How many proteins, fats and carbohydrates are in buckwheat and what else is it rich in?
Buckwheat porridge is a dietary product. It is high-calorie and nutritious, contains carbohydrates that are processed into energy and not stored in subcutaneous fat. In the article we will tell you how many carbohydrates, fats and proteins are in boiled and raw buckwheat and what beneficial properties it has.
Composition of buckwheat
Buckwheat porridge, a hypoallergenic dietary product, is considered a national dish in our country. It is included in the diet of schoolchildren and in the menu of infants from the first feeding. Cereals are especially useful for athletes, pregnant women, and people with diabetes.
Reference. Buckwheat is the seed of the buckwheat plant. This is a pseudocereal honey-bearing crop, a herbaceous plant of the Buckwheat family. “Black rice” has been eaten for more than 5 thousand years.
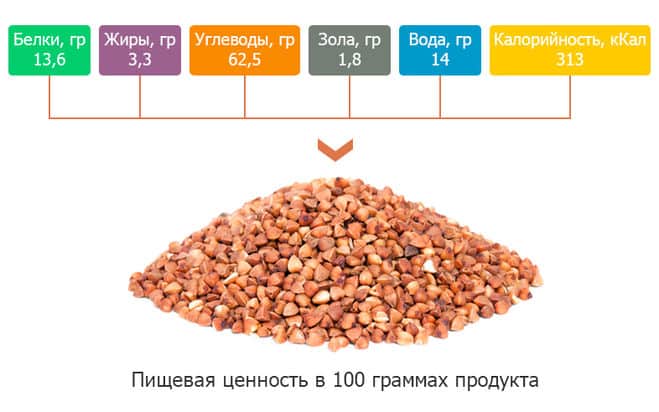
Proteins, fats and carbohydrates
Let's consider the content of proteins, fats and carbohydrates (BJU) in a dry product and a boiled dish.
| Composition per 100 g of product | Groats, g | Porridge on water, g |
|---|---|---|
| Squirrels | 10,8 | up to 4 |
| Fats | 3,2 | 0,63-1 |
| Carbohydrates | up to 56 | 19, 51 |
| BJU ratio, % | 15,7:3,19:80,2 | 15,6:7,4:77,2 |
The calorie content of a dry kernel is 308-310 kcal.
Advice. Nutritionists and Roskontrol experts on food safety and quality recommend consuming kernels - whole grain cereals. Unlike chaff and flour, uncrushed grains contain more useful substances.
Useful material
In addition to proteins, fats and carbohydrates, buckwheat contains rare micro- and macroelements. For example, manganese is responsible for the transmission of nerve impulses, magnesium prevents platelet aggregation, improves blood fluidity, and reduces the risk of blood clots.
Attention! During heat treatment, the loss of minerals is 25-60%.
| Minerals | Yadritsa | Porridge with water (no additives or salt) |
|---|---|---|
| Potassium, mg | 380 | 126,14 |
| Calcium, mg | 20 | 10,3 |
| Silicon, mg | 81 | 27,44 |
| Magnesium, mg | 199 | 67,2 |
| Sodium, mg | 3 | 1,71 |
| Sulfur, mg | 87 | 30,6 |
| Phosphorus, mg | 295 | 99 |
| Chlorine, mg | 34 | 12,3 |
| Iron, mg | 6,6 | 2,22 |
| Manganese, mg | 1,57 | 0,53 |
| Iodine, mcg | 3,4 | 1,2 |
| Cobalt, µg | 3,2 | 1,03 |
| Copper, µg | 635 | 217,3 |
| Molybdenum, mcg | 34,2 | 11,7 |
| Nickel, µg | 10,2 | 3,4 |
| Selenium, mcg | 5,7 | 2,82 |
| Titanium, µg | 33 | 11,2 |
| Fluorine, mcg | 22 | 88,43 |
| Chromium, µg | 4,2 | 1,35 |
| Zinc, mcg | 2,1 | 0,7 |
| Boron, µg | 350 | — |
| Vanadium, mcg | 160 | — |
| Lithium, mcg | 4,1 | — |
| Rubidium, mcg | 53 | — |
| Aluminum, µg | 33 | — |
| Strontium, mcg | 301 | — |
| Zirconium, mcg | 34 | — |
What else is contained in buckwheat?

