What is the difference between buckwheat and buckwheat
At first glance, identical words with the same root – buckwheat and buckwheat – have different meanings. The confusion arose due to their misuse among the common people. Usually buckwheat is buckwheat, which is sold in the store. Let's figure out whether buckwheat and buckwheat are the same thing or not.
Buckwheat and buckwheat - what is the difference
People in Rus' in different villages called the same cereal differently: buckwheat, buckwheat, buckwheat. Ozhegov’s Dictionary of the Russian Language indicates that “grechka” is a derivative of the colloquial “grechka”, and means the same as “buckwheat”. To understand the difference between buckwheat and buckwheat, you need to know their exact definition and differences.
Buckwheat is a honey-bearing herbaceous plant from the Buckwheat family.. There is ordinary and Tatar. Unlike ordinary buckwheat, the grain of Tatary buckwheat grows smaller and thicker-skinned.
Ordinary buckwheat is a cereal grain crop. The seeds of the plant are used for food, songbirds love them, and they are used to feed animals, for example, horses and pigs.
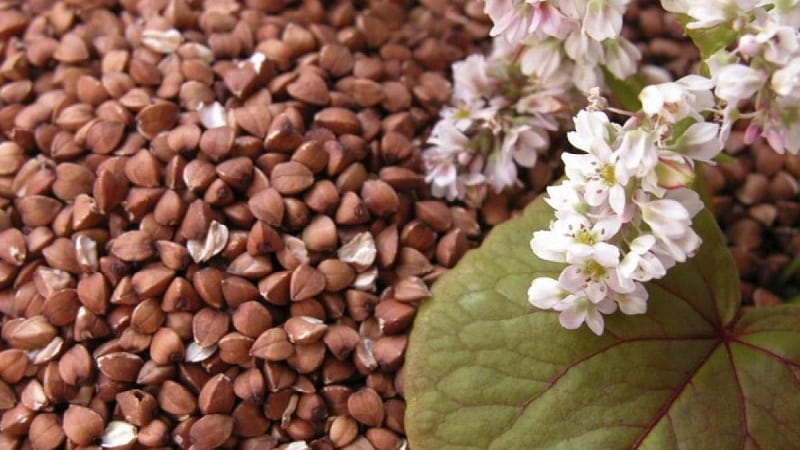

Buckwheat, or buckwheat (folk) is the seeds of the buckwheat plant, which remain after the bush has matured and are popular as a food product. They are used in cooking to prepare cereals and flour.
On a note! Buckwheat is a plant, and buckwheat is the grains that ripen on it.
What else is made from buckwheat?
Annual common buckwheat, after planting on the site, grows in height from 60 cm to 1.3 cm. Green leaves are used as a medicine to stimulate blood circulation, young shoots are added to vegetable salads. Buckwheat grains are eaten in the form of porridge and serve as food for birds and animals. Buckwheat flour and butter are also made from them.
Raw grains have a dark brown shell. They are passed through a metal sieve and the kernel is separated from the husk (husk). It is soft to the touch, smells pleasant, does not cause allergies, allows air to pass through well, has orthopedic properties, and does not clump like padding polyester or cotton wool. That is why buckwheat husk is used as a natural filler for pillows, mattresses, blankets, and toys.
From buckwheat grains
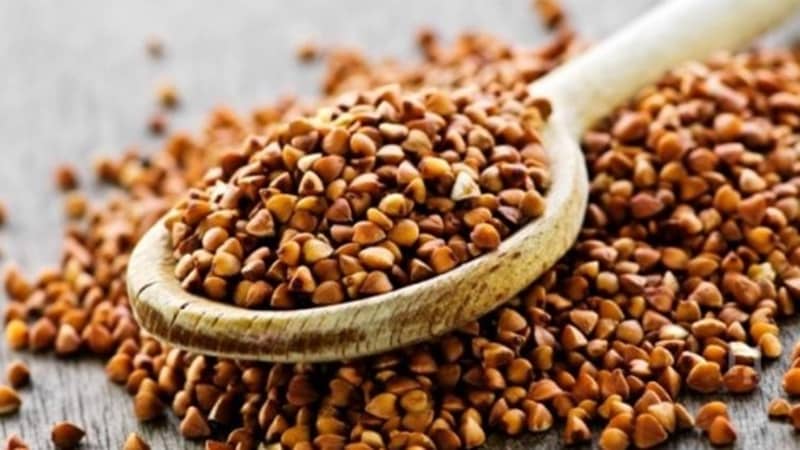

