We treat garlic diseases ourselves and get rid of pests: effective methods and preventive measures
Since childhood, everyone knows that garlic is an excellent means of preventing various diseases. All of him beneficial features so you can’t count it right away. However, garlic itself, like other plants, can be affected by pests and various diseases.
In this article we will take a detailed look at garlic diseases, as well as ways to combat them and methods of prevention.
Garlic diseases: treatment and prevention
Garlic is mainly affected by fungal diseases. There are also viral (yellow dwarfism) and bacterial (bacteriosis) diseases.
The pests that most often attack garlic include garlic mites and stem nematodes.
Pink root rot
Pink rot is a fungal disease (caused by the fungus Phoma terrestris), which is transmitted mainly through soil or contaminated planting material.
The optimal temperature for the development of the disease is from +25 to +30 degrees.
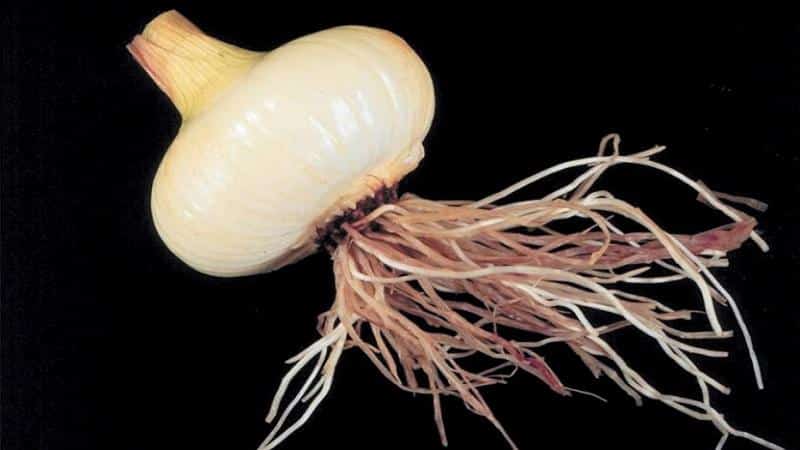
- Signs. Pink rot affects the root and outer scales, almost never leading to the death of the plant. At first the roots turn light pink, then red and purple. Eventually they finally darken and die.
- Treatment. Fungicides can combat pink root rot. For example, "Quadris".
- Prevention. Be sure to follow the rules of crop rotation: garlic cannot be planted for 4 years in the place where bulbous plants grew. Before planting, it is recommended to treat the planting material with disinfectants.
White rot
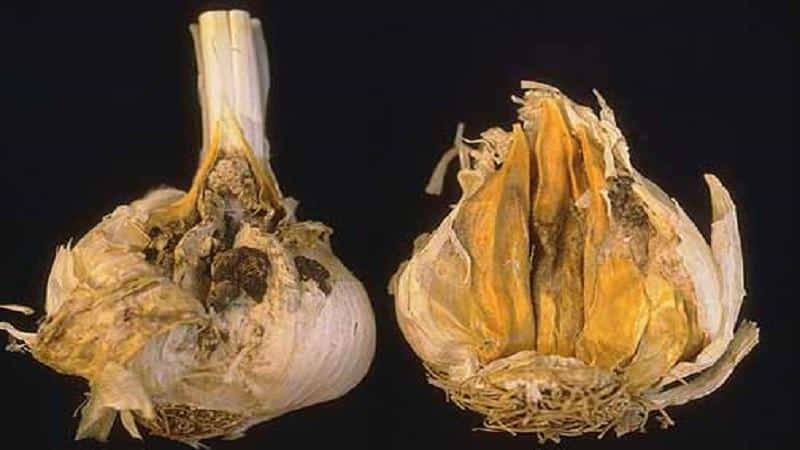
White rot of the bottom - sclerotinia.The causative agent is the fungus Sclerotium cepivorum. Infection occurs through the soil at temperatures from +10 to +24 degrees. White rot is one of the most dangerous diseases for bulbs.
 Signs. White rot destroys the root of the plant, then the bulb gradually disintegrates. The fungus appears in the form of white mycelium on the root and bulb. External signs of the disease include yellowing of the leaves, starting from the tips.
