How to properly plant a lemon at home so that it does not get sick and bears fruit
Grafting a lemon is the easiest way to make a tree bear fruit faster and feel like a breeder. Even on a wild plant grown from a seed, scions of various varieties and hybrids and even other varieties of citrus fruits easily take root. And it is on lemon that the first grafting experience will most likely be positive.
Many people are afraid to undertake this procedure, but, in fact, it does not involve large financial and time expenditures and is simple to perform. The main thing is to choose the appropriate vaccination method and follow the step-by-step instructions. How to vaccinate lemon at home so that it bears fruit - read on.
Benefits of Lemon Grafting
indoor lemon tree, grown from seed, - this is wild. It will produce small, tart and sour fruits. Moreover, the first fruiting is expected no earlier than in five years.

Grafting a lemon is a process that requires following instructions and knowing a number of nuances. Therefore, many beginning flower growers refuse it, preferring to wait a long period for fruiting.
In fact, even a person growing a houseplant for the first time can cope with lemon grafting. A grafted tree has a number of advantages over an ungrafted one.:
- Fruiting approaching. A scion taken from a tree that has already bear fruit can produce a harvest in 1-2 years.At the same time, the chances that the lemon will bear fruit at all increase significantly.
- Varietal characteristics. From the seeds of fruits bought in the supermarket, you can grow only a wild one. If you graft a branch of any variety onto such a plant, the fruits will have varietal or hybrid characteristics. Accordingly, they will be larger and tastier.
- Another plant. Not only lemon branches are grafted onto the lemon tree, but also scions taken from other citrus plants. This allows you to grow an orange or lime from a lemon. If you leave lemon branches, you will get a tree that will bear fruit with lemons and other citrus fruits.
In most cases, the scion takes root. Problems arise only when the vaccination procedure is violated.
Preparing for vaccination
Before you plant lemon at home, you should prepare for this procedure. After all During the grafting process, all tools and materials should be at hand.
Materials and tools
Lemon grafting does not require any monetary costs. For this procedure you will need materials and tools.that every gardener has at home:
 Secateurs or sharp painting knife. These tools make even cuts on the plant. Before use, they are disinfected with alcohol or a dark pink solution of potassium permanganate. Another disinfection option is to hold the metal part over a fire.
Secateurs or sharp painting knife. These tools make even cuts on the plant. Before use, they are disinfected with alcohol or a dark pink solution of potassium permanganate. Another disinfection option is to hold the metal part over a fire.- Special garden tape. It is used to attach the scion to the rootstock. Often, special tape is replaced with ordinary construction tape.
- A piece of pure cotton material. The scion is wrapped in it.
- Garden var. Used to disinfect sections. Accelerates the regeneration of plant tissues.
- Film, bag, cut bottle to create a mini-greenhouse for a grafted plant.
There are special grafting knives and pruners. They produce the most even cuts, which is why the scion takes root faster.
Advice. If you don’t have a garden tool, a surgical scalpel can easily replace it. It costs less at the pharmacy than a paint knife at a hardware store.
Preparation of scion and rootstock
 The best rootstock (base) is a lemon grown from a seed. Such a seedling has increased endurance, and new tissue quickly grows to it. Therefore, the chances that the scion will take root are high.
The best rootstock (base) is a lemon grown from a seed. Such a seedling has increased endurance, and new tissue quickly grows to it. Therefore, the chances that the scion will take root are high.
The rootstock must be at least one year old. Branches are also grafted onto older plants. In this case, you do not have to cut off all the shoots.
Before grafting begins, the tree is replanted. At least two months must pass between these procedures.
The day before grafting, water the lemon generously and feed it with a growth stimulator.. It is important to make sure that the tree is absolutely healthy. The trunk must be cleaned of dust and husks. It is better to wash the lemon in the shower a few days before the procedure.
One-year-old branches are used for scion. They should have a hard but resilient bark. The scion must have at least 1 bud. If the split method is used, branches with 2-3 buds are selected.
The tree from which the branch is separated must have already bear fruit several times.. Otherwise, it will not be possible to bring the harvest closer. Any citrus plant is suitable. The most difficult thing is to cross lemon and tangerine, since the latter takes root slowly.
The end of the branch is used for grafting. There must be enough buds on it for a particular grafting method. The scion is cut at an angle in one quick motion to ensure an even cut. The place from which the branch was cut is covered with garden varnish.

Lemon is grafted at the end of May or in April. It is during this period that the most active sap flow is observed, which allows the branch to quickly grow to the base. Vaccination is also possible in the summer, but not in winter or autumn.
If the procedure is postponed for some reason, the cut stalk is wrapped in a damp cloth. This will prevent it from drying out.
