Instructions for propagating raspberries in summer by cuttings for beginner gardeners
Propagating raspberries by cuttings in summer is a method of propagation that does not require financial or time expenditure and guarantees the preservation of the characteristics of the variety. For this, green cuttings obtained during thinning of plantings in June are used. We will tell you more about how to carry out cuttings and planting in the article.
About raspberry propagation in summer
Raspberry seedlings of new varieties cost a lot, but there is an alternative - to propagate the bush yourself. There are several options. The most popular and simplest is propagation by cuttings and suckers.
The appropriate method is chosen based on the time of year and the type of cuttings that will be used: root, green or lignified. The most popular method of growing raspberries in summer is propagation by root suckers. Unlike cuttings, offspring do not require compliance with the rules of storage, rooting and careful care at the beginning of development.
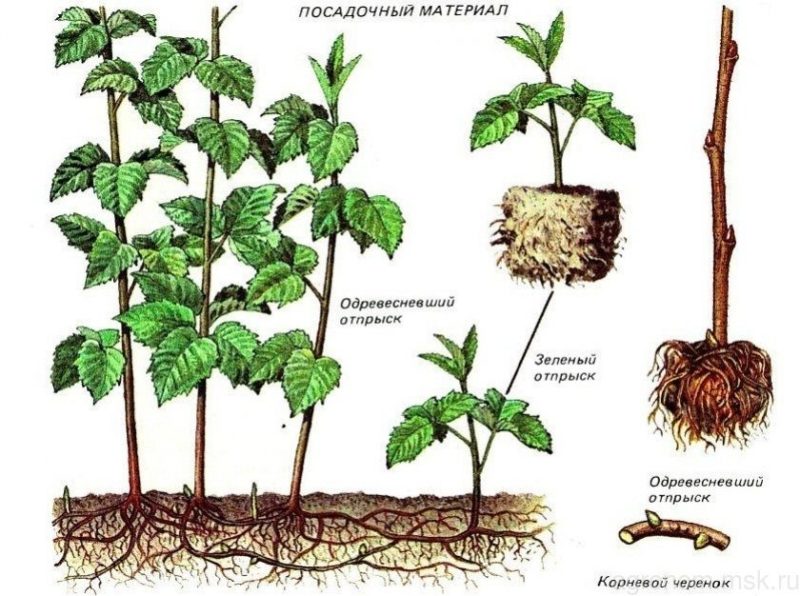
All that is required for propagation by offspring is to identify young shoots in the spring that will not be pruned during thinning of the raspberry tree. In August, these shoots with their own root system, but not yet separated from the mother bush, are dug out along with a lump of earth and planted in a new place.
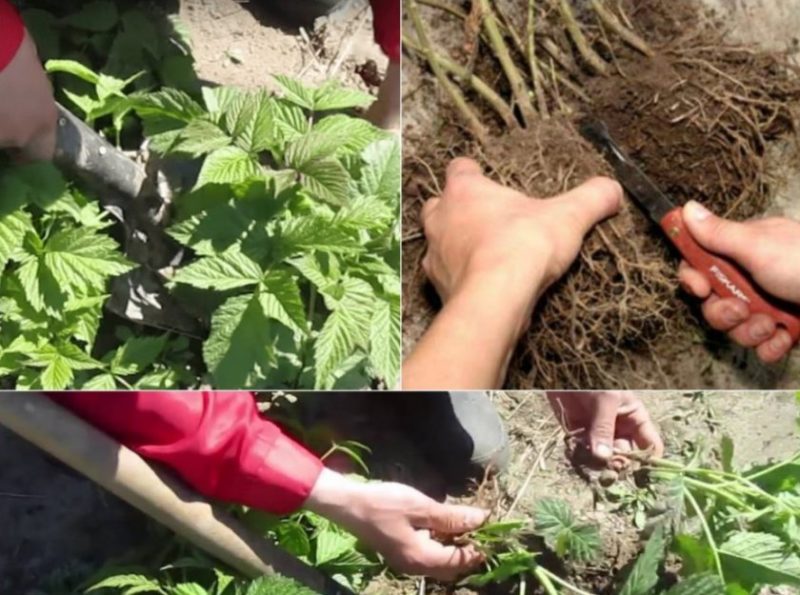
Attention! Green cuttings are cut from young shoots, which are usually removed during thinning of raspberry bushes.
