How and when to form a melon in open ground correctly
Melon is a dessert vegetable with a rich sweet taste and delicate aroma. Despite its sweetness, it is considered a dietary product, since it consists of 90% water and promotes complete digestion. In addition, it is rich in vitamins and minerals.
Homeland melons Central Asia is considered hot, but thanks to the achievements of modern breeders, this honey plant is also grown in central Russia. However, to obtain a rich harvest, you need to know the nuances of caring for the crop. One of them is the formation of a bush.
In this article we will tell you how to pinch a melon and when to start forming in the open ground.
The importance of correct and timely formation of melon
Melon is grown both in open ground and in greenhouses. The crop is sown in prepared soil with seeds or planted as seedlings.
When cultivating in open ground, removing excess shoots from melon is a necessary condition for obtaining a good harvest.
Pinching limits the growth of green mass of the bush and allows you to grow larger fruits. In addition, the melons will ripen earlier and taste sweeter.
When growing large-fruited varieties, part of the fruit ovaries is also removed. From 3 to 6 fruits are left per bush.
Planting dates and site preparation
The site for planting melons begins to be prepared in the fall. Considering the southern origin of the plant, choose a sunny, dry place, protected from cold winds.If the soil in the garden is clayey, add additional river sand (about 1 bucket per 1 sq. m).
The earth is dug up deeply and fertilized. Humus is added at the rate of 3–4 kg per 1 sq. m. m. In the spring, the bed is dug up again, potassium and phosphate fertilizers are added.
In the south of Russia, melon is sown with seeds in open ground in late April - early May. In the central zone of our country, the crop is grown only through seedlings.
Need to know! Melon seedsused for sowing must be at least three years old. Mostly male plants grow from fresh seeds, therefore there will not be a good harvest.
Peat containers are perfect for seedlings. It is convenient to plant such seedlings together with pots, and peat will serve as an additional fertilizer.
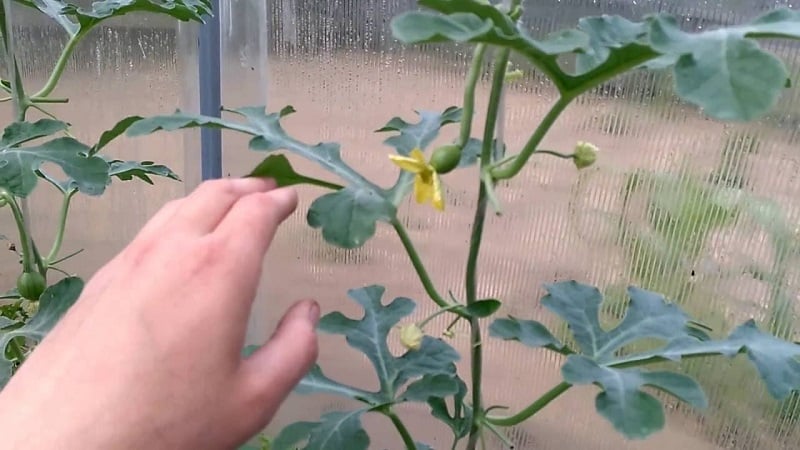

Basic rules for forming a melon in open ground
In the wild, melon bushes grow greatly. This is explained by the southern origin of the culture. However, in our climate there are no conditions for the filling and ripening of all the fruits on the bush. Therefore, only the largest and healthiest ones are left, no more than 3-4 per bush.
Features of culture formation
Pinching melon bushes is one of the main agricultural practices that allows you to grow large fruits. This procedure should not be underestimated. Without it, there simply will not be a good harvest.
The formation of a plant consists of removing excess ovaries and timely pinching out unnecessary shoots.
In addition, pinching helps regulate the growth of vines and guide them so that they do not overlap row spacing.
Formation methods
When grown in open ground, the crop is formed in two ways: vertical and horizontal.
The vertical method involves constructing a strong frame to which ropes or wires are tied. The height of the structure is about 2 m. The lower end of each rope hangs down to the melon. Loose lashes and newly emerging shoots are wound on a rope.
The obvious advantage of this method is that the plant receives more light, which has a positive effect on yield. In addition, caring for the bushes is greatly simplified.
With the horizontal method of formation, the crop grows freely on the ground. Keep in mind that the melon requires a large area for the growth and branching of the vines.
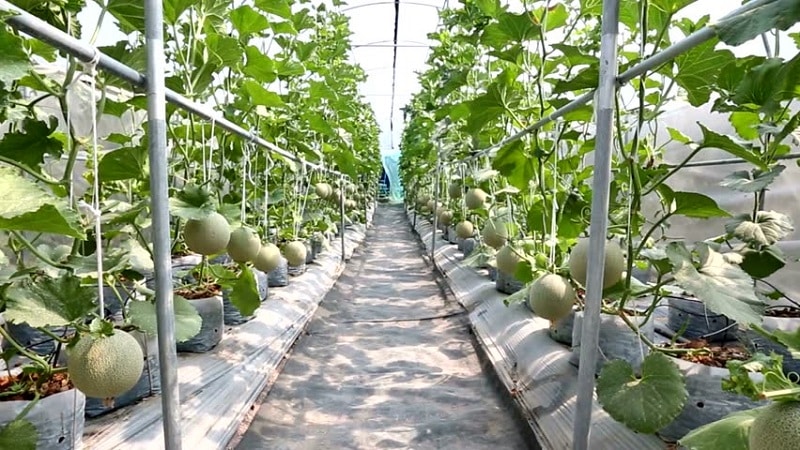