Note! It is recommended to vaccinate on cloudy days. Lack of direct sunlight and high humidity will help the scion and rootstock grow together.
Lemon grafting methods
There are two ways to graft a lemon. They are equally popular, and each has its own merits.
You need to choose the method that seems easier in the case of a specific plant. It is better to try both options and choose the best one for yourself.
Copulation
Copulation involves grafting a lemon sprig into a cleft. This method is considered the easiest to implement. However, it is not suitable for mature lemons. It is used for one-year-old plants.
Correct instructions for vaccination with the copulation method:
 The scion trunk is cut with pruning shears so that a third of the plant remains above the surface of the ground. There will be no leaves or buds on it.
The scion trunk is cut with pruning shears so that a third of the plant remains above the surface of the ground. There will be no leaves or buds on it.- A split 1.5-2 cm deep is made in the center of the scion. To do this, it is convenient to use a scalpel or a painting knife, moving the blade with a rocking motion. It is important not to damage parts of the cleft.
- From the edge of the branch that will be grafted, such a distance is retreated so that 2-3 leaves remain at the top and there are 2-3 live buds. The cut is made at an angle of 45°.
- The lower part of the scion is sharpened on both sides at an angle. You should get a thin wedge equal in length to the depth of the rootstock. It should be thin enough so that the scion does not crack.
- If the leaves on the rootstock are large, they are cut in half. The middle leaf blades are cut by a third. Small leaves are not touched. If there is greenery not only at the top of the scion, it is torn off.
- The stock is inserted into the scion as deeply as possible, expanding the split with a knife blade. In this case, it is important that the scion does not crack, and that the rootstock fits as closely as possible to its walls.
- The junction is tightly wrapped with adhesive tape, leaving no open areas. It is important not to overtighten the trunk so as not to disrupt sap flow.
- From the junction point, they retreat upward such a distance so that 2-3 buds remain on it. The rest of the cutting is cut at an angle. Garden varnish is applied to the cut site.
- The tree is watered and sprayed abundantly. A plastic bag is placed on top and tied around the pot.
The package should remain on the plant until the grafted branch takes root.. This will be indicated by the germination of shoots.
After the first shoots appear, the film is removed for several hours a day., gradually increasing this time. When the lemon gets used to the new conditions, the bag is removed completely.
Budding
Budding involves grafting a lemon with a bud or eye. This is the name given to the junction of the leaf and the trunk, where a new bud is formed.
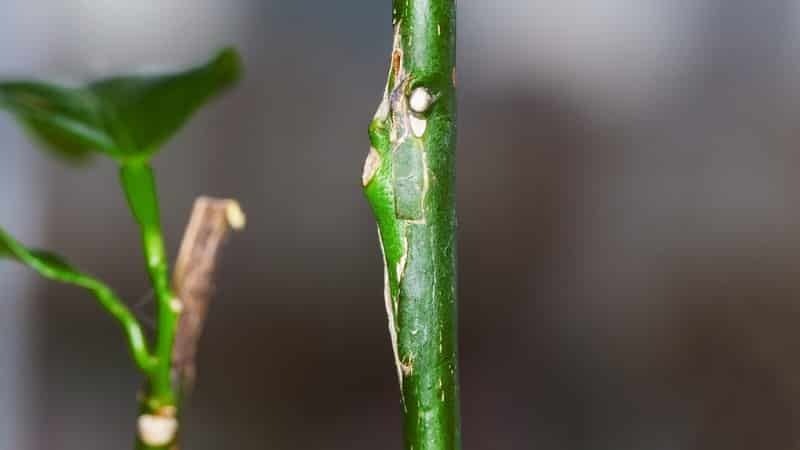

The advantage of budding is that this method is applicable even for adult plants. It does not require cutting off the top of the tree and saving only the trunk.
Reference. When they want to cross a lemon and another citrus fruit so that different fruits grow on the same tree, they use budding.
This is done in two ways. One of them is called budding into a T-shaped incision, the second - into the butt.
T-cut
The good thing about this method is that the bark presses tightly against the bud. Thanks to this, the scion takes root faster:
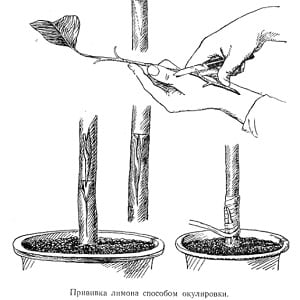 6-8 cm recede upward from the surface of the soil along the lemon trunk. At this level, a horizontal cut 1.5 cm long and a vertical cut 2.5 cm long are made. All layers of the bark are cut through so that it is separated from the trunk.