The use of green cuttings is the second most popular method of propagating varietal raspberries.The procedure is carried out in summer or autumn, the main thing is to have time to plant the rooted shoots in a permanent place at least a month before the arrival of frost.
Features of summer cuttings
Experienced gardeners recommend taking into account several features of cutting raspberries in the summer. Green shoots contain less nutrients than mature shoots, so long-term storage of such planting material is impossible.
When carrying out the procedure, the balance of forces in the cutting itself and in the developing root system is taken into account. This means that it is important to help the roots grow before the strength in the cutting runs out. Otherwise, the escape will die.
Deadlines
To harvest green cuttings, young shoots that grow in large quantities next to the mother bushes are used. Harvesting begins when the shoots grow to approximately 20 cm in height and develop 2-3 leaves. As a rule, this happens at the end of spring or in the first half of June.
Work on cutting blanks is carried out in cool, rainy weather.
Site requirements

Successful propagation of raspberries by green cuttings is impossible without meeting certain requirements for the rooting location of the workpieces:
- high air humidity - up to 90%;
- constant ambient temperature - +25...+30˚C;
- light and moisture-intensive substrate;
- protection from direct sunlight.
Such a microclimate is created in protected soil conditions: in a greenhouse, hotbed or schoolhouse. Propagation by green cuttings produces many plant specimens and allows you to plant an entire raspberry plantation of your favorite variety.
Soil preparation
To root cuttings, use fertile soil mixed with organic and mineral fertilizers.Depending on the fertility of the land, from 5 to 20 kg of organic fertilizers, 100 g of superphosphate, and 20 g of potassium salt are applied per 1 linear meter. If the soil is acidic, add 100–150 g of lime.
Selection and preparation of cuttings
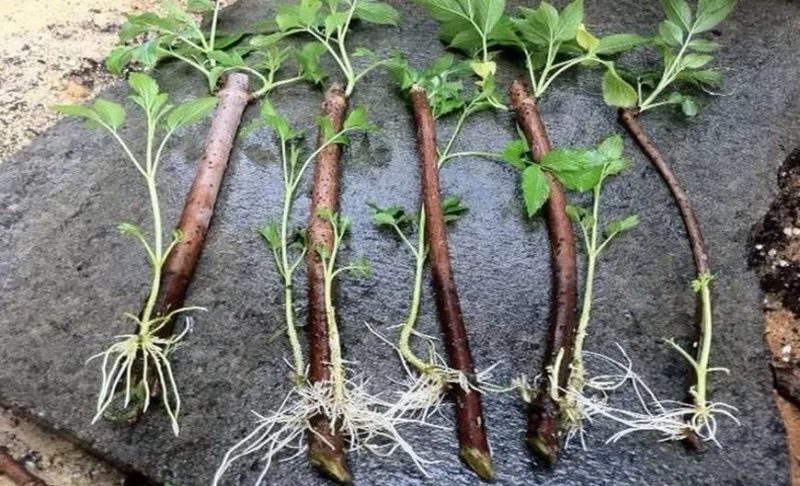

For propagation in June, blanks are cut from young shoots that have not yet had time to harden. This material has a stronger ability to form roots than shoots with a woody structure.
Cuttings are cut from green shoots with pruning shears near the ground or with a slight depth of 1 cm. Further cutting is carried out on a hard board with a sharp tool so as not to squeeze the plant tissue.
The lower cut is made oblique to increase the absorption surface, 1 cm below the kidney, the upper cut is made straight, directly above the kidney. To reduce the area of evaporation, the leaves are cut by half (preferably on the eve of the procedure to reduce moisture loss). The tip of the shoot is shortened so that the total length of the cutting is 8–12 cm.
