When and how to propagate red currants
The propagation process of red currants is in many ways similar to the propagation of the black variety. The only difference is that red currants take root worse due to the low rate of root formation. Therefore, for its propagation, it is recommended to use the method of forming layering, as well as the method of obtaining planting material by cutting lignified or green cuttings. For more information on how to propagate red currants, read our article.
Propagation times for red currants
The timing of red currant propagation depends on the chosen method. In spring, the crop is propagated by woody shoots, and in late summer and early autumn - by green cuttings and layering.
Any of these methods requires experience and skills, since red currants take root much worse compared to black currants. To stimulate root formation, gardeners have to use Kornevin, Zircon or Epin.
To propagate currants, you need to stock up on the following tools:
- shovel for digging earth,
- weed rake,
- a hoe for loosening the soil,
- pruning shears for cutting cuttings.
Preparation of soil and planting material
Red currants are planted in the fall in the middle zone. During the autumn-winter period, the earth has time to sink and become denser. In spring, the bushes actively grow and take root well.
In regions with little snow in winter, roots may freeze, so planting seedlings They are performed in the spring, and they are dug in for the winter.In spring, seedlings are shaded or cut short to prevent buds from opening.
Before planting, the area is plowed, fertilizers are added: organic - 3-4 kg of compost, mineral - 100-150 g of granulated superphosphate, 20-30 g of potassium sulfate.
Reference. Before planting, seedlings are inspected and dry and damaged areas of roots and branches are removed. The root system is immersed in a clay mash to prevent moisture loss.
The planting density of red currants depends on the variety, soil fertility and method of bush formation. Varieties with a spreading crown and vigorous ones are planted sparsely, bushes with a compact crown are planted more densely. The row spacing is 1.5 m.
Rooting
Prepared lignified cuttings are placed in a container with a growth stimulator for 12 hours. The upper cut is sprinkled with crushed activated carbon.
The trench is prepared in the fall, and in the spring the cuttings are planted in moist soil, which by that time should warm up to +8°C. If this cannot be done, the soil is shed generously with water before planting.
A drainage layer of coarse sand or gravel is laid at the bottom of the trench. A nutrient substrate prepared from garden soil, rotted manure, charcoal and river sand is poured on top to increase soil aeration.
Planting material is planted, buried 2-3 cm into the ground. The cuttings are placed at an angle of 45°, maintaining a distance of 60-70 cm.
After planting, the soil is compacted and mulched with peat. The plants are covered with transparent plastic bags, creating a favorable microclimate for better development of the root system.
How red currants propagate: different methods
Experienced gardeners do not experience difficulties in propagating black currants due to its ability to root. Properly prepared cuttings take root in 90% of cases. It is more difficult to cope with red currants, since the rate of root formation in this variety is lower. The simplest way to propagate it is considered to be the method of forming layering. The second most effective method is planting woody cuttings, which allows you to grow many new bushes.
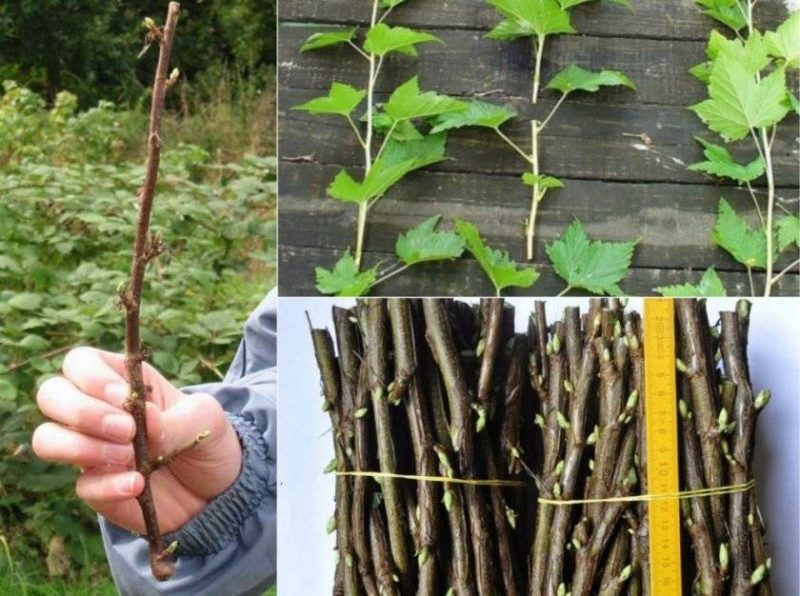

Lignified cuttings
Red ones take root better cuttings from the top of the branch. The optimal length is 4–6 buds. Using a garden knife, make an oblique lower cut 2 cm below the bud. The top cut should be straight. It is performed 1 cm above the upper kidney. The greenery is completely removed.
Then the cuttings are planted in pots with a nutrient substrate or on a seedling bed. Separate containers are good because in the spring the planting material can be placed anywhere. The roots are less damaged during transplantation, since the young plant is removed from the pot along with the earthen lump.
