What to do if onions rot during storage and in the garden
Onion rotting is a common cause of crop damage both during winter storage and during growth.
In this article you will find the answer to the question of why onions are poorly stored, and you will also find out what to do if onions rot in the garden bed or in the cellar.
The main causes of onion rotting
The causes of onion rot are failure to comply with storage conditions, the use of contaminated planting material, and violation of the rules of collection and preparation for storage. Let's look at each in more detail.

Waterlogged soil
Excessive moisture is detrimental to plantings during the growth period and during digging and storage of vegetables. Excessively damp soil provokes the development of fungal diseases during the growing season. Heads dug out of wet soil are more difficult to dry properly and, therefore, to preserve in the future.
Violation of crop rotation rules
Failure to comply with crop rotation rules is another common cause of rot outbreaks. Growing onions in the same place year after year leads to the accumulation of pathogens and pests of bulbous crops in the soil. As a result, the affected heads rot before they have time to ripen.
Violation of dosages when applying fertilizers
Excessive nitrogen content slows down turnip growth and reduces plant resistance to fungal diseases.
Advice. When applying fertilizing, follow the dosage recommended by the manufacturer. Excess nutrients, in particular nitrogen, are detrimental to garden crops.
Watering the area with a solution of wood ash will help restore the balance.
Use of infected planting material
If the seed used for sowing is infected, this will most likely lead to disease and damage to the crop. Therefore, planting material should be purchased only from trusted manufacturers and additionally disinfected before sowing.
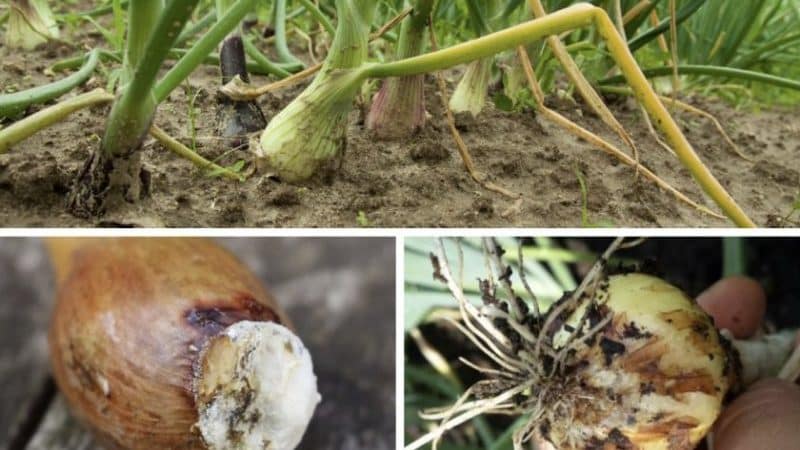
Late harvest
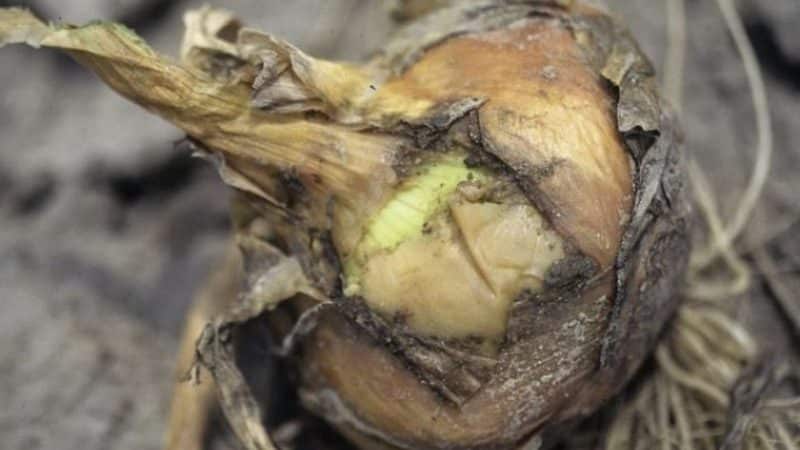
Harvesting on time is another important condition for its preservation. If you dig up the bulbs in the garden too early, the necks will be wet and will not dry out before storage. If you delay harvesting, the bulbs will begin to deteriorate in the ground, especially in wet weather.
Improper storage
Why do onions rot during storage? This happens if several infected bulbs get into the mass of healthy bulbs, from which the rot spreads to neighboring ones.. Either the vegetables were not dried enough before being stored in the cellar.
Violation of storage conditions also leads to damage to the crop. The optimal storage temperature for heads is from +1 to +5°C.
Damage to bulbs by pests
Heads infected, for example, with a nematode, quickly begin to rot during storage. Due to the small size of the pest, it is difficult to detect by visual inspection, so infected vegetables often end up in storage.
Spoilage of onions while growing in the garden