Important! When preparing cuttings, special attention is paid to preserving moisture in the tissues: the success of the entire procedure depends on this. The preparations are cut in the early morning, when plant tissues are saturated with moisture. At all stages of working with cuttings, do not allow them to dry out; cut shoots are immediately placed in a container with water and placed in the shade. The duration of storage of the finished material in the refrigerator is no more than 2 days.
After cutting, the lower part of all workpieces is placed in a nutrient aqueous solution with a root stimulator. Root regeneration is regulated by growth substances - auxins, carbohydrates and nitrogenous substances. Under the influence of growth regulators, the number of rooted cuttings increases and the quality of finished seedlings improves.
Effective root formation stimulators include:
- “Heteroauxin” (β-indoleacetic acid, IAA) - from 50 to 200 mg/l;
- “Kornevin” (indolylbutyric acid, IBA) - 1 g/l of water;
- “Zircon” (a mixture of hydroxycinnamic acids) - 1 ml/l of water.
When preparing a nutrient solution, the growth-stimulating substance is first dissolved in a small amount of alcohol and then added to water. This way the stimulator will work more effectively. The treatment is carried out in the dark, at a temperature of +18…+22°C. The cuttings are immersed in the solution so that no leaves fall into it.
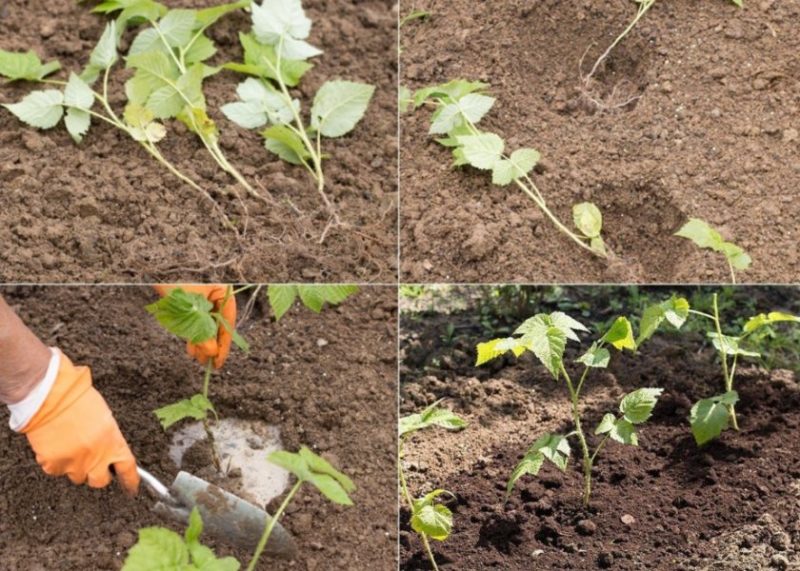
After 12–15 hours, the cuttings are removed from the solution and planted in a prepared place in a greenhouse, greenhouse or garden bed, under a film cover.
Advice! It is convenient to combine green cuttings with thinning of bushes. Strong and healthy removed shoots are not thrown away, but used for rooting.
If possible, a fogging installation is used at the landing site. If it is not there, regular watering and spraying will help create the required level of humidity.
Other rooting methods
Cuttings are rooted not only in the ground. Other methods include germination in water, substrate, and even potatoes.
In water
This is one of the simplest methods that does not require special skills or additional expenses. The prepared cuttings are placed in a container with water (2-3 pieces per 200 ml of liquid) and wait for the roots to appear.
The chances of successful rooting increase if the following rules are observed:

- do not change the water in the glass, but add it if necessary (changing water is stressful for plants);
- The cuttings are placed in water at room temperature;
- For rooting, use opaque containers: in dark glasses, roots form faster;
- Add activated carbon to the water (2 tablets per 1 tbsp.) or phosphorus-potassium fertilizers (according to the instructions for the drug).
Compliance with these rules accelerates the formation of roots and prevents rotting of the lower part of the cuttings.