Buckwheat contains 11 g of fiber (56% of the daily value). In a 100 g serving of ready-made porridge – up to 4 g (20% of the daily dose).
Coarse fiber does not dissolve, remains in the large intestine and removes toxins, bad cholesterol, carcinogens, and harmful bacteria that enter the intestines with food.
Vitamin composition
What is buckwheat rich in:
- A – 2 mcg;
- beta-carotene – 0.01 mg;
- B1 – 0.43 mg;
- B2 – 0.2 mg;
- B4 – 54.1 mg;
- B5 – 0.43 mg;
- B6 – 0.4 mg;
- B9 – 32 mcg;
- RR – up to 4 mg;
- E – 0.8 mg;
- N – 10 µg;
- K – up to 7.5 mcg.
Fat-soluble vitamins (E, K, A) are preserved up to 80% when buckwheat is steamed in a small amount of boiling water. Water-soluble vitamins of group B and PP lose their value by 20-30% when heated (they turn into a decoction).
Buckwheat contains fatty acids that protect the body from viruses and bacteria. For example, stearic and linolenic acids protect against ultraviolet radiation and resist the formation of cancer cells.
Also, grains contain essential and non-essential amino acids - regulators of hormones and metabolic processes.
Thanks to its rutin content, buckwheat strengthens the vascular wall. To achieve a preventive effect, the product is consumed at least 2-3 times a week.
Calorie content of boiled porridge

100 g of boiled buckwheat contains 97-100 kcal.
Counting calorie content of the finished dish, take into account the method of preparation and additives (per 100 g):
- porridge in water with added salt – up to 110 kcal;
- with butter (up to 3-5 g) – up to 140 kcal;
- boiled in milk with the addition of 1 tsp. sugar – 190-200 kcal;
- with boiled chicken and vegetables – up to 160 kcal.
For the convenience of calculating the daily ration, buckwheat porridge measurements are used:
- 1 tsp. – up to 5 g;
- 1 tbsp. l. – 18-20 years
This is interesting:
Calorie content and nutritional value of boiled buckwheat with milk
Calorie content and nutritional value of boiled buckwheat
Calorie content of buckwheat, potatoes and millet – which one is healthier?
Is buckwheat a protein or a carbohydrate?

Glycemic index of buckwheat low – up to 40 units.
Reference. The glycemic index (GI) is a relative indicator of the rate of absorption of carbohydrates, affecting blood sugar levels.
Buckwheat, vegetables, cottage cheese, etc. food products with low GI are classified as complex (slow) carbohydrates. They slowly release energy and provide a supply of glycogen (glucose molecules) in the muscles and liver. This is a reserve, useful “fuel” for muscles that is used for metabolism.
Benefits of slow (complex) carbohydrates:
- reduce blood glucose levels;
- eliminate sudden surges in sugar;
- provide long-term satiety (no feeling of hunger);
- stabilize the insulin index (normalize insulin synthesis);
- reduce the level of bad cholesterol;
- have a positive effect on intestinal function due to fiber;
- maintain the balance of the bacterial microflora of the large intestine (act as a prebiotic).
Fast carbohydrates with a high glycemic index (rice, white bread, chips, muesli, semolina) negatively affect metabolism. When consumed in excess, they are converted into fat reserves.This provokes weight gain and the development of diabetes.
Reference. The daily consumption rate of buckwheat is no more than 200 g per day.
Buckwheat does not contain quickly digestible sugar or glucose. The product provides the necessary energy for sports and physical activity. But it is important to take into account the dose - no more than 200 g per day.
Conclusion
Buckwheat is an inexpensive and healthy cereal. This is a dietary product that does not cause allergies or negative reactions in children and people with diabetes. Has a low glycemic index. Complex carbohydrates are absorbed slowly, without being stored in fat. Along with buckwheat, the diet includes vegetables, herbs and fruits.