What are the diseases of tomatoes and how to treat them?
Even the most experienced gardeners and farmers from time to time encounter diseases or pests of cultivated plants, and in particular tomatoes. There are several causes of tomato diseases: insufficient or excessive nutrition, fungal, viral, bacterial infections. If these problems are not corrected in time, the harvest may decrease and the plant may even die.
In our article we will look at the most common tomato diseases and ways to combat them, and also find out how to prevent diseases.
Causes of tomato diseases in a greenhouse
To protect plants from soil drying out, frosts and other adverse weather conditions, tomatoes are grown in greenhouses. However If the temperature or watering conditions are violated, even in a greenhouse environment, tomatoes may encounter diseases and pests. In addition, as a result of sowing low-quality seeds that are already contaminated, the disease can also develop.
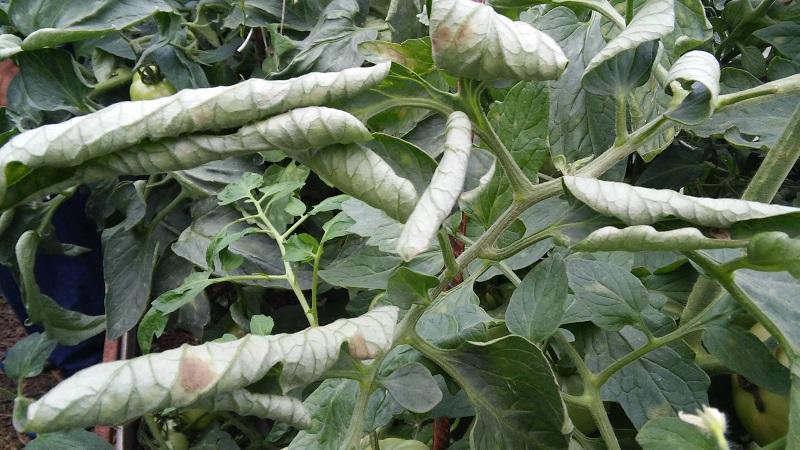

Measures to combat viral diseases of tomatoes when cultivating them in a greenhouse:
- disinfection of seeds, as well as cultivation equipment;
- extermination of insects that carry infection;
- disinfection of the greenhouse (in autumn or spring);
- destruction of plant residues after harvesting, deep plowing and steaming of the soil in the spring, before planting sprouts.
The most common tomato diseases and methods of combating them
To properly fight diseases and prevent them, you need to know what we are dealing with.Let's consider the most common problems gardeners face.
Mosaic
 Mosaic - a viral disease that is common both in open ground and in greenhouses. It manifests itself as brown or yellow spots on the leaves, their curling and death.
Mosaic - a viral disease that is common both in open ground and in greenhouses. It manifests itself as brown or yellow spots on the leaves, their curling and death.
This disease is practically untreatable. Prevention is the only option. Before sowing, tomato seeds must be treated in a solution of potassium permanganate or sodium triphosphate.
Late blight
Late blight — one of the most common fungal diseases. Typical for plants grown in open ground.
 It is manifested by the appearance of brown spots on the leaves and stems. The fruits are covered with brown spots. A white coating appears on the underside of the leaf.
It is manifested by the appearance of brown spots on the leaves and stems. The fruits are covered with brown spots. A white coating appears on the underside of the leaf.
The rapid spread of late blight is facilitated by strong temperature changes and high humidity..
As with many other diseases, late blight is best dealt with through prevention.
For this It is recommended to carefully water the plants at the roots, weekly spraying with cow's milk whey or copper oxychloride. Polychlor can be sprayed once every 2 weeks.
This is done before flowering begins, or at the first signs of disease.
If the tomatoes are already sick, then spraying is carried out 10% solution of table salt, or garlic solution. You need to repeat the procedure once every 2-3 weeks.
Blackleg
 Blackleg or root rot - a fungal disease that primarily affects plant roots. It occurs due to oversaturation of the soil with fertilizers or due to neglect of soil disinfection before planting.
Blackleg or root rot - a fungal disease that primarily affects plant roots. It occurs due to oversaturation of the soil with fertilizers or due to neglect of soil disinfection before planting.
If you notice that at least one of the plants is infected, remove itso as not to put other bushes at risk.
Used to prevent disease copper sulfate solution.
