Are infants allergic to buckwheat?
Buckwheat often included as part of a hypoallergenic diet. However, in some cases, this cereal itself can cause an allergic reaction.
If previously a negative reaction of the body to buckwheat was attributed to individual intolerance, now allergies are more often diagnosed. It can appear at any age, but infants are more susceptible to it.
Buckwheat as an allergenic product
Buckwheat is a second-order allergen. That is, it has an average degree of allergic activity.

Characteristics and description of the allergen
The main cause of allergenicity of all cereals is gluten. However, this substance has nothing to do with buckwheat, because it belongs not to cereals, but to the Buckwheat family.
Nevertheless, buckwheat belongs to the potentially allergenic products of the middle category. In other words, an unpleasant reaction in a child may not appear immediately, but later.
Just a few years ago, a sensitive reaction to buckwheat dishes was explained by individual intolerance to the product, since it was not possible to detect the influence of a specific allergen.
However, scientists were still able to find a reason that allows them to identify the rejection reaction as a food allergy. Buckwheat contains a large amount of protein - from 16 to 19%.The main problem lies in proteins such as albumins, globulins and prolamins, the biological activity of which can lead to an allergic reaction.
Is there an allergy to buckwheat in infants?
Hypersensitivity to the product can be detected already in the first year of life, after the first complementary foods or through milk.
Parents need to carefully monitor all manifestations and seek medical help in a timely manner. After all, only a competent specialist can find out whether it is really an allergy, what is the cause of the unpleasant symptoms and what to do next.
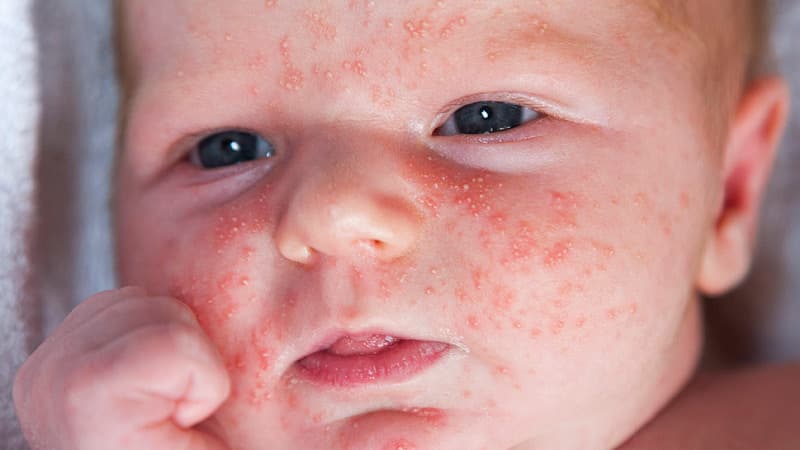
Allergy to new things
The baby’s first reaction to buckwheat can appear already at the beginning of breastfeeding, when food elements reach the baby through mother’s milk. Therefore, mothers are recommended to introduce new products into their nutrition gradually and monitor the child’s symptoms.
Directly myself buckwheat The baby tries it already at 6 months of age when complementary foods are introduced. Some pediatricians advise parents to start complementary feeding with porridge if the child is underweight.
Most often, the choice falls on buckwheat, since it has always been believed that this product practically does not give allergic reactions. However, like any new item on a baby’s menu, buckwheat can cause an undesirable reaction.
Allergens included
If instant buckwheat, which includes various additives, is used as complementary food, then a rejection reaction may appear not only to the main product, but also to the complementary elements in the composition.
Cross allergy
If a newborn is allergic to a product that contains a protein similar in structure to buckwheat protein, then a cross-allergy may develop.Moreover, the process can involve both a food product and a respiratory product, that is, an inhaled one.
Important! The danger is not only from eating buckwheat, but also from inhaling buckwheat dust. Pillows and heating pads are often filled with grain husks.
If a baby has an intolerance to buckwheat protein, then in the future he may develop an allergy to sorrel and rhubarb.
Who is at risk
Parents should be especially vigilant in the following cases:
- The child has a genetic predisposition. If at least one of the parents is allergic to anything, then the child is likely to have this problem. The types of allergens in parents and the baby may not be the same.
- The presence of chronic intestinal diseases.
- Enzyme deficiency in infants.
- If during pregnancy a woman consumed a large amount of allergic foods or suffered from infectious viral diseases.
Causes of buckwheat allergy in infants
An allergic reaction in the body is triggered by high molecular weight proteins - food allergens. They are resistant to high temperatures and enzymes of the gastrointestinal tract, and are highly soluble in water. Therefore, it is impossible to get rid of allergens in the product at home.
The mechanism of formation of an allergic reaction to buckwheat in newborns
At the first contact with an allergen, the child’s body produces the protein immunoglobulin E (Ig E), which is able to recognize antigens and neutralize their effects.
Immunoglobulins attach to the immune cells of those tissues that have contact with the external environment - these are the mucous membranes of the respiratory organs (contact with air), the digestive tract (contact with products).
From the first contact with an irritant to the manifestation of increased sensitivity to it, it can take several days or several months. Sometimes this period is calculated in years. All this time, Ig E accumulates in the body. And upon repeated contact with the allergen, a rejection reaction occurs.
How do symptoms appear?
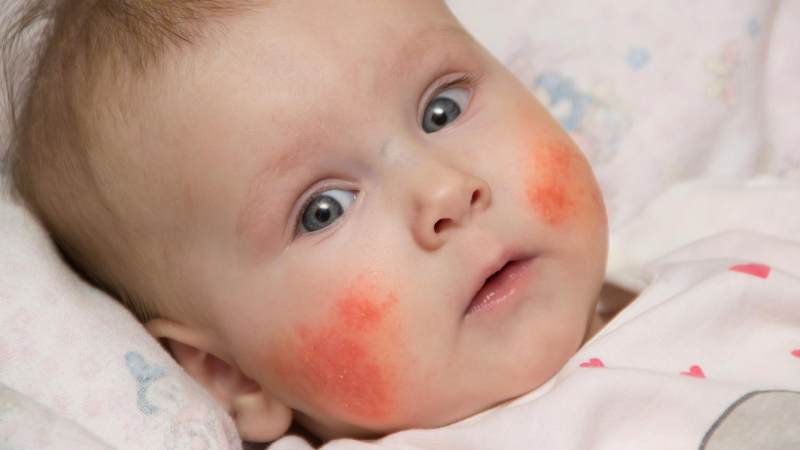

