Instructions for novice gardeners: how to propagate black currants
Black currants are propagated vegetatively. Even a novice gardener can cope with this task if he follows the basic rules for preparing planting material. The most common way is cuttings lignified shoots and the formation of layering based on the mother bush.
Green cuttings can also be taken, but they must be grown in greenhouses with high humidity. In this article we will tell you in detail how to propagate black currants, take cuttings, what propagation by layering is, when and under what conditions to carry out the procedure.
How to propagate black currants
Black currants are propagated by the vegetative method: lignified or green cuttings, layering, rooting two-year-old branches from the mother bush.
As for timing, cuttings can be harvested throughout the year, except winter. Each season has its own rules. In summer, the green cutting method is used; in spring and autumn, lignified shoots are cut. In any case, the material is taken from the mother bush.
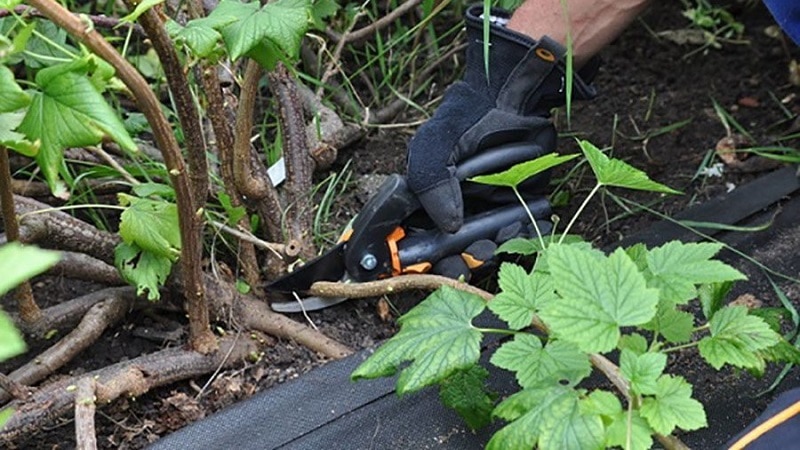

Summer harvesting occurs in mid-June - the first ten days of July. During this period, currants actively grow and gain green mass. For green cuttings, developed annual shoots are chosen.
Many gardeners prefer to combine cuttings with routine spring pruning. The material is prepared from lignified 1-2 year old shoots with a diameter of at least 5 mm. Rods 15-20 cm long are cut from the middle.
Lignified cuttings, cut in the fall, are stored in a cool place: a snowdrift, cellar, refrigerator. They are first dipped in wax or liquid paraffin, then placed in a tight plastic bag and stored until spring, periodically unrolling the film to check for mold on the cuttings.
What does that require
To propagate currants you need to stock up on:
- a shovel for digging earth;
- weed rake;
- a hoe for loosening the soil;
- pruning shears for cutting cuttings.
How to properly propagate black currants in different ways
Cuttings from green and woody shoots, layering and dividing the bush have their own characteristics, if followed, you can grow full-fledged young blackcurrant bushes.
Green cuttings
Propagation by green cuttings is a complex method that involves further planting the material in a greenhouse or greenhouse with fogging. Cuttings 5-10 cm long are prepared from strong, developed shoots. On each cutting 5-10 cm long, 2 green leaves are kept.
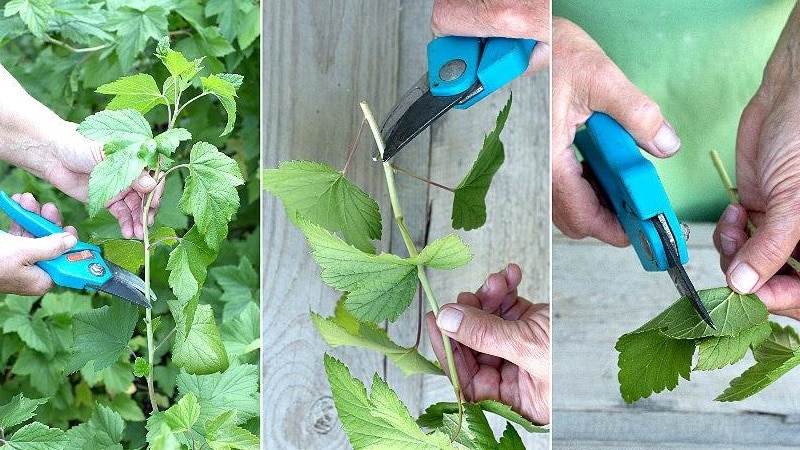

The lower cut is made at an angle under one knot, and the upper cut is made straight under the next knot. The cuttings are placed in a growth stimulator for 12-14 hours, then rooted in the prepared soil. It is important to maintain high humidity and temperature in the range of +18...+24°C.