Cladosporiosis
When preventing this disease take care to disinfect the soil before planting, as well as the timely removal of old leaves. If you notice manifestations of cladosporiosis, it is recommended to limit watering.
Interesting on the topic:
Secrets of planting and caring for tomatoes
Apical rot
Apical rot is not an infectious disease and occurs due to lack of moisture, soil salinity or due to heat. It appears as a flat brown spot with the smell of rot.
You can avoid infection if you do not neglect fertilizer. and regular watering of plants in hot weather.
Brown rot (Fomoz)
 Fomoz - is a fungal infection that appears as a small spot at the base of the tomato.
Fomoz - is a fungal infection that appears as a small spot at the base of the tomato.
The size of the spot is 3-4 cm. The rot spreads from the stalk to all sides of the tomato.
The fruit rots inside. Brown rot appears mainly due to damage to the fruit caused by unfavorable weather conditions.
To prevent Phoma, it is recommended to spray plants with special products., which effectively destroy harmful bacteria and fungal microorganisms.
An infected bush cannot be saved. It needs to be removed.
Gray rot
 A fungal disease that attacks the stems of a plant. A characteristic sign is the appearance of a gray coating on parts of the plant.
A fungal disease that attacks the stems of a plant. A characteristic sign is the appearance of a gray coating on parts of the plant.
Plaque prevents the flow of water, resulting in tissue death.
Infection Injured stems are primarily susceptible, so be careful when caring for the crop.
To prevent the appearance of gray rot, tomatoes are treated "Trichoderminoma".
To combat an already existing disease, use a paste with fungicides or the drug “Bayleton”.
Septoria (white rot)
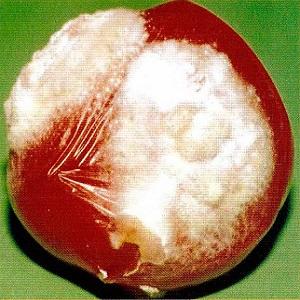 Infection begins from the ground, from where the disease penetrates into the lower part of the plant. The lower leaves are the first to suffer.
Infection begins from the ground, from where the disease penetrates into the lower part of the plant. The lower leaves are the first to suffer.
As a result of the disease, they become watery and lose their color. The plant is covered with a white coating. The likelihood of infection is higher in soils that contain clay and sand.
To avoid infection, strengthen plant immunity with zinc or urea.
To combat an already existing disease, use special products (Zineb, Horus) or treat plants with copper oxychloride.
Stem necrosis
Bacterial disease. It is characterized by spots on the leaves, cracks at the bottom and stripes on the stems.
Prevention: eliminating residues, treating seeds and sprinkling plants. If you notice that a plant is infected, it is better to immediately remove it along with the surrounding soil.
Powdery mildew
Powdery mildew - fungal infectious disease. It first appears as a white coating on the leaves, similar to flour. Then the plaque appears on other parts of the plant. The leaves subsequently turn yellow and die.
 To prevent tomatoes from becoming infected, you need to follow simple rules:
To prevent tomatoes from becoming infected, you need to follow simple rules:
- remove old leaves;
- do not let the top layer of soil dry out;
- add more phosphorus-potassium fertilizers;
- use solutions based on potassium permanganate;
- remove all affected areas immediately.
We considered the issue of What diseases do tomatoes suffer from and how to treat them. However, diseases can be avoided if a number of preventive measures are followed.
Prevention
To get a bountiful harvest, When growing, follow the basic rules:
- Don't forget about the balance of nutrients in fertilizers.
- Handle plants carefully to prevent damage, as this can lead to disease later on.
- Choose a favorable time for planting tomatoes.
- Plant several varieties at once to identify the one most suitable for your site.
- Plant tomatoes in greenhouses or greenhouses to provide them with more favorable conditions.
- Don't forget to keep the distance between plants so that each one has enough nutrients.
Tomato pests and methods of controlling them
Pests for tomatoes are no less dangerous than various infectious and fungal diseases. They are capable of destroying plants both in open ground and in greenhouses. Since grown tomatoes are most often selective hybrids, they do not have natural defense mechanisms against insects and other pests. Therefore, plants require special care.
The most common pests of tomatoes are whiteflies, bugs, mole crickets, aphids and Colorado potato beetles. However, this is only a small part of those insects that can cause irreparable harm to cultivated crops.
Whitefly
 The photo shows that the whitefly is it is a moth-like small white butterfly measuring up to 3 mm.
