What is blackcurrant terry and how to get rid of it
Currant blight is one of the most dangerous and difficult to cure viral diseases. The disease can not only destroy the entire crop, but also infect nearby shrubs and trees. To protect currants from rotting, summer residents use proven chemical and folk remedies, and also pay attention to regular care. In the article you will find a description of the disease with photographs and learn how to treat terry in the garden.
What is blackcurrant terry?
Blackcurrant terry (reversion, curl) is a viral disease that affects all parts of the bush: shoots, leaves, fruits.
If terry disease is not detected at an early stage and treatment is not started, the plant will stop bearing fruit and die.
Description of the disease

Terry is caused by a virus. It develops only in the cells of living organisms and enters the site through planting material or insects.
During the growing season, the causative agents of terry disease spread throughout the plant, primarily attacking the leaves and branches, and later move on to the fruits and root system. Sometimes viruses appear after pruning and penetrate open wounds.
Often the terry disease is disguised - there are no external signs of the disease. The virus can only be recognized by a sharp decrease in yield.
Damage caused
The damage from terry disease is significant: if plantings of fruit bushes are not treated, the plants will die.If a viral disease is detected at an early stage, the crop can be saved.
The disease is dangerous because it spreads quickly and affects neighboring plants. The disease is especially common in the Central and Northwestern regions.
Causes of terry
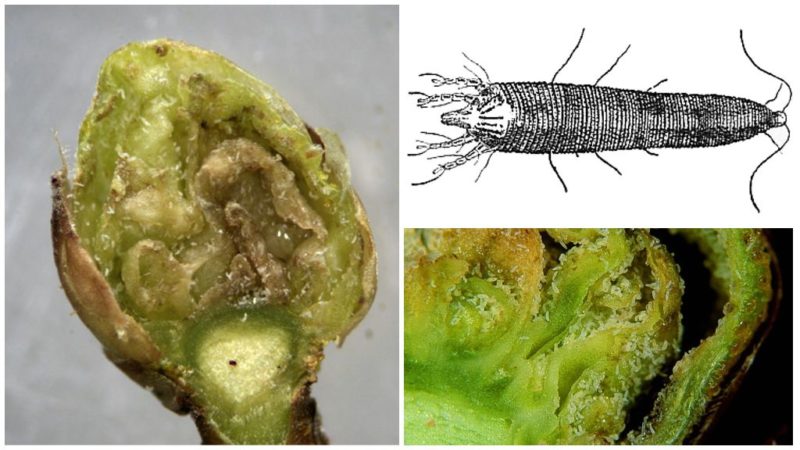
The most common carrier of the disease is the kidney mite. It appears on the site due to infected seedlings. At the moment of flowering of the currant, the affected buds wither, and the female mites get out.
Infection occurs at the end of spring or beginning of summer, depending on the timing of ripening. In addition to the bud mite, aphids, plant bugs and spider mites can carry the virus. They actively develop in hot and humid summer conditions and love weakened plants.
The virus also occurs because the currant seedlings were already infected at the time of planting. The peculiarity is that the planting material is externally healthy - there are no signs of damage. And only after 2-3 years, summer residents observe a decrease in yield and delayed flowering.
Attention! The virus prefers plants with weak immunity. It occurs due to incorrect care: due to lack of watering and fertilizing, irregular pruning, weeds on the site. Therefore, it is important to care for the currant bush, monitor its appearance and conduct inspections.
Symptoms
On young plants, doubleness most often develops hidden. Symptoms appear on shrubs older than 3-4 years. Signs of damage become clear when the incubation period ends.
External signs of damage to black currant by terry

A characteristic symptom of terry growth is the absence of berries on the bushes. Gardeners also notice that the leaf plates are deformed, and the shape and color of the flowers change. Many lateral shoots and green shoots appear, and the strong currant aroma of the plant disappears.
On some shrubs, gardeners notice that the leaves become asymmetrical, with rare coarse veins appearing on one side. Such signs can be detected visually during examination and prevent the development of the disease.
When terry blossoms are detected in the spring, gardeners notice deformed flowers - they seem to be covered with scales and take on a reddish-lilac hue. The petals of the flower are separated, the stamens are elongated. Complete destruction of the bush is accompanied by the fact that the plant becomes dense - a large number of shoots grow.
How to treat shrubs
There are several ways to treat shrubs. Chemicals are used when the virus has already been detected on the plantings. Agrotechnical techniques and traditional methods act as additional methods of protection; to be effective, they are combined with chemicals.
Chemicals
Chemicals are highly aggressive, so they are used with precautions. An effective chemical for treating terry hair is Fufanon. The active components of the drug are malathion. It blocks pathogens within 1-2 hours. Working fluid consumption is 1.5 liters per 1 bush. Spray the solution in dry, windless weather, wetting the currant leaves on all sides. Leftovers cannot be stored; they are disposed of immediately.
Gardeners use the drug “Topaz”. It has a preventive, curative and eradicative effect. The Topaz solution is quickly absorbed by currants, which reduces the risk of being washed off by rain or evaporation due to sunlight.To make a solution, 2 ml are diluted in 10 liters of water, the consumption rate is 1 liter per 10 square meters. m. It is not recommended to mix Topaz with other pesticides. During the season, currants are processed 4 times with an interval of 2 weeks.