Signs. White rot destroys the root of the plant, then the bulb gradually disintegrates. The fungus appears in the form of white mycelium on the root and bulb. External signs of the disease include yellowing of the leaves, starting from the tips.
Treatment. At the first signs of the disease, fungicides will help: “Custodia”, “Switch”, “Uniform”.
Prevention. To prepare planting material, use the drug “Maxim XL”, which helps protect the plant, including from white rot. To prevent white rot, use only clean and healthy planting material, clean tools and containers. Don't forget about proper crop rotation.
The causative agent of garlic white rot (spores) persists in dry form for several years. It can be on boxes, tools and other surfaces that come into contact with the diseased plant. Therefore, it is necessary to disinfect everything inventory.
Fusarium
Fusarium root rot of garlic is caused by fungi of the genus Fusarium. Fusarium infection occurs through the bulb, soil and plant debris.
The disease spreads best in hot weather (28-32 degrees) and high humidity.
- Signs. The leaves begin to turn yellow and brown from the tips, gradually moving down. A pink coating can be seen on the false stem. The root and bulb turn pink and rot. A white fungus is spreading inside the bulb.
- Treatment. The means of combating the first signs of fusarium are the same as for white rot: “Custodia”, “Switch”, “Uniform”.
- Prevention.Use fungicides as disinfectants - for example, the drug "Maxim XL". Remove infected plants along with a clod of soil and burn them. Disinfect tools and maintain crop rotation.
Important! The fungus that causes fusarium produces toxins. It can cause severe poisoning.
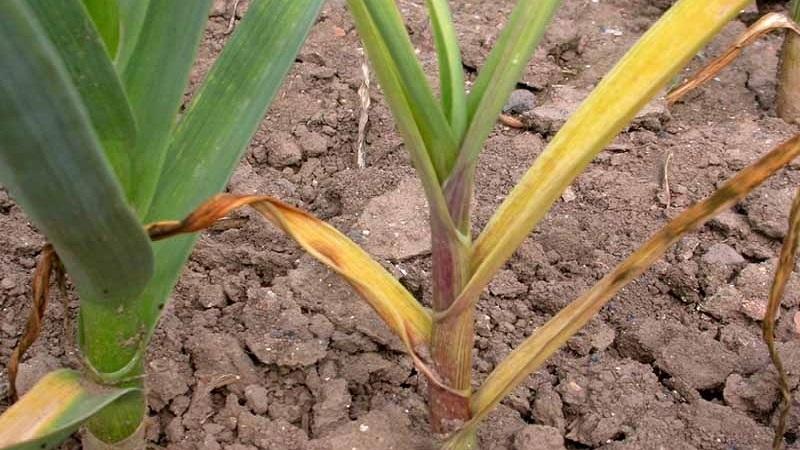

Cervical rot
Cervical rot is caused by a fungus of the genus Botrytis. The disease mainly affects garlic during storage. Infection occurs through soil or diseased planting material. The ideal temperature for the development of the disease is from 15 to 20 degrees.
Signs. The disease appears 1-2 months after harvesting. The neck of the onion begins to rot: the latter becomes soft and slimy, and a gray fluffy coating appears on it.
A gray-brown coating covers the garlic cloves in spots. Over time, the disease spreads throughout the bulb. In 1-2 months, neck rot completely affects the bulb (it rots) and infects healthy garlic.
Treatment. Since the disease does not manifest itself in any way during plant growth, it is almost impossible to take timely measures to combat it. But fungicides effectively combat neck rot during the growing season of garlic. For example, the already mentioned above “Custodia”, “Switch”, “Uniform”, as well as “Ridomil Gold” and “Acrobat”.
Prevention. Dressing with Maxim XL, compliance with crop rotation, fertilizer application procedures, mandatory use of phosphorus fertilizers. It is important to harvest the crop on time and dry the bulbs before storing until the leaves dry out.
Don’t be lazy about sorting your garlic to store only healthy bulbs. Storage conditions: temperature from 0 to -2 degrees, humidity - no higher than 70%.
Penicillosis
Garlic penicillium is also called blue, blue or green mold. The causative agents are fungi of the genus Penicillium. Most often, the disease spreads through the use of contaminated planting material.
During storage, spores move from diseased bulbs to healthy ones. The result is clearly visible in the photo.
 The disease develops at high temperature and humidity in storage.
