Sweet gooseberry variety with dark red berries Hinnonmaki Red
Hinnonmaki Red is one of the varieties of the Hinnonmaki gooseberry variety, which has many positive characteristics: drought and frost resistance, large fruit and a pleasant taste of berries. We will tell you in detail about how to grow this variety so that the bushes develop well and bear fruit abundantly.
Features of the variety
This is a mid-early ripening gooseberry variety. The bushes bear fruit within a month, starting in mid-summer. Productivity – 7-8 kg per bush.
The first picked, not fully ripe berries are stored at 0°C for up to 40-45 days.; ripe, filled with a bright red color and gaining juiciness and sugar content - 3-4 days.
History of origin and distribution
Gooseberry variety Hinnonmaki bred by Finnish breeders in the 80s of the XX century. The goal of the scientists was to obtain a fundamentally new, productive, frost-, drought- and disease-resistant variety of crop.
Based on the resulting variety, breeders created fruit bushes with colorful berries. One of them is Hinnonmaki Red gooseberry (Hinnonmaki Rot, Hinnonmaki Rod).
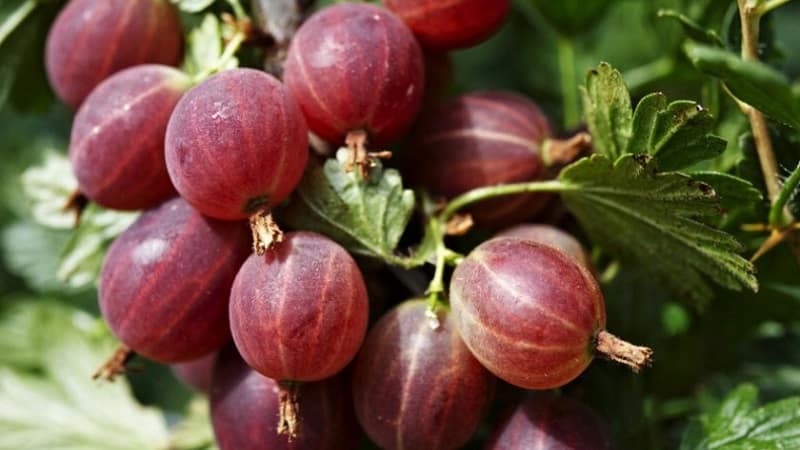

Characteristics and description of bushes
Bushes are fast-growing, medium-branched, up to 1.8 m high with strong erect shoots covered with gray or gray-brown exfoliating bark. Branches and shoots are strewn with short needle-like thorns.
Medium sized leaf blades, three- or five-lobed, colored dull green.
During flowering in leaf axils, located on the upper sections of the stems, a few racemose inflorescences appear, consisting of two or three buds.
Temperature resistance
Frost-resistant variety – bushes tolerate drops in air temperature to -30...-34°C without damage.
Moisture and drought resistance
Thanks to a powerful and deep root system the plant tolerates heat well and can go without watering for up to 30 days.
Hinnonmaki Red is not moisture resistant – When overwatered, plant roots begin to rot.
Resistance to diseases and pests
The variety is resistant to septoria and powdery mildew. With improper care and unfavorable conditions, it can be affected by anthracnose, white spot, gray rot, goblet rust, and root canker.
Pests attack bushes spider mites, moths, sawflies, currant gall midges, aphids.
Characteristics and description of fruits
The berries are oval, almost round in shape, large (weighing 7-7.5 g), are covered with a thin but durable skin, which, after the fruit ripens, acquires a dark red color with stripes.
The pulp is transparent, characterized by a sweet taste. But in combination with the sourish skin, the Hinnonmaki Red fruits do not seem cloying.
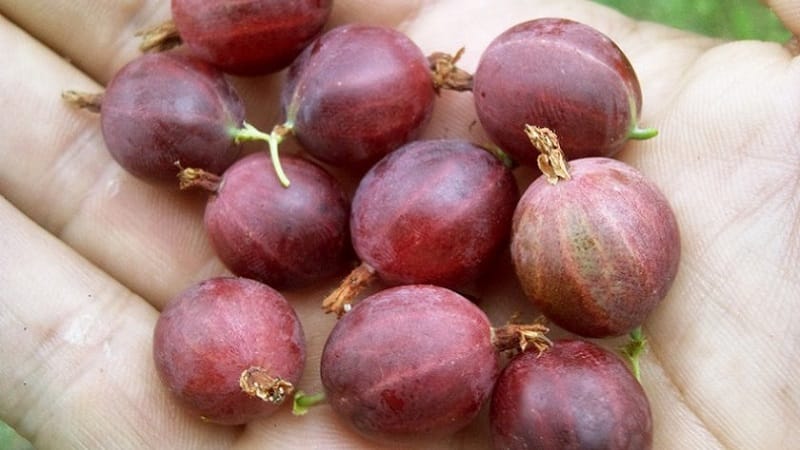

Application area
The berries are consumed fresh and used for cooking desserts, compotes, jelly, marmalade, preserves, jams and even homemade wine.
