Simple recipes for barley moonshine
The market is replete with strong alcoholic drinks. But some lovers, connoisseurs and businessmen prefer not to buy, but to produce alcohol. For example, good old moonshine. It is prepared from sugar, wine, bread, beer, berry and grain mash. There are more than 1000 recipes for making this strong, fragrant drink.
Connoisseurs recognize that the softest and richest product is obtained using mash from grain crops. Moonshine brewing is almost an alchemical process, which has its own subtleties and difficulties for beginners. Therefore, before you decide to prepare a drink at home, we recommend that you study the technology in detail.
Moonshine is a home-made strong alcoholic drink.
Moonshine is any strong drink produced at home by distillation.. The very name of this drink contains the method of its preparation. Moonshine is “distilled,” that is, the original drink with a lower alcohol content is distilled using low-temperature distillation, producing strong alcohol.
During distillation, alcohol and water evaporate from low-alcohol raw materials and then condense. The condensation of alcohol with water and ballast substances is the goal of the process.

The unrefined distillation was called “pervak”. It is subjected to purification, re-distillation, infusion with herbs, and aging in oak barrels, resulting in strong drinks that have a unique taste and are collectively called “moonshine.”
Attention! Drinking alcohol is harmful to your health.
First you need raw materials - a low-alcohol product, obtained by alcoholic fermentation, or simply “mash”. What can it be prepared from: sugar, crackers, jam, fruit - anything that contains sugar or starch.
One of the types of raw materials is barley mash. Barley contains 72% starch, which means that from 100 g of barley, during fermentation and distillation, you can get up to 37 g of alcohol (in terms of 100% pure substance) or 80 ml of an aqueous-alcohol solution of 40% strength. This makes barley an advantageous raw material to use.
Before preparing moonshine
Before you start making moonshine, study the legal side of the issue and purchase the necessary equipment.
The legal side of the issue of moonshine
In the 80s of the last century, administrative and criminal penalties were provided for the production of alcoholic beverages with an alcohol content of more than 4%. Later, with the formation of the Russian Federation, the law was abolished. However, the government continues to control the production of strong alcohol.
Important! Handicraft production of alcoholic beverages for the purpose of sale is prohibited in Russia. There are fines for breaking the law.
 To produce alcohol for sale, you must obtain a license for the production and sale of alcoholic products. The quality of the drink itself is confirmed by a declaration of conformity. An additional tax has been introduced on the production of each commercial alcohol unit - an excise tax, upon payment of which an excise stamp is affixed to the product.
To produce alcohol for sale, you must obtain a license for the production and sale of alcoholic products. The quality of the drink itself is confirmed by a declaration of conformity. An additional tax has been introduced on the production of each commercial alcohol unit - an excise tax, upon payment of which an excise stamp is affixed to the product.
In Russia, several types of moonshine are officially produced (“Good Farmer”, “Derevensky”), which have a declaration of conformity and an excise stamp.
It is allowed to produce moonshine “for yourself” in a volume of up to 200 liters per year. Finished products can be transported in a volume of no more than 10 liters.
Fine for exceeding standards production and transportation:
- 5000 rub. – for individuals;
- 20000-50000 rub. – for officials;
- 100,000-150,000 rub. – for legal entities and individual entrepreneurs.
Equipment for making moonshine
All necessary equipment is purchased in special stores for home brewing.
 Inventory for obtaining mash:
Inventory for obtaining mash:
- containers with a volume of 10-25 liters with a semi-permeable stopper or water seal; in some cases, latex stretchable gloves are suitable;
- wooden spoon with a long handle for stirring;
- alcohol meter with alcohol detection limit up to 30%;
- glass thermometer.
There are household and laboratory alcohol meters. The first has a wide range of alcohol determination, but low accuracy. The second has a detection limit for alcohol in liquid, but is highly accurate.
Using laboratory equipment, you can also determine the amount of sugar in the liquid, which will help in determining the end of fermentation. The more accurate the device, the easier it is to calculate the volume of the future product and prepare the container.
Inventory for obtaining moonshine:
- moonshine still with an accurate thermometer;
- gas or electric heating device;
- source of uninterrupted supply of cold water;
- glass containers for collecting finished products;
- an alcohol meter with an alcohol determination limit of up to 90%.
Preparing barley for mash
Alcoholic yeast does not process complex sugars such as starch and cellulose, so mash will not work if you simply pour water over the grains and add yeast. In order for the fermentation process to take place, starch-containing raw materials must be “saccharified.”To do this, some of the grains are sprouted, during which complex carbohydrates are broken down into glucose under the action of germ enzymes. Sprouted grains are called malt.