The soil for rooting lignified cuttings should be loose and well-permeable to moisture and air. The material is buried in the ground at an angle of 45°, with the lower bud pointing down. One bud is left above the ground.
The cuttings are watered with clean water at room temperature if they were planted in a seedling bed. Cuttings in containers are buried in a convenient place in the garden. Before the onset of cold weather, constantly monitor soil moisture.
The method of propagation by lignified cuttings is used in spring or autumn. Although many gardeners prefer to carry out work at the beginning of the season, combining the cultivation of red currants with pruning after wintering.From one one-year-old stem, 3–5 cuttings are obtained, 15–20 cm long and about 7 mm thick. The entire non-lignified apical part is removed. Roots form under the buds and in the internodes.
The optimal time for planting cuttings is the end of March. After watering, the soil is mulched with sawdust or dry grass. The thickness of the layer is at least 3 cm. By the end of summer, adult bushes grow from the cuttings, which are quickly transplanted to a new location.
More experienced gardeners germinate cuttings in winter, harvesting them in late autumn. During 3–4 months of winter, the cuttings take root in conditions close to summer. In spring, an almost mature plant is planted in the ground. It adapts to return frosts and easily tolerates replanting. The main thing is not to miss the time when the kidneys go into the sleep period. For example, propagation by cuttings in autumn is best done at the end of September.
Green cuttings
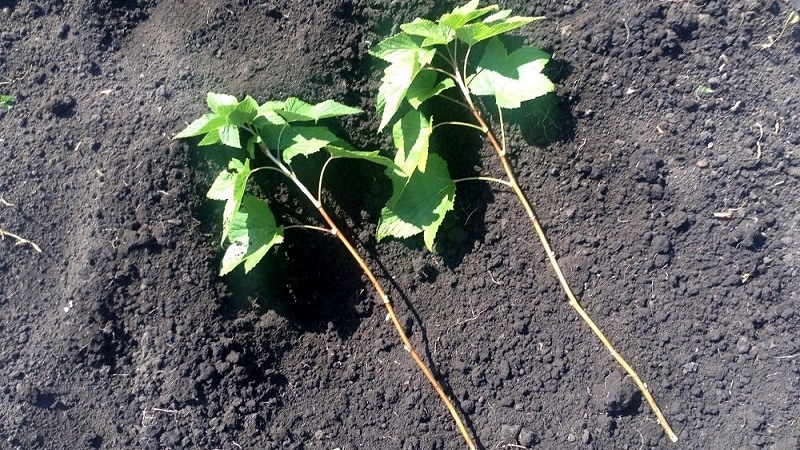

The method of propagation by green cuttings is used if it was not possible to propagate red currants in the spring using lignified cuttings. When bent, the green stalk breaks easily.
Harvesting is done in the morning in cool weather, preferably during the rainy season. Cuttings are cut 12–15 cm long, leaving 4–5 leaves. The upper cut is made at a distance of 5 mm from the kidney, and the lower one at an angle of 45°, but not less than 10 mm under the kidney.
Before planting, the lower leaves are shortened by half, and the cuttings are kept in a growth stimulator for 24 hours. You can prepare the solution yourself by mixing indole-3-butyric acid or indolylacetic acid with water 1:1.
The cuttings are deepened into the nutrient substrate by 3–5 cm. The soil is prepared from peat, compost and sand in equal proportions. Green cuttings are planted in a greenhouse or open ground, but must be covered with plastic wrap.If there is little planting material, it is placed under glass jars or plastic bottles.
Reference. Rooting occurs faster if high humidity conditions are created. Therefore, in a greenhouse, the cuttings are sprayed with warm water several times a day for 20 days, and the soil is also regularly watered.
Non-lignified cuttings should be protected from the scorching sun with dark screens to prevent burns.. After 20 days, the number of waterings is reduced, and the cuttings feed nitrogen fertilizers. After 10 days, they begin to gradually remove the shelter, increasing the time spent in the open air. Hardening lasts a week. Then the young plant is transplanted into the cuttings, where it reaches the desired state within a year. Next, the red currants are transplanted to a permanent place.