6-8 cm recede upward from the surface of the soil along the lemon trunk. At this level, a horizontal cut 1.5 cm long and a vertical cut 2.5 cm long are made. All layers of the bark are cut through so that it is separated from the trunk.- A section with a bud and a leaf is cut vertically from the mother plant. The scion should be 2.5 cm long and 1.5 cm wide. The leaf is torn off, leaving only the petiole.
- The scion is inserted into the cut on the lemon so that it goes completely under the bark and only the bud remains open.
- The junction is tightly wrapped with garden tape, avoiding open areas. Only the kidney should be on top of the tape.
- Water the lemon generously. The pot and tree are covered with a bag.
The package is removed and the leaf petiole is torn off, only when the kidney takes root.
Butt
In this case, the cutting and trunk (or branch) are cut at the same angle. They are simply connected together. The complexity of the method lies in the fact that you need to secure the two parts so that they fit tightly to each other and do not fall off or sag. It's not easy, especially for beginners.
Instructions for grafting in the butt:
- They retreat 6-8 cm from the ground surface. At this level, moving from top to bottom, make a cut at an angle of 45°, which should look like an oval hole 2.5 cm long. It is important to try to ensure that the cut site is as even as possible.
- A scion with 2-3 buds is cut from another tree (fruit-bearing), also at an angle of 45°. The leaf is torn off, leaving only the bud and petiole. In this case, the thickness of the rootstock and the thickness of the scion must match. You need to hold the planting material by the petiole without touching the cut.
- Sections of the scion and rootstock are combined as tightly as possible and tied with electrical tape so that there are no free areas left. Only the kidney itself should be above the adhesive tape. Some gardeners use a toothpick, a straight stick, or an ice cream stick to secure the structure.
- Water the lemon generously. Then they cover it with a bag that is tied tightly around the trunk.
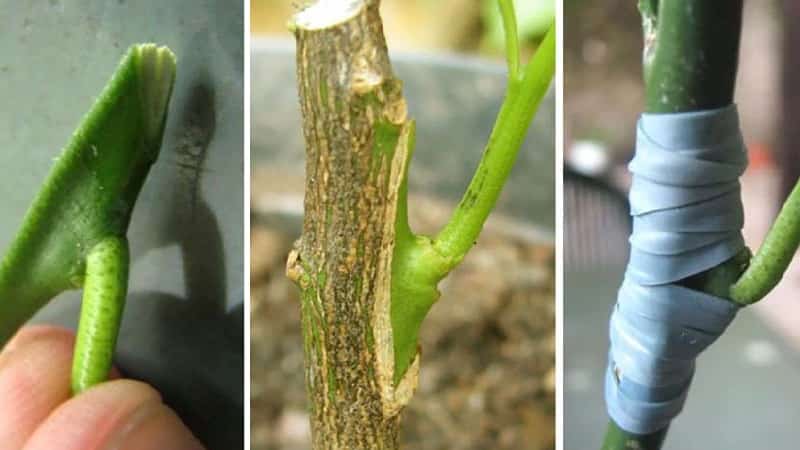

Remove the package only after shoots begin to sprout on the scion.. This indicates that the tissues have grown together.
After the bud takes root and a shoot appears, the lemon begins to ventilate, gradually removing the bag completely. After this, the petiole remaining from the leaf is broken off. If you break off the petiole right away, the scion may not take root.
Note! Such vaccination is not always successful.
Caring for indoor lemon after crossing
During the fusion of the cuts, as well as for some time after this, the lemon needs special care. It is as follows:
- The tree is placed in a shaded place. Direct sunlight reduces the chances of successful grafting.
- Every day the package is opened slightly for 10-15 minutes.
- The soil is moistened as it dries. The above-ground part of the lemon is also sprayed. Use settled water at room temperature.
- To speed up the growth of the scion, it is recommended to cut off a part of the tree located 10 cm above it. When shoots appear on the graft, the shoots around it are removed.
- During grafting, it is recommended to tie the lemon to a support.
Read also:
Useful tips
For the vaccination to be successful, it is important to know some nuances:
- Most often, the cause of unsuccessful grafting is air trapped at the junction of the sections. This happens if the cuts did not fit together or the adhesive tape was not wound tightly enough.
- In order for a cutting or bud to take root, it is important that bacteria do not get on the cut. You need to work with sterile gloves, and the tools (secateurs and knife) should be disinfected. Do not touch the cuts with your hands.
- To create optimal moisture under the bag, it is recommended to place wet cotton wool in the pot. This will help reduce the number of waterings.
Conclusion
Lemon grafting is an optional but desirable procedure. It significantly brings the first fruiting closer, allows you to make a seed-grown plant into a varietal and gives you the opportunity to experiment with crossbreeding.
There is no need to be afraid of citrus fruit grafting. This culture quickly and easily grows tissue. The main thing is to choose the appropriate method, take into account all the nuances and act according to the instructions.