Before preparing malt, barley is checked for germination. To do this, select 100-200 medium grains, which are wrapped in wet gauze, covered with perforated polyethylene and left in a warm place. The gauze is periodically moistened. After 3-7 days, the seedlings are checked. If less than 90 grains out of 100 sprouted, such barley is unsuitable for malt.
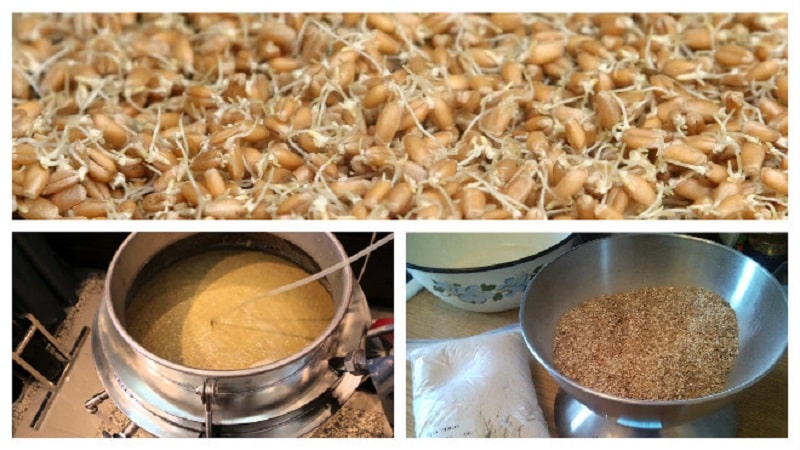

Stages of malt preparation:
- Washing and selection of grains. Barley grains without external damage are washed in cold running water.
- Soak. Barley is poured with clean water in a shallow container so as to cover all the grains. The process lasts 2-2.5 days. During this period, change the water every 8-9 hours, leaving the barley without water for two hours to activate the germ enzymes.
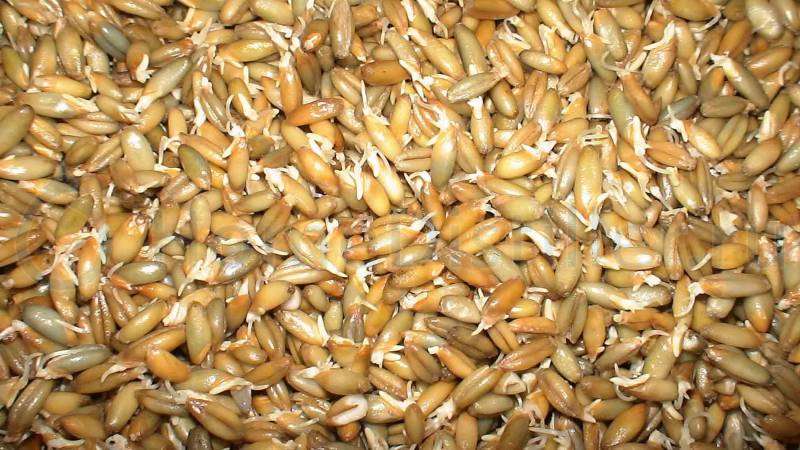
- Germination. Grains without water are spread in a thin layer on a tray, covered with damp gauze and cling film so that the moisture does not evaporate, and left in a warm place. Several holes are made in the film around the perimeter to allow oxygen to enter. The grain is periodically sprayed with clean water from a spray bottle and mixed carefully so as not to damage the sprouts. On the 6-7th day they reach 2-3 cm, the grains themselves become sweetish in taste - which means the malt is ready.
If desired, it is ground into pulp in a meat grinder, mill or blender.
Fresh malt can be stored for up to three days. To make a stock of it, barley seedlings are dried at a temperature of +45-55°C for 16-18 hours. Dry malt, suitable for further use, has a light shade - grains that darken during the drying process are thrown away.
Ingredients for barley moonshine
If you decide to make moonshine for the first time, keep in mind that losses at each stage of preparation will be 10-15%.
Average to obtain about 5 liters of moonshine with a strength of 40% you will need:
- malt – 1-1.5 kg;
- barley grains – 4.5-5 kg;
- water – 27 l.
If desired to speed up the fermentation process, add up to 1 kg of sugar and up to 12 g of dry (or 60 g pressed) yeast.

Stages of moonshine brewing
Making moonshine from barley includes two stages: preparing the mash and distilling it into moonshine.