The disease develops at high temperature and humidity in storage.
- Signs. From the outside, penicillosis can be noticed by yellowing leaves, short stature and a blue-green coating at the base of the plant. The bulb becomes covered with a white coating, which later turns green. The onion falls apart into cloves that are limp to the touch.
- Treatment. At the first sign of disease, use fungicides. For example, “Quadris”, “Shirlan” or “Bumper Super”.
- Prevention. Select planting material carefully - plant only healthy ones, having previously treated it with antifungal drugs. Remember to practice proper crop rotation and destroy infected bulbs rather than compost.
Harvested garlic must be dried for 3-4 weeks before storage. Store garlic at a temperature no higher than 10 degrees and humidity no more than 60%.
Aspergillosis
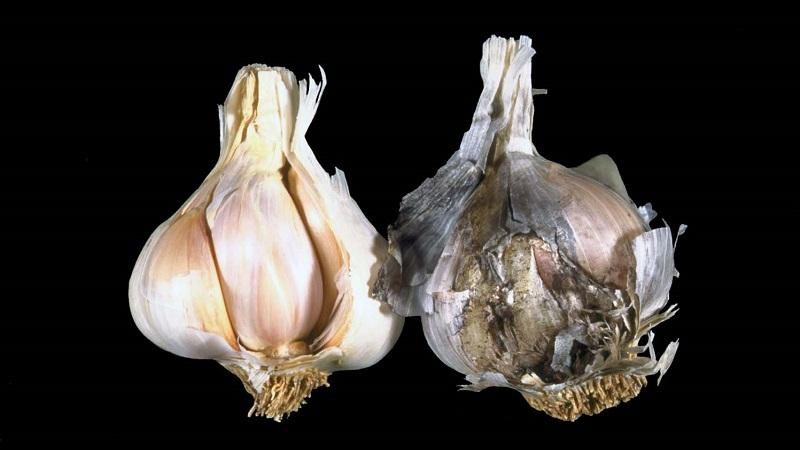
Aspergillosis is also called black mold or garlic sooty. The disease is caused by fungi of the genus Aspergillus. The disease is transmitted through soil (plant debris), air (spores are carried by the wind) and infected planting material. It develops in conditions of high temperature and humidity.
Signs. Black dusty mold around the neck, which subsequently spreads throughout the bulb.
Treatment. To combat black mold during garlic growth, the same fungicides as for penicillosis may be suitable: “Quadris”, “Shirlan” or “Bumper Super”.
Prevention. Treatment of planting material with antifungal disinfectants, storage of garlic and planting material at low temperatures (+1 - +12 degrees, humidity no more than 65%). Drying garlic after harvesting before storage.
Downy mildew
Downy mildew, or downy mildew, destroys most of the garlic crop. The causative agent is Peronospora destructor Casp. Thrives in cool and humid weather.
Transmitted through soil (plant debris), contaminated planting material and garden tools.
- Signs. Yellow spots appear on the shoots of garlic, which are subsequently covered with gray or purple spores. The leaves first curl and then dry out.
- Treatment. To combat downy mildew, it is recommended to use fungicides. For example, “Quadris”, “Areva Gold” or “Ridomil Gold”.
- Prevention. Using only healthy planting material and treating it before planting. Avoid the top glaze, or water the garlic in the morning so that the water on the leaves has time to dry before evening.