If during your next inspection you find yellowed feathers, make sure that the heads have not begun to rot from the inside. If the onion becomes soft, watery and smells unpleasant, it means it is rotting.
Solving the problem begins with determining the cause of the rot.
Violation of the irrigation regime
Too frequent watering, especially in combination with rainy weather and the location of the bed in a lowland, leads to rotting.
The solution would be active watering, carried out only at the beginning of the growing season. After the bulbs form, watering is reduced, and a month before harvesting is stopped altogether.
Excess nitrogen in the soil
Excessive concentration of nitrogen fertilizers provokes softening of the bulb tissue and the development of putrefactive infections.
The solution is to follow the rules when applying fertilizers. If a problem occurs, the soil is washed with a solution of wood ash.
Fusarium bottom rot
The infectious agent lives in the soil. First it affects the feather, then provokes rotting of the bottom.
The infection can spread to neighboring plants, so affected specimens are removed from the garden bed. Crop rotation helps combat the spread of the disease. Onions are planted in their original place only after 3-4 years.
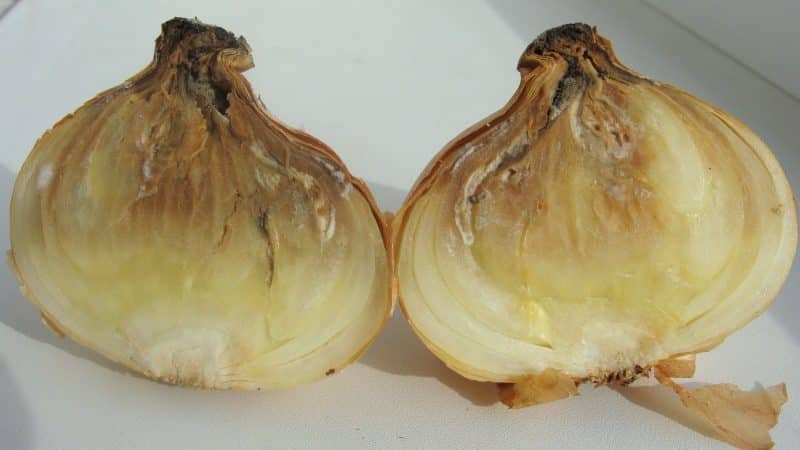
Cervical rot
A fungal disease that develops at high humidity. Appears in the form of mold. A diseased plant takes on a slimy, soft appearance and emits an unpleasant odor.
To prevent it, follow the rules of prevention: plantings are placed in a high, sunny place and maintain optimal soil moisture.
Onion fly
Pest larvae eat plant tissue, causing it to rot and die.
To fight with parasite Spraying with an infusion of ash, tobacco dust and ground pepper helps. Protecting onion beds with covering material during the fly's summer will prevent the pest from laying eggs on the beds.
Stem nematode
Small wormeating onion juice. It reproduces by laying eggs in plant tissues. The affected tissues become loose, rot and acquire an unpleasant odor.
The appearance of the parasite is prevented by observing crop rotation and sowing healthy seed material.Immediately before planting, the seedlings are soaked in a solution of the drug “Fitosporin-M” for 20-30 minutes (38 g of substance per 10 liters of water).
Causes of spoilage during storage
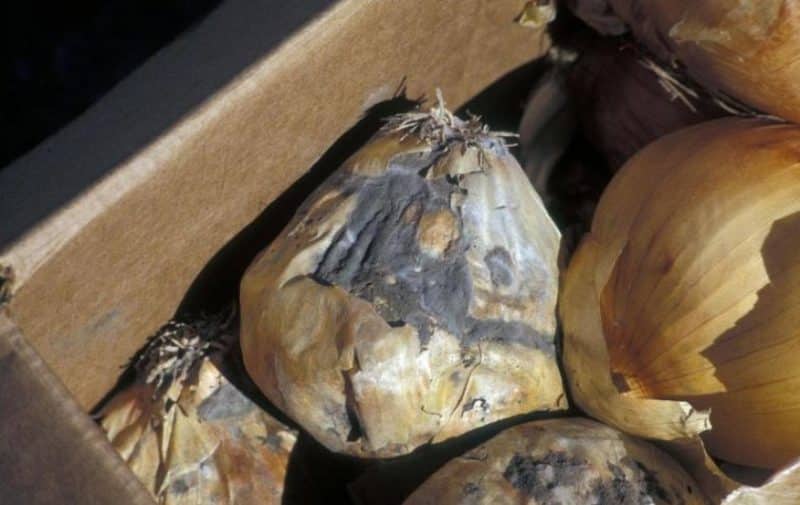

The reasons for rotting during storage are violations of harvesting technology and storage conditions, insufficient drying of the bulbs before storing them in storage.
Dig up vegetables in dry, sunny weather. The bulbs are removed carefully so as not to damage them. The soil is removed from them, carefully inspected, and damaged ones are removed.
Selected vegetables are dried in a dry, ventilated place for several days. If you properly prepare the crop for storage, rot will not appear.
Storing vegetables in one large pile makes it difficult to ventilate them and shortens the storage time. Store dried onions in small boxes or cardboard boxes. A layer of 25-30 cm is poured into each box. Holes are made in the side walls for air access.
Braiding onion heads is a time-tested storage method. Wicker onions have a decorative appearance, are well ventilated, and are also convenient to inspect for damage. Braids can be stored in the kitchen for 1-2 months.
Read also:
What to do if potatoes rot in the cellar, why does this happen.
Why pepper rots on the bush: identifying the cause of the problem.
Why does the pumpkin rot in the garden, what to do about this problem.
Prevention of rot during storage
To avoid spoilage of onion stocks, the heads are inspected from time to time and those that have begun to deteriorate are removed.
Advice. Use sharp varieties of onions for winter storage. They are the ones that last the longest.
Only hard and dry heads, fully protected by dry scales, are sent to storage.
For long-term storage over several months, a cellar or basement with a temperature of +1 to +5°C is suitable. Optimal humidity levels are 50-75%.
Another secret to long-term storage without loss is sorting the heads by size. Medium onions last the longest; large and small ones are more susceptible to spoilage.
How to preserve onions if they start to rot? Carefully sort and place healthy heads in clean, dry boxes. Remove all bulbs with the slightest signs of rot.
Conclusion
The appearance of areas of rot is the main cause of crop losses when growing and storing onions. Pre-sowing treatment of the seedlings, adherence to crop cultivation technology and thorough drying of the bulbs before storing them for winter will help to avoid problems.