Barley mash
Grain mash produces a softer and more aromatic distillate compared to sugar mash. Barley mash is produced using yeast or barley starter. If it is made without yeast, the barley is not washed before use, so as not to wash off the yeast fungi from the surface of the barley.
Making barley starter includes the following stages:
- 100-150 g of pure barley are soaked in clean water and left in a dark place at +25°C.
- After 1-1.5 days, add 50-75 g of sugar.
- The container is sealed with a water seal or wet gauze and a glove and left to ferment for a week.
The finished starter has a sour smell and foams. The difficulty of producing mash without yeast is the unpredictable composition of the microflora on the surface of barley grains. Instead of fermenting, the mash can sour, go rancid or become moldy, so experienced moonshine traders and brewers add ready-made yeast.
Getting mash:
 Dried malt is crushed into coarse flour and poured into a deep saucepan.
Dried malt is crushed into coarse flour and poured into a deep saucepan.- Then it is poured with hot water +50-55°C in a ratio of 1:4 with constant stirring so that lumps do not form until the mass becomes homogeneous. Malt with water the consistency of liquid sour cream is called wort.
- It is heated to +63°C, thoroughly mixed again and covered with a lid. At a temperature of +55-62°C it simmers for 60-80 minutes. It is stirred every 15 minutes. When the upper part of the wort becomes light and the slurry settles, stop heating. If it is too intense and the temperature rises to +70°C, the wort will be spoiled.
- It is quickly cooled in an ice bath to +24-27°C so that it does not sour ahead of time.
- The cooled wort is poured into a fermentation container, yeast or barley starter and sugar (if desired) are added, and mixed thoroughly. Select the volume of the fermentation container so that after adding water there remains 25% empty space. During fermentation, the liquid rises and can overflow or clog the water seal. Use glass or food-grade plastic containers.
- The container is sealed, covered with a bag or rags from the sun's rays and placed in a warm place.
In order for the raw material to ferment faster and not spoil, a temperature of at least +18-25°C is required. Once a day, stir the mash with a wooden stirrer. If the container is covered with a glove, air is released as it is inflated. Fermentation lasts 3-7 days. After three days, samples are taken daily to measure sugar and alcohol levels.
Signs of the end of the fermentation process:
- the turbidity settles to the bottom, the mash becomes lighter;
- gas separation stops;
- the liquid acquires a bitter-sour taste without sweetness;
- The alcohol meter shows the absence of sugar and at least 10% alcohol.
See the continuation of the video below.
It can be useful:
Making moonshine
Pure moonshine from malt and barley is obtained by double distillation of mash.
First stage:
- The mash is filtered through a fine sieve or cheesecloth. There should be no grain particles in the filtrate, as they will burn in the distillation cube and spoil the taste of the drink.
- Filtered mash is poured into the distillation cube and heating begins, connecting the water to the coil cooler.
- The first portions of the distillation (“heads”), obtained at temperatures up to +76°C, are poured into a separate container.
- When the temperature in the cube reaches +76-78°C, the collection of moonshine begins. The liquid will be cloudy due to ballast substances. Check the strength of the distillation periodically. When the selected sample contains less than 30% alcohol, the distillation is stopped. The last portion of the distillation is called the “tail”. “Heads” and “tails” contain substances hazardous to health and are used only for technical purposes. Only the “body” – the middle part of the distillation – is suitable for drinking.
- The strength of the distillate is measured using an alcohol meter.
- The total volume of alcohol is determined by the formula V alcohol = V distillate × % strength × 0.01 (for example, 10 liters of distillation with 45% strength contain 10 × 45 × 0.01 = 4.5 liters of alcohol).
- The distillate is diluted with water to a strength of 20%.
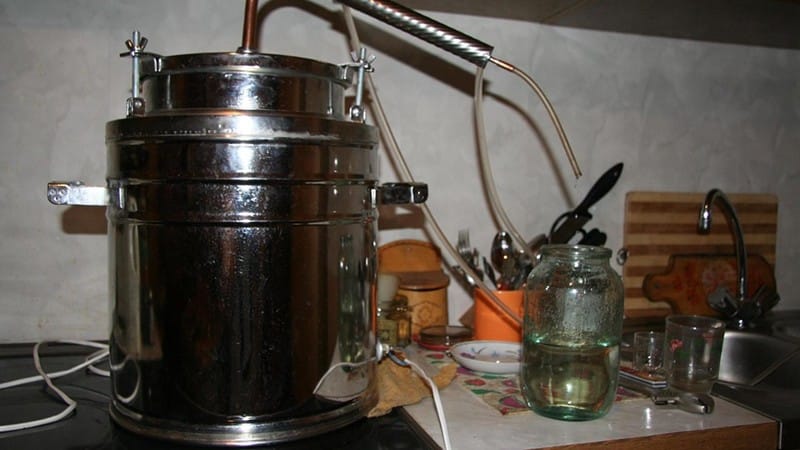

If desired, the first stage is cleaned with coal from ballast substances. To do this, crushed activated carbon is poured into the distillate, mixed and left alone for 1.5-2 hours. After this, the liquid is filtered through a paper filter or blotter (a paper towel or napkins will do). After filtration, the first distillation becomes transparent and unpleasant odors disappear.