The photo shows that the whitefly is it is a moth-like small white butterfly measuring up to 3 mm.
Belongs to a group of pests that can destroy plantings in 2-3 weeks. Most often it lives in greenhouses and greenhouses.
Whiteflies have the ability to reproduce rapidly, laying larvae on the undersides of leaves. The hatched caterpillars feed on the sap of the plant, which is why the bush quickly dies.
Due to the molasses secreted by the whitefly, the mouth of the leaf becomes clogged and it stops breathing. The processes of photosynthesis in greenery are disrupted. Tomatoes lose their ability to grow and bloom. Leaves and flowers fall.
To combat the pest, the undersides of the leaves are sprayed special preparations (“Fitoverm” or “Aktara”). Since the chemicals only affect adults, this treatment must be carried out every week for 4-5 weeks.
Medvedka
Medvedka - large insect with an oblong body, which reaches a length of up to 5 cm.
 Individuals have the ability to move on and under the ground, as well as fly. The larvae dig tunnels in the soil in which they live. Insects are found both in greenhouses and in open ground.
Individuals have the ability to move on and under the ground, as well as fly. The larvae dig tunnels in the soil in which they live. Insects are found both in greenhouses and in open ground.
Moving in the soil insect damages plant roots, as a result of which they die.
There are many ways to deal with mole crickets:
- soil treatment with ammonia;
- special traps;
- bait;
- the passages left by mole crickets are filled with foamed water;
- lay special granules, etc.
Aphid
Aphids - small insects yellow or black. Appear on plants in June-July. Insects feed on plant sap, which is why the leaves quickly become limp. Aphids can destroy a seedling in a matter of days.
To combat insects, use special chemical or soap solutions, infusions of garlic, wormwood or hot pepper.
Interesting on the topic:
Khrushchev
Khrushchev larvae move underground and destroy plant roots. Adults (chafer beetles) feed on the leaves of bushes.
The larvae are destroyed when they dig up the garden. They are simply collected in a bucket and disposed of. To prevent the appearance of larvae, nitrogen mineral fertilizers are added to the soil.
Drotyanka
Drotyanka – Click beetle larva, also known as wireworm. It has a bright yellow or orange color. The darter feeds on tomato roots, which leads to a slowdown in plant growth.
They fight the dart with the help of traps. They are placed a few days before the seedlings are planted. It is also recommended to add mineral fertilizers to the soil.
Scoops
 This is a whole family of pests that are similar in appearance. The damage is caused by the caterpillar stage.
This is a whole family of pests that are similar in appearance. The damage is caused by the caterpillar stage.
Winter caterpillars are earthy-gray in color. Greenish color is less common.
The potato cutworm is often lemon-yellow in color. The length of the cutworms reaches up to 5 cm.
Fall armyworm feeds on stems at ground level and is particularly voracious. Gardening destroys the pulp of the leaf or gnaws through it. Potato - will gnaw holes inside the stem, thereby killing the bush.
The easiest way to combat cutworms is with special insecticides. (“Inta-Vir”, “Decis Expert”, “Arrivo”). Folk methods of struggle include tinctures of garlic arrows or decoctions of wormwood.
Spider mite
 Mite sizes – from 0.2 to 2 mm. An adult tick has 4 pairs of legs. The color varies: there are gray, green, red or completely colorless mites.
Mite sizes – from 0.2 to 2 mm. An adult tick has 4 pairs of legs. The color varies: there are gray, green, red or completely colorless mites.
Almost weightless pests are easily carried by the wind, creating a threat to plants. There are many of them among the remains of old plants. When settling on tomato bushes, mites damage the leaves. This leads to spotted wilt, mosaic lesions of the plate and viral shedding (streak). Large accumulations provoke the appearance of gray rot.
You can fight ticks both with special preparations (Fitoverm, Agrovertin and Karbofos), and folk remedies, such as a soap solution or wiping the leaves with medical alcohol.
Conclusion
In the article we looked at the most common diseases of tomato leaves and fruits and methods of treating them. Plant immunity plays a crucial role in preventing diseases. With a lack of microelements such as potassium, iodine, manganese, and copper, tomatoes weaken and the risk of infection increases.
To protect tomatoes from various diseases and pests, follow simple prevention rules. It is equally important to improve the soil environment and follow the rules of crop rotation. Then your plants will be healthy and will delight you with a rich harvest.