Is ornamental cabbage edible?
Ornamental cabbage is an unpretentious exotic plant. Bright, colorful inflorescences decorate plots, cottages and front gardens on gloomy autumn days. From the article you will find out whether ornamental cabbage can be eaten, why it is useful and how it is used.
Is it possible to eat ornamental cabbage, is it edible or not?
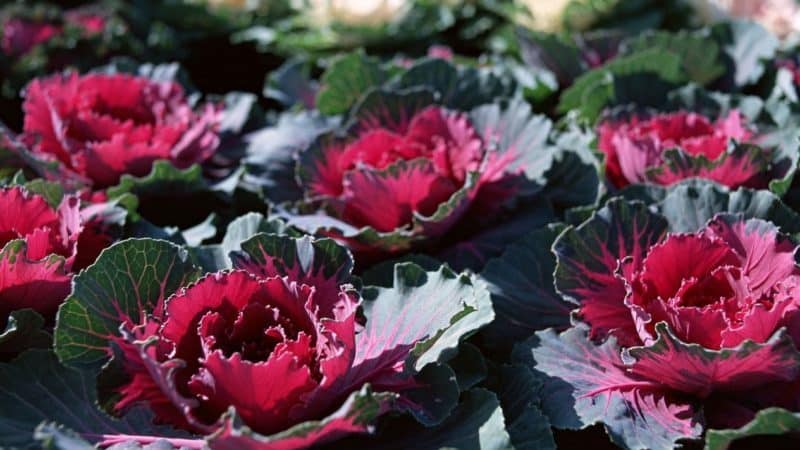

Ornamental cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. Acephala) is a type of garden headless cabbage. The herbaceous biennial is grown as an annual plant. Belongs to the huge family of Cruciferous (Brassica).
The ancestors are considered to be wild plants of the Mediterranean coast. Decorative varieties were developed in Japan and later became widespread throughout Europe and Asia.
Cabbage is divided into leaf and cabbage.
Leaf varieties are distinguished by feathery corrugated leaves and openwork fringe. Cabbages have a rounded leaf blade.
The leaves, depending on the variety, are white, purple, burgundy, and greenish. Different shades are often mixed in one inflorescence.
Feature - they quickly grow green mass and throw out elongated peduncles. In cool weather, starting from the end of August, when the night temperature drops to +10...+13°C, the plant becomes especially bright thanks to specific anthocyanin pigments. In autumn, the color of the leaves becomes colorful and rich; the first frosts are not scary for them.
It is during the autumn period that dietary indoles are synthesized in the leaves of ornamental cabbage.These are aromatic compounds, natural bioactive substances, glucosinolates of cruciferous crops.
All varieties of ornamental cabbage are eaten. It is believed that leaf varieties are tastier and more tender. The plant is classified as a vegetative vegetable, not inferior in chemical composition and nutritional value to onions, garlic, spinach, sorrel, etc.
Reference. In vegetative vegetables, stems, leaves, bulbs and other vegetative organs are used for food, but not fruits.
What vitamins does it contain?
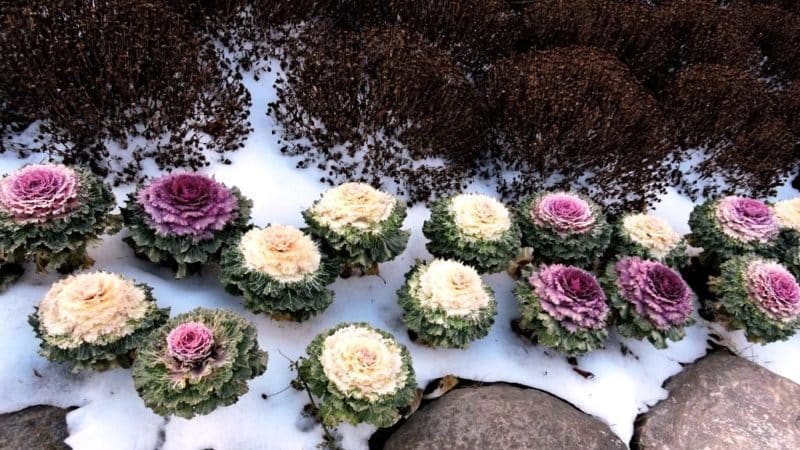