Other gooseberry varieties:
Advantages and disadvantages compared to other varieties and hybrids
The main advantages of the variety:
- rapid growth of bushes;
- high productivity;
- large fruit;
- pleasant taste and aroma of berries;
- drought and frost resistance;
- immunity to certain diseases;
- lack of tendency to cracking of fruits;
- good keeping quality and transportability;
- possibility of mechanized harvesting.
Among the disadvantages of Hinnonmaki Red are noted the presence of multiple thorns on the stems and a tendency for ripe berries to shed.

Growing technology
In order for the seedlings to take root, begin to develop and bear fruit, it is first of all important carry out planting correctly - choose a suitable place on the site, prepare the soil and planting material - and properly care for the plants.
Optimal conditions
Bushes are planted in a well-ventilated and lit place. The variety prefers fertile, loose soil with good moisture and breathability and neutral or weak acidity. The best option is loam and sandy loam.
Reference. In the shade, the bushes develop poorly, and the crop yield decreases.
The landing site should be located on a hill, groundwater depth is at least 1 m.
When purchasing planting material, select seedlings without signs of damage stems or root system, with fibrous developed roots and at least three strong elastic shoots, which are shortened to 10 cm before planting.
For better rooting, seedlings are soaked for a day in a solution of a growth stimulator (“Kornevin”, “Heteroauxin”).
Landing dates and rules
Planting is carried out in the spring, at the end of March, or in autumn, from the second ten days of September until mid-October, so that the bushes have time to take root and take root before frost.
Landing rules:
 Two weeks before planting, dig planting holes in the area with a diameter of 50 cm and a depth of 20-25 cm at a distance of 1.5-2 m from each other.
Two weeks before planting, dig planting holes in the area with a diameter of 50 cm and a depth of 20-25 cm at a distance of 1.5-2 m from each other.- Pour into each nutrient mixture (half of the dug up soil, a bucket of manure, 300 g of ash and 200 g of mineral fertilizers).
- Form a small hill in the hole, place a seedling on it and spread its roots along the slopes.
- Fill the voids with soil so that the root collar is buried a maximum of 5 cm.
- Compact and water the soil, add more soil, form a hole around the bush and water again, spending 5 liters of water per seedling.
- Mulch the soil with peat.
Further care
The bushes are watered for the first time 10-15 days after planting., then once a week at the rate of 8 liters of water per bush.
Reference. The optimal method of watering is drip.
After watering, the soil is loosened to improve aeration and moisture permeability.. At the same time, weeding is carried out.
Provided that the seedlings are planted in nutritious soil and fertilizers are added to the holes They begin to feed the plants after two years according to the following scheme:
- March-April - compost, rotted manure (5-6 kg per bush) and spraying with a solution of mineral fertilizers (20 g of potassium nitrate, ammonium nitrate and superphosphate per bucket of water) at the rate of 1-1.5 liters per plant;
- May - mineral fertilizers (for example, Ammophos, Kemira);
- end of June - 1 liter of slurry (a bucket of manure, a quarter of a bucket of compost per 100 liters of water), diluted in a bucket of water;
- autumn - 5-6 kg of compost or humus and a mixture of 1 liter of wood ash, 120 g of simple superphosphate and 100 g of potassium sulfate per bush.
Pruning is carried out twice a year. In early spring, damaged, poorly overwintered branches are removed, and weak shoots are shortened by 10-15 cm. In autumn, after harvesting, shoots older than 6 years are pruned, leaving a maximum of 15 strong and healthy stems on the bush.
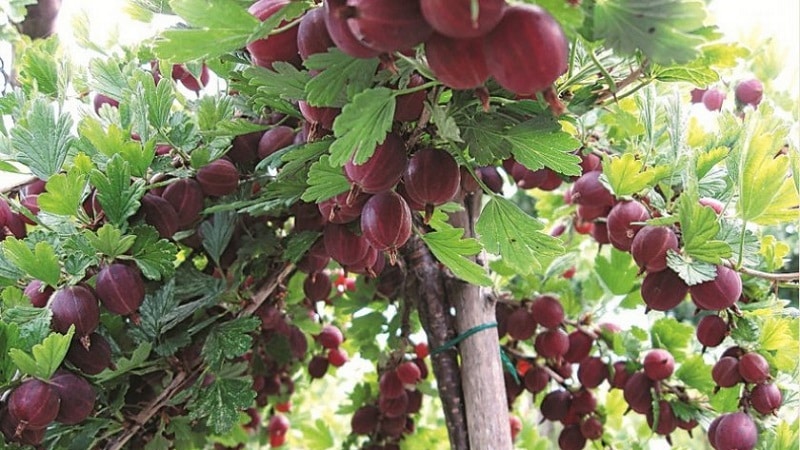

So that during fruiting the branches do not sink to the ground, and it is easier to harvest, they use trellis support. To do this, wooden stakes are driven along the edges of the bushes, between which a wire is pulled in three strips so that the bottom is 0.5 m above the ground, the middle is 0.8 m, the top is 1.2-1.3 m.
For prevention diseases and pests promptly remove damaged and dry stems, weed and loosen the soil, treat the bushes with insecticidal and fungicidal preparations, using iron sulfate or “Profilaktin” before the buds swell and “Fitoverm” or “Fitosporin” during budding.