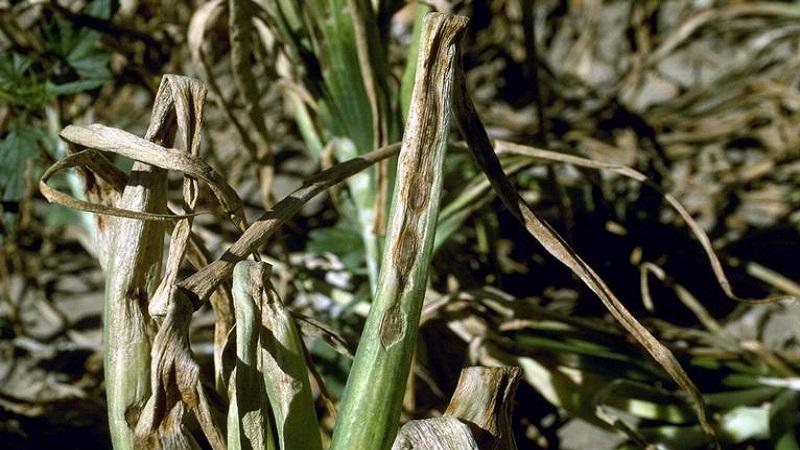

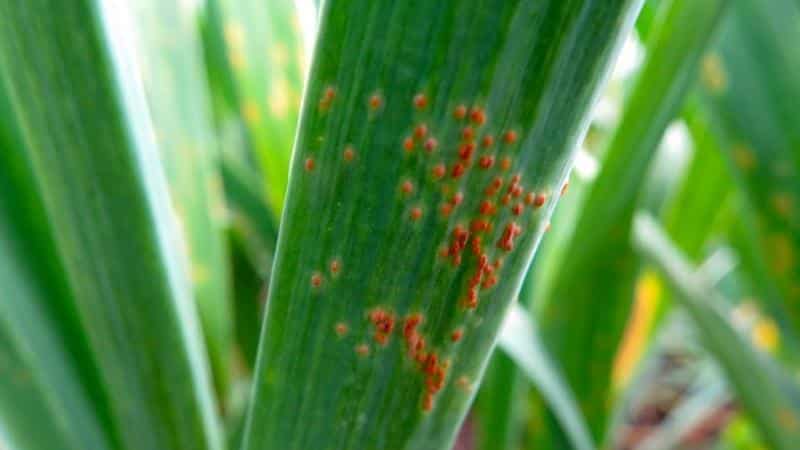
Rust
Garlic rust is caused by the fungus Puccinia alli. This disease does not kill the plant, but slows down its growth. Thrives in cool and humid weather.
Signs. Rusty spots or spots appear on the leaves, which later turn black.
Treatment. To combat the spread of rust, it is recommended to immediately cut off the affected leaves. The best results in combating this disease were shown by such fungicides as Quadris, Bayer, Nativo and Syngenta.
Prevention. Crop rotation, access to sunlight. Avoid evening watering.

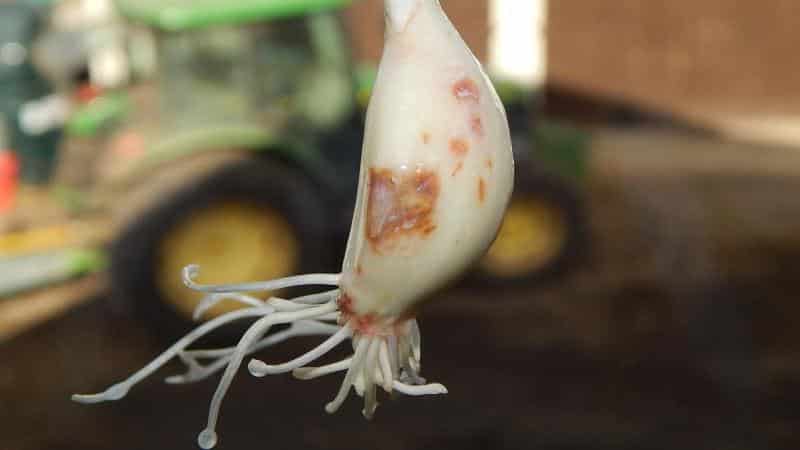
Yellow dwarfism
 Yellow dwarfism is a viral disease of garlic.The virus is transmitted by pests (aphids, garlic mites, stem nematodes) and through infected planting material.
Yellow dwarfism is a viral disease of garlic.The virus is transmitted by pests (aphids, garlic mites, stem nematodes) and through infected planting material.
- Signs. The leaves become covered with yellow spots, bend at the base and bend toward the ground. Sick plants are stunted compared to healthy ones.
- Treatment. There are no chemical methods to combat yellow dwarfism of garlic, so take precautions.
- Prevention. Use only healthy planting material, fight pests that carry the virus. Destroy infested plants rather than compost.
Bacteriosis
 Garlic bacteriosis, or soft bacterial rot. The causative agent is the bacteria Erwinia carotovora. Spread by insects, rain and irrigation water. Develops in warm and humid weather.