Second stage:
- The purified primary distillate is poured into the cube of a moonshine still and re-distilled.
- The first 12-15% of the resulting distillation is collected in a separate container - this is the “head”.
- The “body” is collected until the strength drops below 45%.The “tail”, like the “head”, is collected in a separate container for technical needs.
- Determine the alcohol content in the distillate.
- The secondary distillation is diluted with water to the desired strength and poured into a glass container for storage. The finished product will be clear and may have a faint amber tint.
The secondary distillate is left for 3-4 days to stabilize the taste. It can be re-purified with milk, steeped in an oak barrel, and aromatic herbs added, but even without these procedures you will get a strong drink with a bready aroma and a mild taste.
Barley moonshine recipes
Not only whole barley grains are used as raw materials for moonshine., but also other cereals, flour. Let's talk about a few simple recipes.
Moonshine from sprouted barley
Preparation does not take much time, since fully saccharified raw materials ferment faster.
Ingredients:
- barley grains – 2.5 kg;
- sugar – 4 kg;
- water – 23 l;
- baker's yeast – 50 g.
Cooking steps:
- Malt is obtained from the entire volume of barley grains.
- The malt is saccharified to produce wort.
- The wort is poured into a fermentation container, filled with water, sugar and yeast are added and left until the mash is ready.
- The mash is filtered and distilled twice in a moonshine still.

Moonshine from yeast-free mash with sugar
In this case, yeast is not needed, which will reduce the cost of raw materials.
Ingredients:
- barley grains – 5 kg;
- sugar – 6.5 kg;
- water – 25 l.
Cooking steps:
- A third of the barley is fermented with 1.5 kg of sugar.
- The remaining barley is sprouted to produce malt.
- Wort is prepared from malt.
- The wort, barley starter, remaining sugar, and water are mixed in a fermentation container and left in a warm place to make mash.
- The resulting mash is filtered and subjected to double distillation in a moonshine still.
Moonshine made from barley flour
 If you don't have whole grains, you can use this recipe.
If you don't have whole grains, you can use this recipe.
Ingredients:
- coarse barley flour – 10 kg;
- baker's yeast – 200 g;
- water – 15 l.
Cooking steps:
- Barley flour is poured with hot, unboiled water, stirred and left for three hours.
- When the mixture has cooled to +27-30°C, yeast is added to it and the container is closed for fermentation.
- The finished mash is filtered and distilled twice in a moonshine still.
Moonshine from a cell
Even a beginner can master this simple recipe.
Ingredients:
- finely ground barley – 4 kg;
- alpha-amylase – 4 ml;
- glucoamylase – 4 ml;
- pressed baker's yeast – 150 g;
- water – 12 l.
For reference. Amylase enzymes are sold in home brewing stores.
Cooking steps:
 Boil 12 liters of water in a deep saucepan.
Boil 12 liters of water in a deep saucepan.- With continuous stirring, add barley grits and bring to a boil.
- Remove the pan from the heat, seal it tightly, wrap it in a blanket and leave for three hours.
- Add alpha-amylase with continuous stirring until the consistency becomes more liquid.
- When the temperature of the mixture drops to +65°C, add glucoamylase and mix again.
- The container is closed again, wrapped and left for 60 minutes.
- The mixture is cooled to +29°C and yeast is added.
- The ingredients are poured into a fermentation container and a water seal is installed.
- The finished mash is filtered and distilled twice in a moonshine still.
Barley drinks
Barley moonshine can be used to make vodka and liqueurswith a more refined taste and aroma. In addition to strong alcoholic drinks and beer, barley, rich in starch, is suitable for making kvass.
Barley kvass
Kvass from grain crops famous for its healing properties and benefits for the gastrointestinal tract. Barley kvass is no exception.