Possible problems, diseases, pests
Diseases and pests that affect Hinnonmaki Red are described in the table:
| Disease, pest | Signs | Treatment |
| Anthracnose | Dark brown spots form on the leaves, gradually the leaf blades darken and fall off. | Treating bushes with fungicidal preparations, for example, Karbofos or Topaz. |
| White spot | Light spots with dark edges and dots with spores in the middle appear on the leaves. In the middle of the growing season, the leaves dry out, crumble and fall off. | |
| Gray rot | A light coating appears on the leaves and shoots. | |
| glass-shaped rust | Bright orange swellings appear on the leaves and shoots, and the shoots become bent. | |
| Root cancer | Growths form on the rhizome and the plant dies. | There is no treatment. Affected bushes are dug up and burned. |
| Spider mite | The inside of the leaves becomes covered with a thin web, the leaves dry out and fall off. | Insects are fought with the help of drugs “Fufanon”, “Aktara”, “Karbofos”, “Iskra”, “Gardona”, “Fitoverm”. |
| Ognevka | The bushes lag behind in development and lose their ovaries. | |
| Sawfly | The ovaries are damaged by insects, the berries and seeds are damaged by their larvae. | |
| Currant gall midge | Branches, leaves and ovaries dry up on the bushes. | |
| Aphid | The internodes are noticeably deformed. |
Wintering
In autumn, after pruning bushes, the soil is weeded, loosened and cleared of plant debris and other garbage. Plants are watered abundantly (3-4 buckets per bush), and to protect against pests they are sprayed with Bordeaux mixture. The ground is mulched with peat or humus.
Due to their frost resistance, plants do not need to be covered for the winter. – a layer of mulch and a sprinkling of snow is enough for them.
Reproduction
Bushes are propagated by cuttings or layering. In the first case, at the end of summer, a healthy branch is selected and cut into pieces no longer than 15 cm. The resulting cuttings are soaked for a day in a solution of a growth stimulator, then planted in moist and loose soil and germinated under a film at a temperature of +28...+30°C . They are planted in a permanent place in the spring.
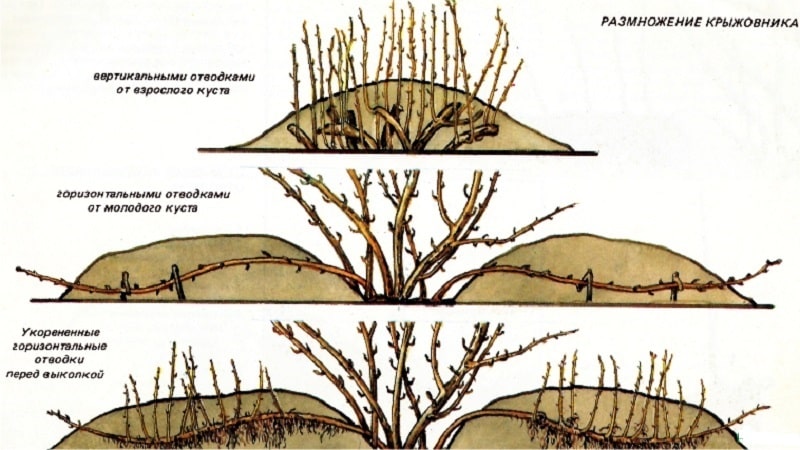
For propagation by layering in early spring, choose strong side stems, bend them to the ground, lay them in dug shallow (up to 10 cm) trenches and fix them. After the young growth appears, the trenches are covered with soil. After rooting, the cuttings are separated from the mother bush and replanted.
Features of growing varieties depending on the region
The variety tolerates both heat and drought, as well as frost., therefore it is successfully grown in all regions, without making significant adjustments to the rules of planting and caring for bushes.
Pollinator varieties
Hinnonmaki Red is a self-fertile variety, that is, pollinated by its own pollen.. At the same time, planting different varieties of crops nearby helps increase productivity.
Reference. For better pollination, gooseberries are treated with “Boron Chelate” and “Maxicrop”.
Reviews from summer residents
Summer residents are satisfied with Hinnonmaki Red gooseberries, which is confirmed by their reviews.
 Maxim, Leningrad region.: “I’ve been growing this gooseberry for 6 years now. The bushes winter well without shelter, bear fruit regularly and abundantly, the berries form large, dense, beautiful and tasty.”.
Maxim, Leningrad region.: “I’ve been growing this gooseberry for 6 years now. The bushes winter well without shelter, bear fruit regularly and abundantly, the berries form large, dense, beautiful and tasty.”.
Elena, Yelets: “I really like this variety. It is unpretentious, self-pollinating and large-fruited. The berries are beautiful and tasty. On the minus side, I would like to note that for some reason I have already failed twice to propagate the bushes with cuttings - they do not take root at all. But they reproduce well by layering.”.
Conclusion
The gooseberry variety Hinnonmaki Red consistently bears fruit with minimal care, does not require pollinating varieties, and is able to tolerate drought and frost.
The berries have a pleasant sweet and slightly sour taste and are suitable for both fresh consumption and processing.