Organic compounds per 100 g:
- 10-21% (depending on the variety) of dry matter;
- up to 6% sugar;
- 0.6% starch;
- 1.5-1.8% dietary fiber;
- up to 3.5 crude protein.
The fiber content in ornamental cabbage is 2 times higher than in cabbage, Chinese cabbage, kohlrabi and broccoli.
The vitamin complex includes per 100 g:
- 150 mg – C;
- more than 5 mg – carotene;
- 0.18 mg – B1;
- 0.02 mg – B2;
- 0.06 mg – B6;
- 0.07 mg – PP;
- 100-150 mcg – K.
In small quantities, ornamental cabbage contains rare vitamin U, which is not produced by the body and promotes the healing of wounds and damage to the mucous membrane of the digestive tract. You can only get it from raw vegetables.
100 g of the raw material of ornamental cabbage contains the following minerals:
- 350 mg – potassium;
- 150-200 mg – calcium;
- up to 60 mg – phosphorus;
- 15 mg – sodium;
- more than 4 mg – iron;
- 35-40 mg – magnesium.
Ornamental cabbage contains more than 16 types of amino acids:
- lysine;
- tryptophan;
- tyrosine;
- methionine;
- histidine, etc.
The composition of enzymes that perform oxidative and degrading functions in the body:
- ascorbinase;
- peroxidase;
- cytochrome oxidase;
- amylase;
- sucrose;
- hemicellulose.
Read also:
Ornamental cabbage: cultural features
Why is it useful?
Ornamental cabbage is a record holder in terms of the amount of ascorbic acid. Vitamin C is a natural immunomodulator and immunostimulant that protects the body from bacteria and viruses.
Vitamin K, responsible for the transport of calcium, directly affects blood clotting and its composition.
Ornamental cabbage is an excellent antioxidant.
Indigestible fiber gently cleanse the intestines, improve peristalsis, and relieve constipation. Vitamin U has an antihistamine effect, removes heavy metal salts, heals and restores the mucous membrane of the digestive tract.
Mineral salts and trace elements replenish the daily human need for nutrients. Support all vital functions of the body. They strengthen the skeleton, participate in metabolic processes, and affect hormonal levels.
Potassium stimulates the transmission of nerve impulses, maintains the acid-base balance of the blood, ensures carbohydrate metabolism in the body, prevents cramps and spasms of muscle tissue.
Calcium regulates blood pressure and reduces the level of bad cholesterol, affects the elasticity of blood vessels, resists atherosclerosis and the formation of blood clots. Ornamental cabbage is useful for strengthening bones, tissue regeneration, kidney function and excretory system organs.
Essential and non-essential amino acids – building protein material for muscle tissue. They improve the condition of the skin and hair, increase performance and endurance, and reduce fatigue. Leucine, for example, promotes fat burning and lowers blood sugar levels.Tryptophan regulates appetite and prevents insomnia. Amino acids affect the emotional state - reduce anxiety levels, resist depressive disorders.
Important. Digestive enzymes present in ornamental cabbage eliminate insufficiency of the enzymatic system and optimize the digestion process at all stages. They eliminate the feeling of heaviness (when overeating), eliminate bloating, and improve intestinal function.
Benefits for people in general
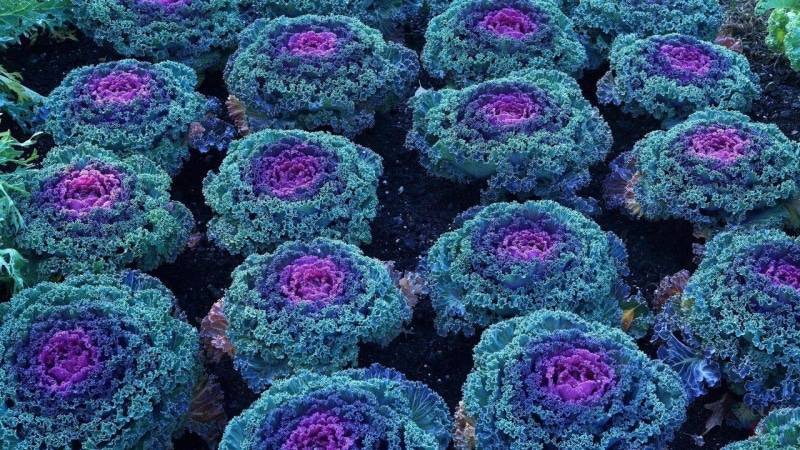