Ingredients:
 barley – 250 g;
barley – 250 g;- sugar or honey - 2 tbsp. l.;
- raisins – 50 g;
- water – 6 l.
Cooking steps:
- The barley is washed several times until the water is clear, and any floating debris is removed. Pure barley is poured into a three-liter jar.
- Add a handful of unwashed raisins.
- Add 1 tbsp. l. Sahara.
- Pour cold boiled water over the ingredients and stir until the sugar dissolves.
- The jar is closed with damp two-layer gauze, which is pressed to the edges of the jar with an elastic band, and left in a warm place for a day.
- The liquid is drained, the remainder is poured back into 3 liters of water, sugar is dissolved in it and left in a warm place until ready.
Kvass from barley is prepared on average 3-5 days. Store it in the refrigerator and, if desired, add honey, mint, grated berries and fruits.
It can be useful:
Barley vodka
Many people know this drink under the more plausible name “whiskey.”. But in essence, whiskey is the vodka made from barley that was produced in England. At home, unfortunately, it is impossible to observe all the subtleties of the technology, but the effect of long aging of barley vodka in an oak barrel can be skillfully imitated.
 Ingredients:
Ingredients:
- barley moonshine 45% – 3 l;
- oak bark - 3 tbsp. l.;
- charcoal – 50 g;
- dried apricots or prunes – 6-8 pcs.
Cooking steps:
- The coal is ground into fine powder. Oak bark is scalded with boiling water.
- Oak bark, coal and dried fruits are poured into the jar. Then pour in half the volume of moonshine and mix.
- Add the remaining moonshine. The jar is not filled to the neck, leaving empty space.
- The jar is tightly closed with a lid and left to infuse for two weeks in a dark, cool place.
- The finished product is filtered and poured into containers for storage.
Problems in the production of moonshine and ways to solve them
Let's look at the difficulties moonshiners face and provide instructions on how to deal with them.
Moonshine smells like acetone
Acetone is a dangerous toxin for the body. Consuming an alcoholic product with its participation can lead to acute intoxication and irreversible damage to the stomach and liver. Acetone begins to release into the distillate if the mash is peroxided.
Solutions:
- Follow the mash infusion mode. Do not distill old spoiled mash.
- Increase the volume of separated “heads” and “tails”. Do not collect the “body” until the moonshine flow ceases to have an acetone smell.
- If moonshine has already been obtained, clean it with activated carbon and re-distill it. Observe the temperature regime for re-distillation.

Persistent unpleasant odor of moonshine
This is a sign of the presence of a large amount of fusel oils in the finished product.. They are a mixture of oily volatile products that negatively affect the liver and gastrointestinal tract.
Solutions:
- The distillate is purified using potassium permanganate. 2-3 g of powder are dissolved in 3 liters of moonshine. When potassium permanganate precipitates, shake the jar, close the lid and heat for 15 minutes in a water bath at +50-70°C, then filter.
- Cleaning with baking soda. Dissolve 10 g of soda in 1 liter of moonshine and leave in a dark place for 12 hours. The purified moonshine is filtered and the precipitate is drained.
- Cleaning with activated carbon. The coal is crushed, poured into a container with moonshine, mixed and infused in a dark place for 12-24 hours.The purified product is filtered.
After all the cleaning methods we have tried, moonshine still has an unpleasant smell and taste.
Some harmful volatile components remain in moonshine after traditional purification methods. This problem occurs if the mash was infused in metal or plastic containers of poor quality. Then the distillation may contain formaldehyde, methyl, isopropyl, butyl alcohols, esters and ethers of organic acids and other substances hazardous to health.

Another danger – if barley treated with chemicals was used, the moonshine will contain oxidized organic nitrates, which can cause liver failure when consumed even in small doses.
Solutions:
- Discard the product. Don't risk your health. Prepare a new batch of moonshine from high-quality raw materials, following the technology.
- If you still regret the effort spent and you are a risky person, the only way to save the product is to drive it through a rectifier column. Multi-stage filtration in this device will help get rid of toxic substances. Moonshine is passed through a rectifier once, producing alcohol with a strength of up to 96%. It can be diluted or used to make tinctures.
Conclusion
Moonshine is a drink that requires special equipment and skills to prepare. To successfully produce pure and safe alcohol, follow the recipe proportions and choose good quality raw materials.
Do not overcook the malt and mash so that the raw materials for distillation do not deteriorate. Distill the distillate twice to get rid of ballast substances. If you detect an unpleasant odor or taste, clean the distillate using one of the suggested methods.