Black currants can be rooted in winter so that by spring you will already have seedlings for planting. The material is placed in water at the end of winter. After 10 days, roots will begin to form on the seedlings. As soon as the longest one reaches 10 mm, the cuttings are transplanted into containers with drainage holes or into thick black bags, with holes punctured at the bottom to allow water to drain out.
The cuttings are watered abundantly and often - every 2-3 days. The soil should have the consistency of sour cream.10 days after landing frequency of watering reduced to 2 times a week. The cuttings are kept in such conditions until the first days of May, then they are removed from the containers and planted 10-15 cm deeper than they were planted in the container.
Lignified cuttings
Propagation by lignified cuttings produces weaker seedlings, but has an undeniable advantage: this method can produce new varieties.
Cuttings are planted in autumn or early spring. In October, cuttings are prepared for spring planting. Their length should be 18-20 cm. It is important to catch them before frosts, which can destroy the buds. The material is cut from one-year-old shoots or 2-3-year-old branches. The best cuttings are taken from the middle part of the shoot. The optimal cutting thickness is 8-10 mm.
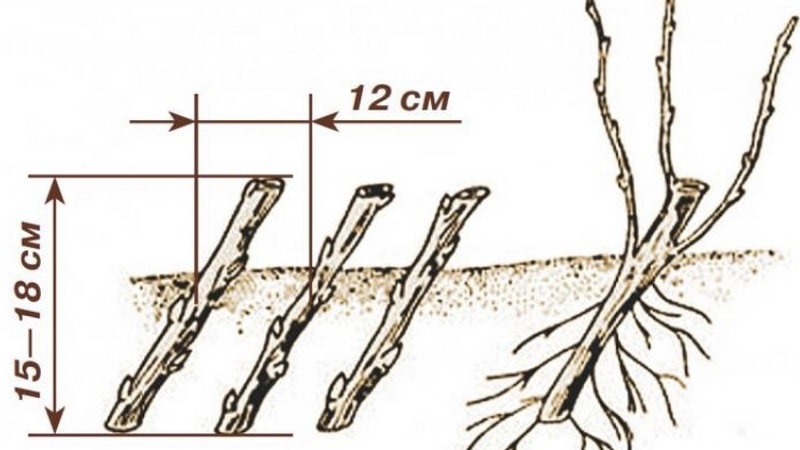
After cutting, both ends are dipped in liquid paraffin or melted garden pitch to retain moisture inside. Then the planting material is tied into bundles, wrapped in damp paper and polyethylene, and sent for storage in a snowdrift or refrigerator.
In spring, cuttings are planted on prepared beds every 15 cm, maintaining a row spacing of 20 cm.
Before planting, make an oblique bottom cut with a sharp knife and place the cuttings on the bed at an angle of 45°. 1-2 buds are left on the surface. The soil is watered abundantly, mulched with humus, peat or sawdust. Metal arcs up to 0.5 m high are installed above the bed and covered with polyethylene. After the first leaves appear, the film is removed and watered moderately every 3-4 days.
At the rooting stage, the cuttings are very weak, so they need to be watered regularly: even a slight moisture deficit is detrimental to the plants.
In summer, the ridges are weeded and moderate humidity is maintained.From the moment young shoots form from the buds, organic fertilizer is added: 5 liters of mullein are poured with 5 buckets of water, 500 g of ash and 10 g of superphosphate are added, then left for 48 hours. This amount is enough for a 5 m² plot. By autumn, young bushes grow with 1-2 shoots up to 0.5 m long.
Reference. Strong seedlings are transplanted to a permanent place in the fall, while weak ones are left to ripen and transplanted a year later.
By layering
The easiest way to propagate black currants is by layering. In a year you will get strong seedlings with a strong and healthy root system.
