What are the advantages of propagating honeysuckle by layering and how to carry out the procedure correctly
Honeysuckle is so easy to care for that even a novice gardener can grow it. Its decorative appearance and healthy berries make this plant popular in all regions of the country. Proper propagation of honeysuckle allows you to obtain large harvests and form a beautiful garden area or hedge. Let's consider how to propagate honeysuckle so as not to harm the bush and obtain high-quality planting material.
What are layering
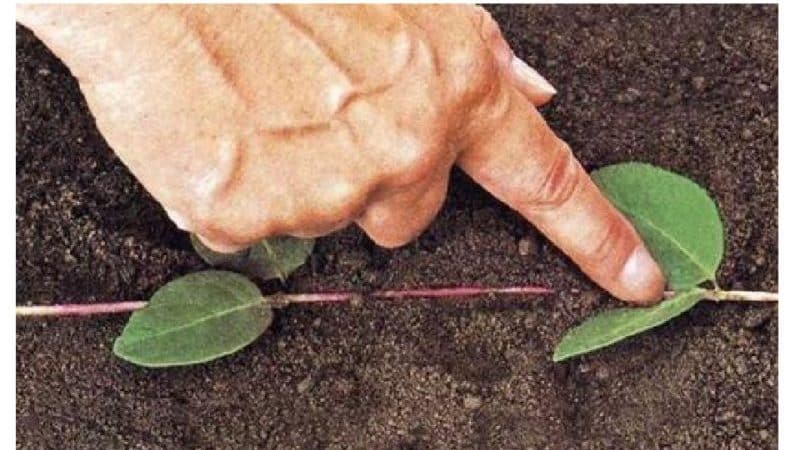

Shrubs are propagated in different ways. One of them is layering. These are rooted shoots of the above-ground part of the plant. Until their own roots and vertical branches appear, the cuttings remain part of the parent bush.
Important! Honeysuckle easily tolerates frosts down to -50°C, so it is grown in almost all climatic zones.
Features of honeysuckle propagation by layering
Plants have good survival rate and rapid growth. Layering is the easiest way to get from one bush to 40-50 seedlings.
Advantages and disadvantages of the method
Vegetative propagation of honeysuckle by layering is used when one wants to preserve a good variety or quickly obtain new plants.
Advantages of the method:
- does not injure the mother bush;
- young seedlings quickly begin to bear fruit;
- obtaining decorative varieties.
Minuses:
- the complexity of the method;
- a new seedling runs the risk of getting an infection from the parent bush.
There are 14 species of wild honeysuckle found in our country, and gardeners often simply transplant forest shrubs into their garden.
Reproduction by root layering
To obtain high-quality seedlings, choose healthy, powerful honeysuckle bushes. All work is carried out in early spring, immediately after the snow melts. For the middle zone - in March, for Siberia and the Urals - in early April.

Horizontal
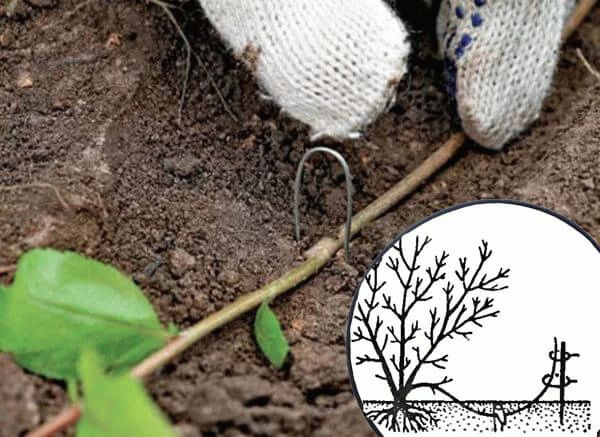
The soil around the parent honeysuckle bush is carefully dug up to create a circle 1-1.2 m in diameter. Then radial grooves 1 cm deep are made. Healthy, strong lower shoots are carefully bent, lowered into the furrows and secured in this position with wooden or metal pins. The branches are sprinkled with earth on top, leaving only the top 4-5 cm free.
For successful survival, the cuttings are lightly watered once a week. Twice during the growing season the parent bush is fed with complex fertilizers. Emerging young shoots on layering are spud to ¼ height.
By the end of summer, the cuttings will form strong roots. The branches are separated from the mother bush and cut with pruning shears according to the number of shoots. The seedlings are immediately rooted in the prepared area and watered.
Important! Edible species of honeysuckle have long been used in folk medicine. Moreover, all parts of the plant have medicinal properties.
By air
If honeysuckle does not have lower horizontal branches, layering is done on vertical ones. To do this, select adult healthy shoots and use a sharp knife to cut grooves in the bark 2-3 cm below the buds. A plastic cup is cut in half and each half is filled with peat. Then both parts of the cup are applied to the branch, wrapping them around the groove made.The top is secured with tape or wire. Peat is kept moist throughout the growing season. In autumn, the shoot is separated, the cup is carefully removed and the branch is cut below and above the formed roots. Immediately planted in a permanent place.
When to replant cuttings - in spring, summer, autumn
Horizontal and air layering is done in early spring, after the snow has melted. Throughout the summer season they develop roots and shoots. In autumn, the cuttings are separated from the parent bush and planted in a prepared area.
Important! The smell of honeysuckle flowers and fruits relieves stress, improves mood and increases appetite.
Mistakes to Avoid
If certain propagation rules are not followed, the gardener will not receive large harvests of honeysuckle. To preserve the varietal qualities of the bush, mature, healthy branches are chosen. If the cuttings are not watered enough, the root system will form weak and will rot if there is excess moisture. Most honeysuckle varieties bear fruit only when different varieties are planted in the same area.
The site for the plants is chosen to be well-lit; the bushes are planted not in rows, but in clumps. In the southern regions, the cuttings are immediately planted in a permanent place. In the middle zone, in the Urals, in Siberia, young seedlings are grown in a greenhouse and only after a year are moved to a permanent place.
Other methods of growing honeysuckle
Forming layering is the easiest way to grow a shrub. Although there are vegetative and generative methods of propagating honeysuckle.
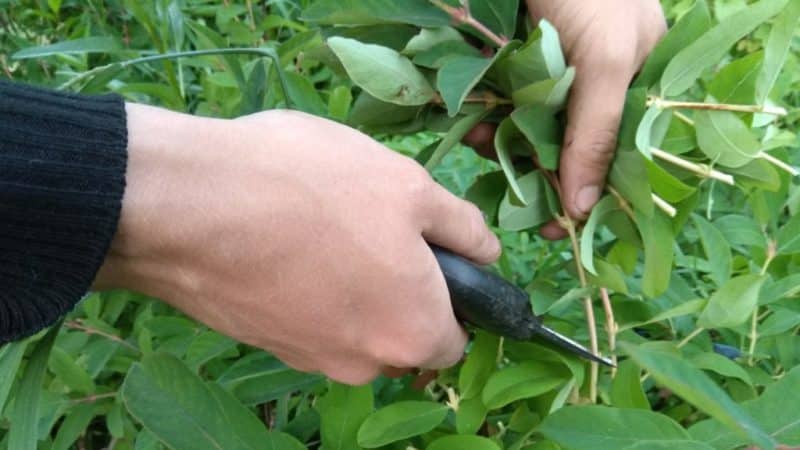
By cuttings