Attention! To work with chemicals, summer residents prepare protective clothing, a respirator, gloves and goggles. During treatment, it is forbidden to drink or eat, and there should be no children or animals nearby. Do not mix the working solution in containers for food and water; it is better to use a household basin or other container for these purposes.
Agrotechnical techniques
Agrotechnical techniques are not able to completely cure black currants from terry disease, but they help strengthen the bush’s immunity and slow down the spread of the disease.
Summer residents pay attention to the following recommendations:

- If a source of infection is detected, the affected bushes are removed and burned away from the site. The remaining plants are treated with Fufanon, a solution of Bordeaux mixture or copper sulfate. And the soil under the bush is watered with a solution of wood ash.
- In early spring and the first half of summer, shrubs are sprayed with a solution of colloidal sulfur. The treatment destroys pathogens, protects currants from aphids and bud mites, and prevents the appearance of fungi. During the season, the event is held 2 times with an interval of 1 month.
- To strengthen the immunity of currants, add mineral and organic feeding. In April, the bush is watered with mullein solution, in mid-June it is fertilized with double superphosphate, and in August it is watered with a herbal infusion of chamomile, tansy and sage. Comprehensive care not only protects against viruses, but also increases productivity.
Traditional methods
Folk remedies are used only in conjunction with professional treatment methods.
To prevent and treat terry, use an infusion of tomato tops. It contains solanine, a poisonous compound that fights diseases and pests. To prepare, take 4 kg of fresh tomato leaves, chop them and pour 10 liters of warm water. Leave for 4 hours and put on the stove for half an hour to boil. Afterwards, the broth is filtered, diluted with water in a ratio of 1:4 and 40 g of grated soap is added so that the solution sticks to the bushes. Damaged plants are sprayed early in the morning.
To prepare a green medicinal infusion, chamomile, dandelion, sage, calendula and other medicinal herbs are used in equal parts. They are soaked in boiling water for a day, filtered and diluted in a ratio of 100 ml of herbs per 1 liter of water. Currants are sprayed 2 times a month; pesticides are used in between such treatments.
Preventive measures
The causative agents of the disease are viruses; the fight against them is long and not always fruitful.
To prevent the development of the disease, summer residents take simple measures as preventive measures:
- buy two-year-old seedlings from trusted sellers;
- before planting, treat the soil with Bordeaux mixture and dig it thoroughly;
- plant currants next to gooseberries, avoid proximity to raspberries;
- at the end of February or beginning of March, water the bushes with boiling water - it destroys viruses and pest larvae overwintering in the soil;
- watered currants 1 time every 2 weeks with water at room temperature;
- regularly inspect the plants and monitor the amount of harvest;
- remove and burn all weeds and debris from the plantings.
Terry-resistant blackcurrant varieties
Choosing a resistant variety is one of the preventative measures that helps prevent the appearance of terry. Summer residents from central Russia are advised to pay attention to varieties Ilya Muromets and Titania. In addition to strong immunity, they are distinguished by their ease of care, large and juicy berries, and balanced taste.
For the northern regions, choose the Sakharnaya or Sokrovische varieties. They can withstand temperatures down to -40°C and rarely suffer from rot, powdery mildew, or rot. The varieties are resistant to drought and can easily tolerate long-term lack of watering.
In the south they grow Gamma or Sevchanka currants. Plants are not afraid kidney mite, are rarely damaged by other pests. The berries are sweet and sour, the taste is refreshing.
Attention! Even when planting terry-resistant varieties, we must not forget about preventive and agrotechnical measures. There is no plant that is 100% immune to leaf blight. It is also recommended to study reviews from experienced gardeners when choosing a variety.
Advice from experienced gardeners
To protect the bush from terry, gardeners make sure that the soil is nutritious and balanced. When planting, the pit is fertilized with organic matter, a distance between seedlings of 1-1.5 m is maintained. Every year in early spring, pruning — remove dry and weakened branches, thereby reducing the likelihood of pests and diseases. Every year, shrubs are treated with a solution of Bordeaux mixture - a simple and powerful remedy that protects against viruses and fungi.
It is recommended to remove currants from the area if currants have affected more than 40% of the bush.In this case, it is useless to save the plant - it is better to remove it immediately so as not to infect nearby bushes and save the remaining harvest.
Conclusion
Measures to combat currant terry include the use of chemicals, folk remedies and agrotechnical measures. To cure shrubs, summer residents use Fufanon or Topaz, as well as infusions of tomato tops or medicinal herbs.
The difficulty of treatment is that terry disease does not always manifest itself symptomatically - sometimes there are no external signs of infection, the bushes simply stop bearing fruit. Therefore, it is important to regularly carry out preventive treatments and select varieties that are resistant to terry in advance.