In the substrate
This method involves the use of breathable materials, since oxygen is required for root formation. Suitable substrates are mixtures of:
- vermiculite and river sand;
- perlite, earth, peat and sand;
- peat, vermiculite, perlite and sand.
All ingredients are mixed in 1:1 proportions, poured into a box of a suitable size and moistened. Cuttings are stuck into the prepared substrate and wait for new leaves to appear.
In potatoes
Raw potatoes are a natural source of root formation stimulants, so they are successfully used for rooting raspberry cuttings. For each shoot, take 1 large potato with cut out eyes. They stick a piece of stem into the tuber with 1-2 buds, and the vegetable itself is buried in the ground and watered. Cover everything with a plastic bottle.
Cuttings planted in this way are regularly watered and ventilated, removing the bottles. If everything is done correctly, the first roots will appear within a week.
Cuttings with green shoots
Using green cuttings, not only raspberries are propagated, but also other shrubs or trees. The ability to root shoots depends on the type and variety of the plant.
This method of propagation is due to the ability of stem cuttings to form adventitious roots. The easiest ways to root are vines (clematis, grapes, actinidia, hydrangea) and shrubs (mock oranges, lilacs, privet, raspberries, honeysuckle).
Cuttings with woody shoots
Lignified cuttings for propagating raspberries are harvested in the fall and planted in the spring. Step-by-step instructions for growing raspberries this way:
- After the first frost, several annual woody shoots are divided into cuttings 20–30 cm long. As with propagation by green shoots, one cut is made at an angle, and the second is made straight.
- The blanks are wrapped in paper and placed in the cellar, sprinkled with moistened peat or sand.
- In spring, the lower cut of the cuttings is renewed and placed in a solution with a root formation stimulator for 10–15 hours.
- Place the preparations in a container with sweetened water (1 teaspoon of sugar per 1 liter of water), cover with a plastic bag and place in a warm place.
After about a month, roots appear, then the plants are planted in a greenhouse.
Landing
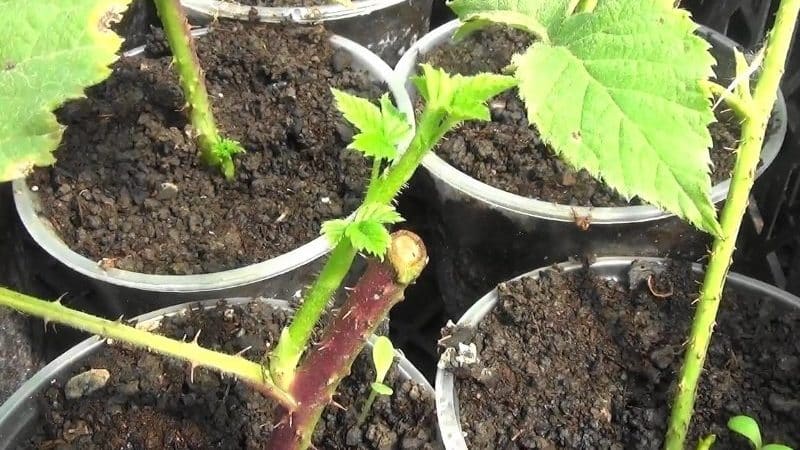

The finished material is planted in pre-prepared distribution beds in a greenhouse or hotbed. It is useful to pre-water the soil with one of the preparations for suppressing pathogenic microflora (for example, “Shining”, “Baikal”, “Vozrozhdenie”, “Fitosporin”). These products are also used in the care of landings, adding to water for irrigation once every 1-2 weeks.
The cuttings are planted at a distance of 5–7 cm from each other to a depth of 1.5–2 cm. For rooting raspberries, the optimal temperature is +25…+26˚C and humidity 80–90%.
In industrial environments, humidity is maintained using fogging units that spray moisture at certain intervals. At home, cuttings are sprayed with water several times a day. It is important to inspect them regularly, removing fallen leaves and dead specimens.
This is interesting:
Which raspberry varieties are the most productive?