A hypersensitivity reaction to buckwheat is manifested by a number of symptoms that are grouped into groups.
- Skin manifestations. Most often, the disease makes itself felt by red spots, which are accompanied by prickly heat and peeling. Subsequently, a dry thick crust and clusters of microscopic blisters form. The areas most affected by allergies are the face, head, neck and throat, limbs, and groin. Symptoms may also appear in other areas, but much less frequently.
- Digestive disorder. Mild allergic forms are associated with constipation or loose stools, a feeling of nausea, heartburn, and in infants a coating appears on the tongue. If the situation develops rapidly or no therapeutic measures are taken for a long time, inflammation appears in the intestines, cutting pain in the stomach occurs, accompanied by vomiting and frequent bowel movements. The latter symptoms are dangerous due to the possibility of dehydration.
- Irritation of the nervous system. Babies become restless, fussy, or overly active, and routine disruptions are common.
- Respiratory manifestations. Sneezing, runny nose, cough, painful swallowing. The child's voice may change - the cry becomes hoarse or hoarse. More serious consequences are bronchial swelling, suffocation, fainting, anaphylactic shock.
Diagnosis and treatment of buckwheat allergy in infants
An allergic reaction can easily be confused with other diseases and conditions. Skin rashes may begin as miliaria, and food symptoms may begin as signs of rotavirus infection, poisoning or dysbacteriosis.
How to understand that it is an allergy
At home, the involvement of symptoms in allergies is checked using antihistamines. For allergies, after taking medications, the symptoms go away or weaken.
However, more accurate information will be provided by an analysis that detects specific immunoglobulin E to buckwheat in the blood. For research, venous blood is donated on an empty stomach.
Elimination treatment
The most obvious way to treat allergies is to stop contact with the irritant. This method is called “allergen elimination.”
Important! If the connection of an undesirable reaction with the consumption of buckwheat is proven, not only buckwheat itself is excluded from the diet, but also all products that may contain protein that is part of the cereal. Often artificial mixtures and flour are made based on buckwheat. Buckwheat dust can also be contained in pillows with such filling or heating pads.
Drugs
Pharmaceutical therapy for buckwheat allergy includes the same groups of drugs that are prescribed for other allergic manifestations. They are divided into several categories:
- Antihistamines. These remedies relieve acute symptoms: eliminate rashes, itching, and redness on the skin. The result becomes noticeable within a short time. Not all antihistamines can be given to infants. For children under three years of age, only medicines in the form of drops are recommended. Among the permitted ones are “Fenistil” (from birth, but is addictive), “Zyrtec” (from six months), “Zodak” (from birth).In addition to drops, infants are also allowed ointments and, if necessary, injections.
- Sorbents. These drugs help cleanse the body of toxins that are formed as a result of an allergic reaction. Children are given Smecta, Enterosgel, and Polysorb from birth.
- Probiotics. To restore intestinal flora, “Linex”, “Acipol”, “Bakset-baby” are used.
Creams and ointments
Skin manifestations of allergies appear in the form of redness, peeling, and cracks. In this case, ointments help. They contain an active ingredient, as well as various oils and additives that help enhance the effect.
From infancy, “Bepanten”, “Skin-cap”, “Elidel”, “La-cree” are used. In especially severe cases, ointments containing hormones are prescribed - for example, Advantan (allowed from six months).
Features of introducing buckwheat into complementary foods

To start complementary feeding, prepare porridge for your baby separately from the whole family. What adults eat is not suitable for babies. To begin with, it is recommended to serve the dish pureed. Feed your baby only freshly cooked porridge - using yesterday's portion is unacceptable.
When breastfeeding
It is recommended to start complementary feeding at six months of age if the child is breastfed. The first pureed food is introduced gradually, starting with half a teaspoon and adding one teaspoon every day.
For a month, the child is given one type of porridge, and if the baby does not have a negative reaction, then another type of cereal is introduced into the diet.
Rules for choosing porridge
For the first complementary feeding, choose dairy-free monoporridge, which consists of one ingredient and does not contain additives. It is better to introduce special baby cereals into complementary feeding, which can be bought at pharmacies or specialized stores.Children develop allergies to such porridges much less often than to regular ones prepared independently.
Advice from pediatricians

If allergic symptoms appear, pediatricians recommend that parents do not self-medicate, but immediately seek medical help. Otherwise, in infants, such reactions can quickly take a dangerous form in the form of Quincke's edema and other serious manifestations.
Conclusion
A negative reaction of the body to buckwheat is not always a consequence of an allergy. It is quite possible that the whole point is that the immature enzymatic system of the infant cannot yet cope with digestion specific product.
There is a chance that this problem will go away on its own over time. Therefore, it is important for parents to find out the nature of the negative reaction before drawing any conclusions.