Depending on the condition and processing of the grain, buckwheat is divided into several types:
- Steamed. After harvesting, the husks are removed and heat-treated under pressure. This is a traditional way of roasting, as a result of which the buckwheat turns brown in color and produces a characteristic buckwheat aroma. People call it “fried”.
- Unsteamed – grains that have not undergone heat treatment. This is a raw cereal without roasting, green in color. It contains the largest amount of vegetable proteins (12.6 g per 100 g of cereal). This cereal is popular among raw foodists and vegetarians.
- Peeled and unpeeled. After ripening and harvesting the grain, unhulled buckwheat is obtained. This is a natural raw material for the further production of green unsteamed buckwheat. Unhusked grain is dark brown in color and can be stored for 3-5 years without harming the inner kernel. It is also used for sowing on the site.
After heat treatment under high pressure, buckwheat grains are divided into several varieties and used for other purposes.
Yadritsa
By passing the grains through a metal sieve, the husks are separated from the kernels. Minimal mechanical processing allows them to maintain their natural triangular shape.
On a note! Yadritsa You can call any grain from which the outer shell has been removed and not crushed, for example, wheat.
Done
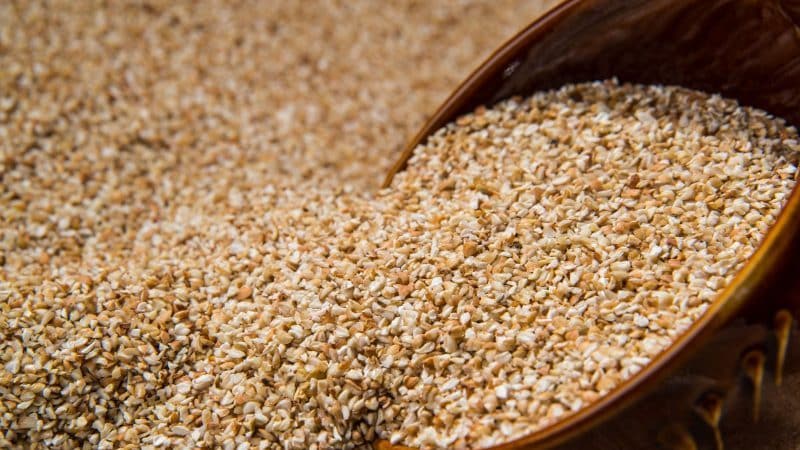

Done, or cut - these are kernels that have undergone the crushing process, i.e. the grains have been split, lost their integrity, but partially retained the upper brown shell. Available in coarse or fine crushing. Buckwheat porridge is prepared from the chaff, which is excellent for feeding children, as it is easier to digest and digest.
In terms of price, the product was cheaper than the kernels, because the grains had lost their integrity and presentability. At the same time, they are not inferior in nutritional quality to whole grains.
The table will help you see the difference between these two types:
| Characteristic | Yadritsa | Done |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Whole grains | Crushed or cracked grains |
| Cooking time | Takes longer to prepare | Prepare faster |
| For what dishes | For crumbly porridges | For viscous porridges, add to the composition of meatballs, cutlets |
| Price | Expensive | Cheaper |
Smolensk groats
Smolensk buckwheat is obtained by grinding grains into grains and then into smaller grains. This is not flour yet, but its consistency resembles semolina. In Smolensk cereals, only the light brown center remains of the grains; the top layer is completely removed and the flour dust is removed. The triangular shape of the original grain is not retained.
Smolensk grain is used to prepare liquid or viscous porridges, meatballs, and casseroles.Well absorbed by the body.
Read also:
Life hacks for Cinderellas: how to quickly separate rice from buckwheat
Buckwheat flour
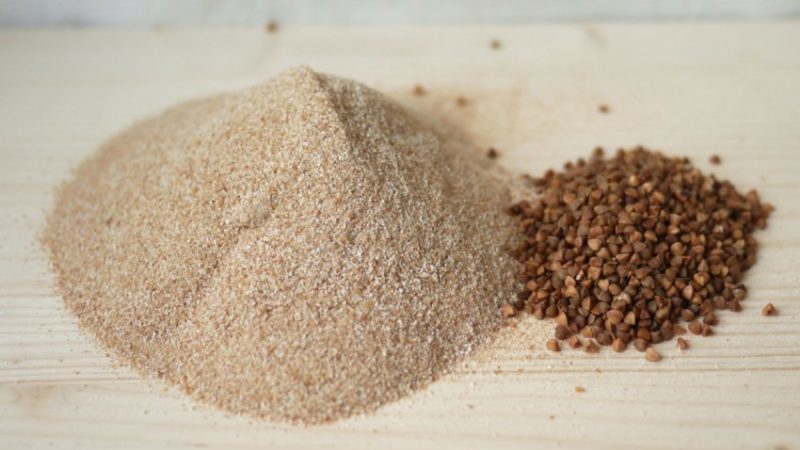

Buckwheat flour - another type of product that is obtained from buckwheat grains by thoroughly grinding. In structure it is very similar to wheat flour, but differs in color - it has a light brown, almost beige tint. It is not very popular among housewives, unlike wheat, because it is more difficult to knead.
Buckwheat flour made at home is healthier than wheat flour. During the home process of peeling grains from husks and subsequent grinding, it is impossible to completely separate the husks from the grains, as in production. But this is for the best, because most of the nutrients are stored in the upper shell.
On a note! Wheat flour can be replaced with buckwheat. It is used in the preparation of dietary and children's dishes, and added to baked goods.
Medicines
Buckwheat, rich in its medicinal properties, is used in both folk and traditional medicine for the production of infusions and medicines. A large amount of folic acid (32 mcg per 100 g) in the composition stimulates hematopoiesis, strengthens the immune system, and increases the body's resistance to harmful environmental factors.
Buckwheat flowers are collected during the ripening period along with young leaves, when rutin (vitamin P) in them reaches its highest concentration. On its basis in pharmacology, medications are produced that help stimulate blood circulation, restore heart function, prevent tissue death during frostbite, as well as products that protect against radioactive and x-ray radiation.
Attention! “Tsukronorm-biol” is a herbal medicine that contains green buckwheat. Used for diabetes mellitus and vascular disorders.
Medicines containing herbal rutin:
- "Urutin";
- "Rutamin";
- "Routin";
- "Ascorutin" and others.
Conclusion
It is not difficult to distinguish between the concepts “buckwheat” and “buckwheat”. Buckwheat is the name of a herbaceous plant, and buckwheat is its seeds. The grains are used to make kernels, prodel, cereals and flour, and buckwheat is used to treat diseases.