Further care

Caring for green cuttings involves regular ventilation of the greenhouse, watering, creating high air humidity, loosening the soil and removing weeds.
Ventilation of the shelter begins by slightly opening the film for 1-2 hours. Gradually increase the time, while simultaneously reducing the number of sprays. After hardening the rooted cuttings, the film is removed. To maintain soil and air moisture, daily watering and spraying are carried out. After 4 weeks, the plants are fed with liquid complex mineral fertilizer.
With proper care, the first green shoots appear about a month after planting. Shoots begin to grow and the root system branches out. At this stage, the film cover is completely removed during the day, leaving it only at night. The frequency of watering is reduced.
If there are few cuttings, they are rooted in boxes, pouring about 10 cm of earth and 2 cm of river sand on the bottom. 1-3 shoots can be rooted in a pot, covered with a transparent plastic bottle with the bottom cut off. Ventilate such a structure by removing the lid from the neck.
On a note! It is convenient to place pots or boxes with cuttings in a cellar or basement for the winter, and in the spring to plant the shoots in a permanent place.
2-3 months after planting, the grown and rooted shoots are transplanted to a permanent site in fertilized fertile soil or left in place, covered with dry leaves for the winter, and replanted in the spring.
The nuances of propagating remontant raspberries

Remontant varieties They form shoots differently, so not all traditional methods of propagation are applicable in this case. One of the characteristic features of remontant varieties is the weak formation of shoots, especially in the first years after planting. A small number of green shoots and root shoots makes it easier to care for raspberries, but complicates its cultivation.
In this case, carefully remove the central part of the bush. In a 2-3 year old plant, in the fall or early spring, carefully cut out the central area with a diameter of up to 15 cm. In response to this pruning raspberries begin to grow root mass and form green shoots.
This technique allows you to prepare a lot of high-quality green cuttings for growing seedlings in the spring, and a lot of root cuttings in the fall. Certain varieties of remontant raspberries, with good care, produce a sufficient number of replacement shoots. When removing excess growth in early spring, it is used as green cuttings.
How to propagate yellow raspberries
Most varieties of yellow raspberries belong to repairable. These varieties have high yields, large berries, and increased resistance to diseases and pests. The agricultural technology for propagating yellow raspberries is similar to growing traditional red varieties.
Propagation by root cuttings is considered the most convenient for remontant varieties. Planting material from the mother bush is dug up in the fall, when the plants are dormant.
Root sections are prepared at least 2 cm thick and 8–12 cm long. Root cuttings are planted in grooves 6–10 cm deep, at a distance of 15–20 cm from each other. The grooves are filled with fertile soil, watered, mulched and covered with tops or spruce branches to protect them from freezing.
In the spring, the shelter is removed along with the snow melting, and the planting site is covered with an air-permeable protective film (until green shoots appear).Further care for raspberries does not differ from usual and includes watering, loosening the soil, killing weeds, applying fertilizers, and protecting them from diseases and pests.
Advice from experienced gardeners
In order for the cuttings to take root faster after planting, adhere to the following recommendations:
- the material is planted in soil fertilized with mineral and organic agents;
- rooted cuttings are covered for the winter with spruce branches or special protective materials;
- Raspberries are planted in a permanent place in well-lit areas with fertile soil and without stagnant water;
- when propagated by green cuttings, they are pre-treated with root formation stimulants;
- after planting, young seedlings are regularly fed with mineral and organic products;
- To prepare cuttings, use only disinfected sharp instruments to prevent tissue loosening and creases in the cut areas.
With proper care, the cuttings will quickly take root in a new place, and the next year after planting they will begin to bear fruit.
Read also:
Conclusion
Raspberries are a biennial crop loved by many gardeners. Fragrant berries are tasty and healthy. Therefore, the bush grows in almost every summer cottage or garden.
It happens that seedlings of the variety you like are not sold on the market or cost a lot. In this case, seedlings are harvested independently from green shoots. Knowing how to cut raspberries, you can grow an entire plantation with only one bush. The main thing is to provide the cuttings with optimal conditions for survival and rapid root growth.