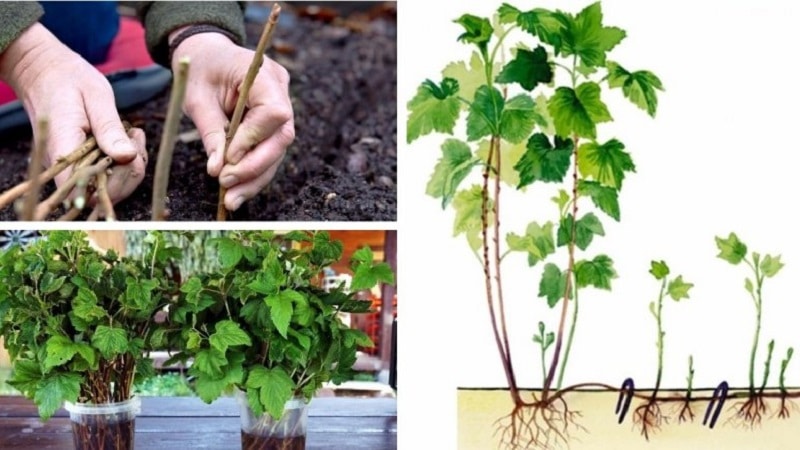

In early spring, select a two-year-old branch growing at an angle and bend it to the ground. Under the shoot, dig a hole 10 cm deep and tilt it towards the ground so that the middle part is in the recess, and the top 30 cm long looks out of the hole. Secure the branch in the desired position with a thick wire hook. Fill the hole with soil and water regularly throughout the summer.
By autumn, the cuttings will take root, and you will have a full-fledged seedling. Cut off the cuttings and replant them in the chosen location.
Dividing the bush
With this method of propagation, the mother bush is divided into parts. The method is used in late autumn, after the end of the growing season. To do this, choose a new place for planting, dig holes 60-70 cm deep, fill them with a mixture of humus, ash, turf and spill with clean water.
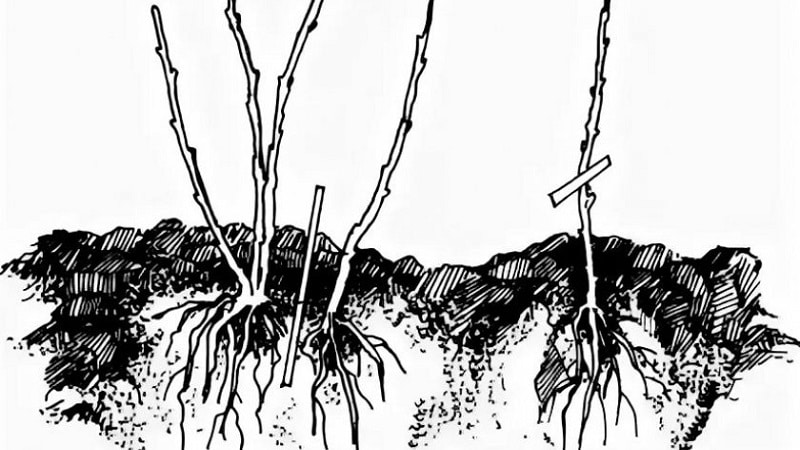
Carefully dig up the bush, trying not to damage the roots, inspect it and select an area that can be cut off with a shovel. As a result, one-year-old non-lignified shoots should remain. They are shortened to 25 cm. Old branches are removed with pruning shears.The bush is divided into 2-3 parts so that each of them has its own strong roots and shoots, then they are planted in a permanent place, watered and hilled.
Soil preparation and planting
Planting black currants is best done in damp, low-lying areas, protected from gusty winds and scorching sun. The shrub is planted along fences at a distance of 1.5 m, as well as along the boundaries of the site.
The selected location is plowed and leveled so that there are no depressions or sudden changes in ground level. For every 1 m², add 3 kg of humus, 150 g of superphosphate, 30 g of potassium sulfate or wood ash. The optimal soil acidity is 4-5.5 pH. If necessary, slaked lime is added to the digging - 0.3-0.8 kg/m².
Planting density The number of currants in the garden depends on the fertility of the soil, lighting, the method of forming the bush, as well as the variety. Currants with a spreading crown are planted sparsely, while those with a compact, straight crown are planted more densely. The optimal distance between bushes is 1-1.5 m. When planted densely, the yield decreases.
Autumn planting is carried out in the first half of October. In 2-3 weeks, holes are dug in the area 35-40 cm deep and 60 cm in diameter. The same rules are followed when planting in spring. The soil should settle well.
The top layer of soil is thrown aside, and the bottom layer is mixed with fertilizers. 10 kg of compost, 150 g of superphosphate, 30 g of wood ash are added to each pit. It is important that mineral fertilizers do not touch the roots when planting. This will help prevent burns to plant tissue.
When groundwater is close to the ground (above 800 cm), planting holes are not dug. Instead, the soil is treated and mixed with fertilizers, and an earthen embankment 15-20 cm high is organized at the planting site.