Formation schemes
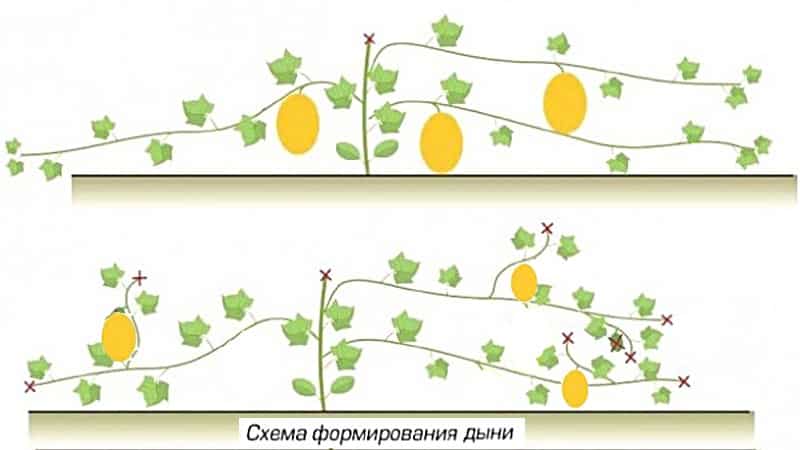
The formation of the plant is carried out by pinching the shoots. Hybrid and non-hybrid varieties have different formation patterns.
In hybrid varieties, the main vine is not pinched - the female flowers are located on it. In non-hybrid ones, the main shoot is pinched, leaving 2-3 most developed side shoots.
Stages of the procedure
The formation of a bush begins early, even at the stage of growing seedlings. When 3-4 true leaves have formed on the sprout, the main shoot grows in the axil of the main leaf. He is immediately pinched.
After this operation, lateral shoots are formed in the axils of the lower leaves. It is on these lateral branches that most of the fruits will subsequently form.
When growing melon in open ground, 2-3 of the strongest shoots are left from the first side shoots. This is the second stage of bush formation.
The third stage is carried out at the beginning of the formation of ovaries. At this last stage, all underdeveloped lashes and branches without ovaries are mercilessly removed.
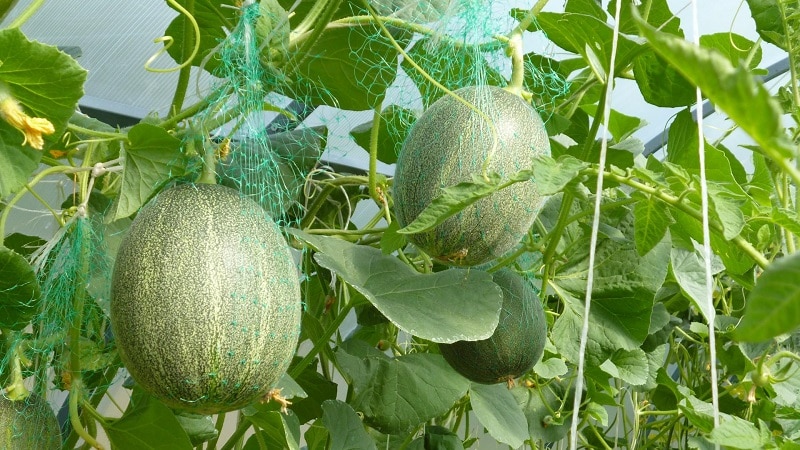

How and where to pinch a melon
The shoots are removed carefully so as not to pinch the main stem of the plant. The side branches that grew after the main shoot was removed are pinched above the 4-6 leaf.
After the fruits have formed on the bush and begun to swell, the fruiting vines are pinched. Trim the vine 3-4 leaves above the fruit.
Leave 2-3 melons on one plant if it is a large-fruited variety, and 4-6 if the fruits are medium-sized.
To protect against diseases and pests, the cutting sites are treated with a mixture of sulfur, coal and lime. The components are mixed in equal parts and the damaged areas are lubricated.
Feeding before and after pinching
All work on the soil, including fertilizing, is carried out until the leaves of the bush close. Fertilizers are applied 2-3 times. Before the first removal of shoots, the melon is fertilized with Kemira, Kristalon, and ammonium nitrate.
When buds begin to form on the vines, the bushes are watered with a solution of organic fertilizers.
Lastly, phosphate-potassium fertilizers are applied. Fertilizing is done 3-4 weeks after the budding phase.
Most common mistakes
Stepping is not the simplest agrotechnical technique. If done incorrectly, the quantity and quality of the harvest is reduced.
We list the main mistakes made by gardeners:
- Pinching a melon bush in the same way as a watermelon bush. Although melon and watermelon - related plants, fruit set in them occurs differently. In watermelon, fruits are formed on the main shoot, and in melon - on the side shoots.
- Thickening of plantings. Melon bushes need a lot of space to grow and develop. Even pinching, carried out according to all the rules, will not help to get a good harvest if the plants are planted too densely.
- Insufficient removal of shoots. There is no point in sparing the extra lashes. Otherwise, all the nutrients will go into the leaves and stems, few ovaries will form, and the fruits will be small and unsweetened.

Read also:
A variety with a melon aroma and high yield - Russian pumpkin and the secrets of its cultivation.
How to cook a simple but very tasty melon jam.
How does melon affect the intestines: does it weaken or strengthen?
Conclusion
The formation of a melon bush is a prerequisite for obtaining a rich harvest of sweet, aromatic fruits. The pinching procedure is carried out regularly throughout the growth of the crop.
On average, no more than 3–4 fruits are left per plant. Following these simple rules will help you grow a tasty and healthy dessert vegetable in your garden.