect
Harvest collect in June. Remove the berries by hand. It is not advisable to shake them off, since the Siberian fruits have a very thin skin, which is damaged when dropped.
What difficulties may there be when growing
There is a chance of re-blooming if the autumn is too warm. The bushes bloom when the temperature first briefly drops to below zero, and then a thaw comes. Subsequent cooling will lead to the death of the buds, which will greatly reduce the harvest next year.
If this happens, the buds are immediately removed. This will minimize damage from re-blooming. In early spring, damaged branches are cut off from bushes to stimulate the appearance of new shoots.
Tips and reviews from experienced gardeners about the variety
Nikolay, Ryazan: “I really love honeysuckle. At my dacha I grow not only Sibiryachka, but also several other varieties so that there is pollination. The berries ripen at the same time. The main advantage of Siberians is considered to be taste. Its berries are juicy and tender.”
Victor, Vologda: “I’ve been growing Siberian for several years. I can't say that I'm completely satisfied with the variety. The berry is sweet and tasty, but quite small. The bushes are creeping, which is why we had to build supports.”
Conclusion
Siberian is able to develop well and bear fruit in any region. This variety perfectly combines decorative qualities and pleasant taste. The main thing is to water on time, feed and trim the bushes. Then the crop will produce abundant harvests for many years.