Seedlings with a developed root system take root best - with 3-5 skeletal lignified roots 15-20 cm long, with yellowed bark and a formed fibrous system. The above-ground part should consist of 1-2 shoots 30 cm long.
During transportation, seedlings are wrapped in damp cloth and polyethylene. Before planting, damaged roots or above-ground shoots are pruned. To retain moisture, the roots are dipped in a clay mash or temporarily covered with soil.
Reference. After planting, the tree trunk circle is watered abundantly with water and mulched with peat or sawdust.
Caring for currants after the procedure
In the first year after planting, it is important to provide the seedlings with ideal conditions for growth and development. Proper tillage, watering, regular fertilization, pruning, prevention diseases and pests will help you achieve the desired result.

Black currant loves moisture and needs frequent loosening and weeding. The optimal frequency of cleaning the tree trunk circle is once every 3 weeks. The root system is concentrated in the upper layers of the soil, so loosening is carried out carefully, no deeper than 8 cm. In the inter-row spaces, the soil is loosened to a depth of 10-12 cm.
Mulching retains moisture in the soil well and eliminates the need for gardeners to frequently loosen the area. Instead of peat and sawdust, you can use synthetic materials (black film, agrofibre). In autumn, the covering is removed to improve soil aeration. fertilize and carry out agricultural work before wintering.
In the fall, heavy loam is plowed shallowly and clumps are left under the bushes for the winter to retain moisture. The areas between the bushes and rows are dug up to a depth of 10 cm. The loose soil is plowed with a garden fork to a depth of 5-8 cm.
If the bushes were planted in fertile soil in the fall, an additional portion is not added in the spring. If planting was done in the spring, 2 weeks after the snow melts, the currants are fed with urea (15 g per 1 m²) and immediately watered with clean, settled water. At the end of the third year after planting in the fall, 50 g of superphosphate, 10 g of potassium sulfate and 5 kg of humus are added to the soil for each bush.
Starting from the fourth year, currants are fed with nitrogen fertilizers every year: 2/3 doses in the spring and 1/2 immediately after flowering. For every 1 m², add 20-25 g of urea. Organic, potassium-phosphorus fertilizers on loam are applied once every 3 years in the fall or spring in the following proportions: 16 kg of organic matter, 120 g of superphosphate, and 30 g of potassium sulfate. On sandy loam, sandy and peaty soils, these fertilizers are applied every year in the spring, taking into account the norms for 3-year-old bushes.
On loamy fertile soils, fertilizing is limited to autumn or spring. On poor loams, sands and sandy loams, additional liquid fertilizers are added, which should preferably be combined with irrigation. Instead of organic fertilizers, you can use mineral ones, for example, Riga mixture: 30 g per 10 liters of water, consumption - 10-20 liters per bush.
In June, foliar feeding is carried out: 2 g of copper sulfate, 2–2.5 g of boric acid, 5-10 g of manganese sulfate, 2-3 g of zinc sulfate, 2-3 g of ammonium molybdate per 10 liters of water. Consumption - 10 liters for each bush. Fertilizers are poured into the furrows around the bushes to a depth of 10 cm. After watering, the grooves are mulched with peat.
Tips and tricks from experienced gardeners
Pay special attention to watering currants during the period of green mass growth, ovary formation, berry filling and after harvesting.It is important to carry out winter watering to a depth of 40-60 cm. Water consumption per 1 m² is 30-50 l.

Plant currants with two people: one holds the seedling, the other fills the hole with soil. Plant the bush at an angle of 45°. In the future, the plant will straighten, and the roots will receive their portion of moisture and nutritional components.
Sloping planting promotes the formation of additional roots and new shoots from the buds of the root collar. When planted directly, you will get a single-stem standard bush. If your goal is compact intense cultivation scheme, plant the bushes straight.
When planting, straighten the roots and cover them with soil, gradually compacting it. Shake the seedling periodically so that the soil evenly fills the space between the roots. Deepen the root collar by 6-8 cm.
Conclusion
The best ways to propagate black currants are to take cuttings from woody shoots or form layerings and then separate them from the mother bush. In second place is the method of cutting green cuttings, but it is important to create a humid environment for them and provide a high temperature. This material is best grown in greenhouses. Dividing the bush is the least common method, since it is considered the most traumatic. It is not so easy to carefully divide a bush into parts without damaging the root system.
Further care of planting material consists of controlling humidity and applying fertilizing until planting in a new location. Next, the gardener must provide watering to the seedlings, loosen and weed the soil, and apply organic and mineral fertilizers.