This method is a little more complicated than propagation by layering. Cuttings made from green or woody shoots. In the fall, a powerful, healthy branch is divided into parts as follows:
- the cut part must have at least two internodes;
- the lower cut is at an angle of 45°, the upper is horizontal.
The cuttings are wrapped in a wet cloth and stored in a cool place. With the onset of spring, they are planted in prepared soil and covered with a cut plastic bottle to create a greenhouse effect.

Dividing the bush
Only adult honeysuckle is propagated in this way. The bush is dug in from all sides and carefully removed from the soil, shaking off the soil. Large honeysuckle is divided into 3-4 parts, evenly dividing roots and shoots.
Growing shoots
If the honeysuckle has produced shoots from the basal bud, they are allowed to grow for a year, then separated from the parent bush and transplanted to a permanent place.
Important! The best time for propagation by shoots is autumn, after leaf fall. In this case, the bush is less injured and tolerates separation from the mother bush well.
Seeds
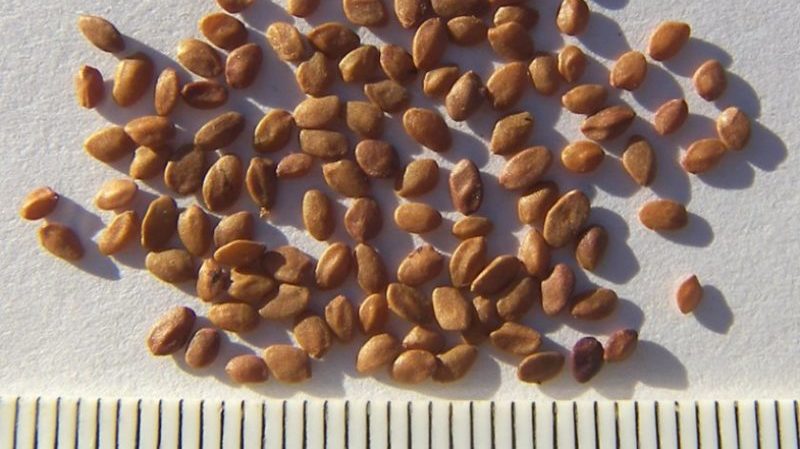

The generative method has one significant drawback - it will not be possible to predict the varietal qualities of a variety. Honeysuckle is propagated by seeds in spring, autumn or summer.
In early spring, planting material is sown in seedling boxes to a depth of 1 cm and covered with film or glass. Within a month, shoots will appear and the shelter will be removed. Honeysuckle is grown in boxes for a year, then transplanted into open ground.
In summer, seeds are sown immediately after picking berries. By autumn they will sprout. For the winter they are covered with mulch or film. The growing season will continue in spring.
The best period for propagating honeysuckle by seeds is autumn. The seeds will not have time to hatch, but will be well stratified and hardened. In the spring, such seeds will produce powerful shoots.
Peculiarities of propagation of edible and decorative honeysuckle

All the methods described above are applicable to any variety of shrub. Decorative honeysuckle has dozens of varieties. It looks great in group and single plantings. climbing honeysuckle entwined with arbors and trellises. Decorative varieties are also beautiful as hedges.
Regardless of whether honeysuckle is edible or not, it is propagated vegetatively (by layering, cuttings, dividing a bush, shoots) and generatively (by seeds).
This is interesting:
Growing honeysuckle honeysuckle: planting, care, propagation
Description, cultivation and use of Brown's Honeysuckle Dropmore Scarlet
Conclusion
Propagating honeysuckle is not at all difficult. Beginner gardeners are better off using layering. Experienced people can easily handle any method. The best time to propagate honeysuckle is: early spring for vegetative methods and late autumn for generative methods.