By layering
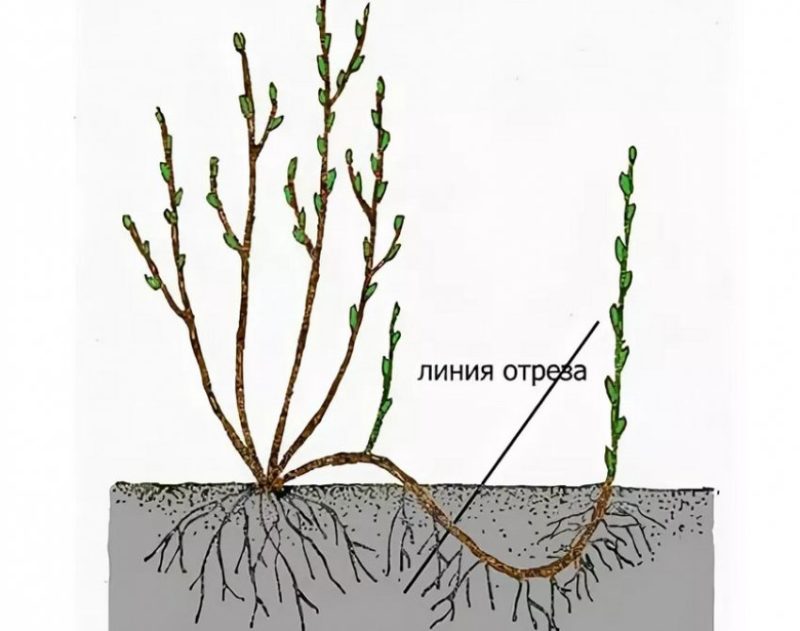
Propagation of red currants by layering is the easiest way. In the spring, the strongest and longest cuttings from the mother bush are selected and buried. Sometimes the plant is secured with pegs.
First, grooves 15 cm deep are dug under the bush, into which the cuttings are placed. A mixture of compost, manure, turf or peat is placed at the bottom. Branches 2–3 years old are used as layering. The fixed material is covered with nutrient substrate to the soil level. The ditch is sprinkled with clean soil on top and compacted so that the height of the hill does not exceed 5 cm.
By autumn, the cuttings will take root, after which they are separated from the mother bush. From one cutting, 3–5 bushes are obtained, and in the fall they are transplanted to a new location. Rooting of cuttings takes up to 2 years. During this period, an adult currant bush is formed, which in the 3rd year bears fruit in the same way as the mother one.From 2–3 cuttings you can get 10–15 new plants.
Dividing the bush
Gardeners practice propagation by dividing a bush much less often, because they consider this method ineffective and traumatic. Its essence lies in dividing the bush into parts that are completely ready for planting. The method is used in late autumn, after the end of the growing season.
First, choose a new place for planting, dig holes 60–70 cm deep, fill them with a mixture of humus, ash, turf and spill water. The bush is carefully dug up, trying not to damage the root system. Annual non-lignified shoots are left on the bush and shortened to 25 cm. Old branches are cut off with pruning shears. The bush is divided into 2-3 parts so that each has its own strong roots and shoots. The plant is planted in a permanent place, watered and spud.
Further care for currants
Rules of care for red currants after propagation:
- In the first 3 weeks, the plantings are provided with high humidity. The cover is removed every day and the bushes are sprayed. Green cuttings are irrigated up to 5 times a day.
- The temperature around the planting material is maintained at +25°C during the day and at least +6°C at night.
- The soil is watered moderately in the morning and evening hours. It should always remain slightly damp. Even short-term moisture deficiency leads to the death of a young plant.
- Root formation begins 2–3 weeks after planting. During this period, the amount of watering is reduced and complex fertilizers with a high nitrogen content begin to be applied to quickly gain green mass.
- Feeding Mineral fertilizers are made with a specially prepared composition: 50 g of ash and 10 g of superphosphate are taken per 10 liters of water. The solution is kept for 48 hours, and then the seedlings are watered.Feeding is carried out every 2 weeks until the beginning of September. After complete rooting, young leaves appear on the cuttings. This means that the shelter can be gradually removed.
With proper care, by mid-autumn the seedlings grow into small bushes 50 cm high. Young shoots form on them. If rooting was carried out in a greenhouse, the plants are transplanted to a permanent place. Weakened bushes are left until spring. If for some reason the seedlings do not develop, they must be removed.
Tips and tricks from experienced gardeners
A few tips from experienced gardeners will help you propagate and grow red currants on your plot without any problems:
- Plant the seedlings in well-lit areas in the middle of the garden.
- The distance between bushes should be at least 1.5 m.
- Plants can be planted next to fruit trees with a sparse crown.
- Prepare the soil in advance: apply organic or mineral fertilizers 6 months before planting the bush in a new location.
- Plant currants at an angle so that the roots can better absorb moisture. Over time, the bush will straighten out.
- Red currants love abundant watering and grow best in high soil moisture. Therefore, bushes can be planted in low-lying areas with standing water or near streams or rivers.
- In the spring, water deeply 3-4 times a day for 2-3 weeks, in the fall - for 1-2 weeks before frost.
Conclusion
The process of propagating red currants by cuttings allows you to obtain a large number of young bushes. But the most effective method is considered to be the method of obtaining cuttings from the mother bush. The planting material takes root quickly, and in 2–3 years the gardener will be able to harvest a rich harvest of juicy, sweet and sour berries.
Caring for red currants after propagation involves maintaining optimal water balance, creating a greenhouse effect for better development of the root system and young leaves, as well as applying mineral and organic fertilizers.