The main purpose of ornamental cabbage is the decoration and design of a garden, summer cottage, front garden. It is planted along paths, on alpine slides, multi-level mixborders, multi-row mixed flower beds, selected according to height and color scheme.
In apartments it grows well at cool temperatures on balconies, loggias, mini-greenhouses as a potted plant. In the house and at the dacha, the crop is planted in flowerpots, placing them at the entrance, along the perimeter of the stairs.
The plant is planted in open sunny areas in May. The culture does not require special conditions or care. Moderate watering, mineral and organic fertilizing during the growing season and sufficient lighting - and the flowerbed will be full of bright colors until late autumn.
The most popular and popular varieties of ornamental cabbage:
- Tokyo - distinguished by soft green wavy outer leaves and contrasting inner leaves;
- Osaka grows up to 50-60 cm in height, the diameter of the rosette is up to 50 cm;
- Nagoya - forms a large inflorescence of a bright red hue;
- The lark's tongue produces a stem up to 1-1.2 m in height, the leaf blades are a rich dark green color.
In mixed plantings and cut flowers in bouquets, ornamental cabbage harmonizes with large red cannas, purple September flowers, cereal plants, and chrysanthemums.
Medicinal properties
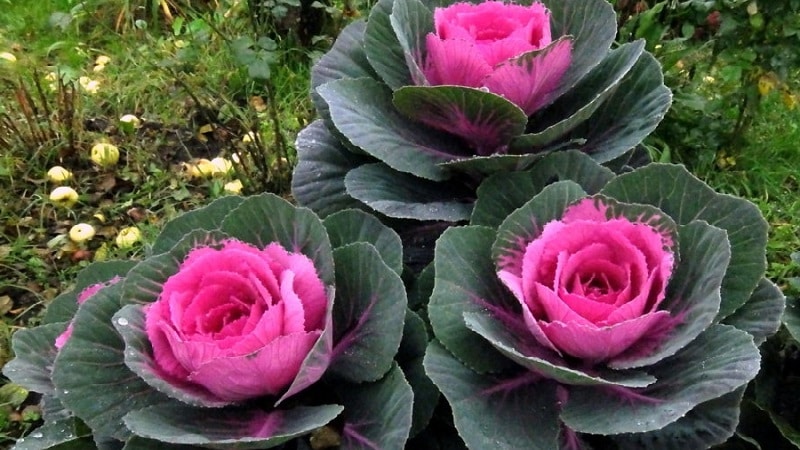

Food indoles contained in ornamental varieties of cabbage have unique properties:
- prevent and limit the accumulation of carcinogens-aflatoxins in the body,
- resist the appearance of cancer cells,
- protect DNA from negative environmental influences,
- prevent inflammation of the prostate gland.
In the journal “Issues of Biological and Medical Chemistry” for 2008, the results of a study of food indoles were announced. It has been proven that these substances protect cell membranes from destruction, resist breast cancer, mastopathy, and the formation of fibromatous nodes in the uterus and breast.
Plant anthocyanin glycosides are contained in the juice of ornamental cabbage leaves. These are useful natural dietary supplements. They protect against ultraviolet rays, free radicals, and remove toxins and waste.
Plant pigments neutralize bacterial infections, resist diabetes and endocrine pathologies. Reduce the risk of developing cancer in case of hereditary predisposition.
Fact. Due to its high antioxidant content, ornamental cabbage is recommended to be included in the diet of those who actively use mobile communications.
Dietary fiber gently cleanses the intestines and normalizes its microflora, helping to reduce body weight.
How to eat
Farmers and summer residents advise adding leaves to the diet in late autumn. At the beginning of winter, they are “mined” from under the snow, then kept in cold water for 10-15 minutes, washed and added to food. A vitamin salad or side dish with cabbage leaves will add variety to your lunch or dinner.
For garnish, red and white subspecies of the Nagoya variety are usually used. Delicate leaves do not require long heat treatment.
Variety Chidori with wavy fringe are used for food after the first frost. The bitterness and hardness of the leaf plate goes away.

Ornamental cabbage is stewed, baked, and added to omelettes. When serving, sprinkle generously with fresh herbs and drizzle with olive oil. Stew for no more than 2-4 minutes so that the leaves do not lose color and nutritional properties.
The leaves are added to puree soup, vegetable stews, and sauces. Used to prepare cabbage rolls and dolma. They go great with rice.
Young leaves are used for dietary salads, cocktail mixes, fresh vegetable juices and smoothies. They do not need to be soaked or scalded with boiling water.. Vitamins and mineral salts are retained in their entirety.
Vitamins are also preserved when frozen - the leaves are perfectly stored in the freezer and do not lose their nutritional value for 6-10 months.
Read also:
Conclusion
All varieties of ornamental cabbage are suitable for consumption. In terms of chemical composition, the plant is not inferior to garden species - cabbage, Beijing, broccoli, cauliflower, kohlrabi, etc. Unique plant components - fiber, anthocyanins, dietary indoles - absorb toxins, reduce the risk of cancer, and are beneficial for men's and women's health.
Ornamental cabbage is recommended for people with diabetes, pathologies of the digestive tract, and has no age restrictions or contraindications. It is a natural immunostimulant and immunomodulator. Replenishes vitamin deficiency in the autumn-winter period, protects against depression and loss of strength.