Garlic bacteriosis, or soft bacterial rot. The causative agent is the bacteria Erwinia carotovora. Spread by insects, rain and irrigation water. Develops in warm and humid weather.
Signs. One or more cloves are softened and saturated with liquid. The neck is soft when pressed and releases a foul-smelling liquid.
Treatment. Fungicides: “Pergado”, “Kurzat R”.
Prevention. Drying before storage, storage at low temperature and humidity not more than 65%. Avoid overhead watering, kill pests, and use copper-based bactericides.
Stem nematode
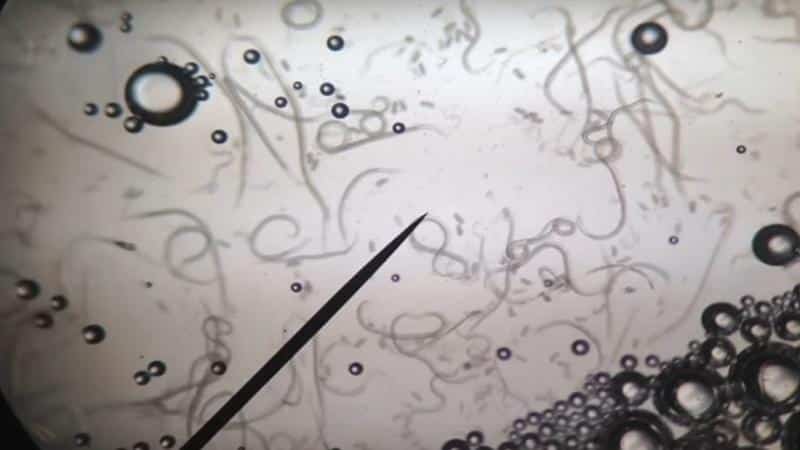
A nematode is a microscopic worm that attacks all parts of garlic except the roots. It feeds on the sap of the plant and completely destroys it.
- Signs. Light stripes on the leaves, curling and drying of feathers and bulbs. Unpleasant smell of rot.
- Treatment. To combat stem nematodes, it is recommended to use nematicidal insecticides, for example, Akarin, Fitoverm, Nemabakt. They can be dissolved in water for irrigation or embedded in the soil.
- Prevention. Compliance with 4-5 year crop rotation.Treatment of planting material with hot water: 10-15 minutes at 40 degrees, 5-6 minutes at 45 degrees or 2-4 minutes at 55 degrees. It is necessary to carefully select planting material and disinfect garden tools.
Garlic mite
The four-legged garlic mite infects garlic both during the growth and storage periods. Infection occurs through the ground, wind and contaminated planting material.
The size of the tick is no more than 0.25 mm. The female lays eggs on the tissues of the plant, which overwinter on the heads of garlic after harvesting.
Signs. The appearance of light brown or yellow spots on the green parts of the plant and cloves, the juices of which the mite and its larva feed on. Poor development and curvature of leaves. A white coating may occur.
Treatment. If mites are detected, the plant must be treated with acaricides or insectoacaricides (Vertimek, Bi-58 Novy).
Prevention. Deep plowing of the beds, compliance with crop rotation. High acidity of the soil promotes the development of mites. Pre-planting treatment of teeth with acaricides or insectoacaricides.

General recommendations for the prevention and protection of garlic
The main rules for the prevention of garlic diseases and pest damage are adherence to a 4-5 year crop rotation and careful selection of only healthy planting material. Never compost infected plants; they must be burned.
Many garlic diseases develop during storage. Therefore, it is necessary to follow the rules for harvesting and preparing the crop for storage, as well as the storage conditions for garlic.
For prevention, it is also recommended to pre-treat the planting material - by drying, hot water or chemicals.Don’t forget about disinfecting garden tools, shoes and clothing that may have come into contact with infected plants.
At the first signs of disease or pest damage, the only methods of control are chemicals: fungicides, insecticides, acaricides, etc.
Important! You need to use chemicals very carefully: plants can only be treated with chemicals intended for them, aimed at combating a specific disease or group of diseases. Carefully follow the instructions for use of these medications.
Conclusion
Garlic is a useful crop that every gardener and gardener simply must grow. Simple preventive measures will help protect it from diseases and pests.
If the disease does affect the garlic, do not be discouraged. Almost any disease can be treated, the main thing is to notice its first signs in time.