Where did onion grief come from: why do we cry when we cut onions?
Onions are one of the most widespread vegetable crops on the planet. It is used not only in cooking, but also as a traditional medicine for colds.
Anyone who has ever “undressed” this multi-layered vegetable knows firsthand about the “onion mountain”. Burning onions can make even the toughest men cry. Let's figure out why we cry when we cut onions, and what secrets are hidden in the long-known sharp onions among the people.
Description and history of the origin of the onion
Onion is a genus of perennial and biennial plants of the Amaryllis family. (Amaryllidaceae), including more than 900 different species. Among them, about 25 species are used for food, each of which includes up to 20 different varieties. There are also types of decorative onions, for example, giant onions and Christoph's onions.
Onions are used not only for food and decorative purposes, but also for obtaining medicines and dyes. There are wild poisonous species of this plant.

The first historical evidence of onion cultivation dates back to 4000 BC. This fragrant plant was popular in Ancient Greece, Ancient Rome, Egypt, India, and Ancient China. Hippocrates, Aristotle, Paracelsus and other scientists and doctors of the past mentioned onions in their writings as a medicinal plant. The feathers and bulbs of the plant were used in religious rites; their pungent smell was believed to ward off evil spirits.The ancient Romans believed that tears from onions would remove bad spirits from the body.
Onions came to the territory of Rus' in the 12th-13th centuries thanks to trade with the Byzantine state. Then the fragrant vegetable was used as a folk medicine; it was also used to make protective amulets and amulets against damage, the evil eye and evil spirits. From the banks of the Danube River, different types of onions spread throughout the territory of the ancient Russian state.
Onion species widespread in Russia (Allium cepa), which is used as a spicy seasoning for soups, side dishes, salads, meat and fish dishes.
It can be useful:
Onion hair masks for the treatment of baldness
How to eat onions for weight loss: recipes for dietary dishes
Chemical composition of bulbs
It was not without reason that ancient scientists considered onions to be valuable medicinal raw materials. The juicy pulp of onions contains a number of useful vitamins and minerals.
| Biologically active nutrient | Amount per 100 g of fresh onion pulp | % of recommended daily intake |
| Vitamin E | 0.2 mg | 1% |
| Vitamin C | 10 mg | 11% |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.05 mg | 3% |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.02 mg | 1% |
| Vitamin B5 | 0.1 mg | 2% |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.12 mg | 6% |
| Vitamins N | 0.9 mcg | 2% |
| Vitamin PP | 0.7 mg | 4% |
| Vitamin B9 | 9 mcg | 2% |
| Potassium | 175 mg | 7% |
| Calcium | 31 mg | 3% |
| Magnesium | 14 mg | 4% |
| Sodium | 4 mg | 0% |
| Sulfur | 65 mg | — |
| Phosphorus | 58 mg | 7% |
| Chlorine | 25 mg | 1% |
| Bor | 200 mcg | — |
| Iron | 0.8 mg | 4% |
| Iodine | 3 mcg | 2% |
| Cobalt | 5 mcg | 50% |
| Manganese | 0.23 mg | 12% |
| Copper | 0.09 mg | 9% |
| Fluorine | 31 mcg | 1% |
| Chromium | 2 mcg | 4% |
| Zinc | 0.85 mg | 7% |
In addition to biologically active components, onion pulp contains 3 g dietary fiber, 8.2 g carbohydrates, 0.2 g fat and 1.4 g protein.

Cause of tearing when cutting onions
Proteins are the reason why we cry when we cut onions. The structural components of proteins - amino acids - are always present in cell sap, of which cysteine and methionine contain sulfur in their chemical structure.
When the integrity of the cell membrane is violated, a number of intracellular enzymatic reactions are triggered, as a result of which 1-propenesulfenic acid is formed from sulfur-containing amino acids. This acid is converted to 1-sulfinylpropane, a volatile, unstable compound called a lachrymator. When lachrymator reacts with water on the surface of the mucous membrane of the eyes, nose or mouth, sulfur-containing acids and disulfides are formed, which cause irritation and burning.
The paradox of “onion grief” is that, when the mucous membrane of the eyes is reflexively irritated, tear fluid is released, but the more tears, the more fluid and the more disulfides are formed from 1-sulfinylpropane, and the more the eyes water. This biochemical mechanism was developed by the plant during evolution to protect itself from being eaten by animals.
Small amounts of disulfides formed in the mouth when eating fresh onions give this vegetable its pungency and pungency., which stimulates appetite and the secretion of gastric juice.

Possible dangers and precautions when cutting onions
When the lachrymator acts on the mucous membranes, an insufficient amount of sulfur-containing acids and disulfides is releasedto harm human health. The amount of acid produced is negligible (less than 0.01%), while the tear fluid contains neutralizing substances that protect the eyes from aggressive environments.
A few minutes after contact with the volatile substances of onion juice, the normal pH of the tear fluid is restored, but the eyes hurt for some time even after rinsing. The severity of pain is individual and depends on the degree of sensitivity. The eye membranes and mucous membranes cannot be harmed by onions unless there is an individual intolerance or allergy.
In case of allergies, intolerances or hypersensitivity Be careful when chopping onions:
- Use safety glasses and gauze moistened with water to protect the mucous membranes of the eyes, nose and mouth from volatile substances.
- Ventilate the room.
- After slicing, thoroughly wash your hands, knife and cutting board.
If drops of onion juice come into contact with the sensitive mucous membranes of the nasal cavity, it is washed with a 1% solution of baking soda. In case of contact with eyes, wash them with regular running water. If an immediate allergic reaction develops - anaphylactic shock, swelling of the larynx with obstruction of the airways, call an ambulance immediately.
Read also:
Scientific research on “onion grief”
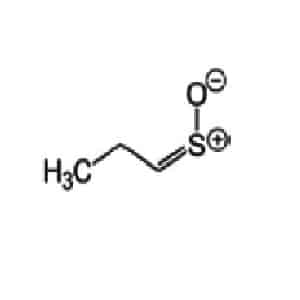 The chemical composition of the tear substance released when cutting onions was studied by an American chemist from Texas, Eric Block, who wondered why onions make people cry. During the experiments, Block encountered the difficulty of determining the chemical composition of the lachrymator, since 1-sulfinylpropane is unstable and instantly decomposes in water. Eric Block also determined which acid is formed in onions as a precursor to 1-sulfinylpropane.
The chemical composition of the tear substance released when cutting onions was studied by an American chemist from Texas, Eric Block, who wondered why onions make people cry. During the experiments, Block encountered the difficulty of determining the chemical composition of the lachrymator, since 1-sulfinylpropane is unstable and instantly decomposes in water. Eric Block also determined which acid is formed in onions as a precursor to 1-sulfinylpropane.
Scientists from Case Western University in Ohio have determined the structure of the enzyme that triggers the synthesis of lachrymator in onion cells. Thanks to this research, Japanese breeders, together with colleagues from New Zealand, developed an onion variety without a lacrimogenic enzyme, which can be cut without shedding tears. It is noteworthy that such onions not only do not cause tearing, but also do not have the characteristic pungent odor and bitterness.
The mechanism of lachrymator formation and the complete chain of chemical transformations occurring in onion cells during damage to the membranes was studied by Dwayne Mellor, a senior lecturer at Coventry University in the UK. The scientist notes that not all types of onions cause lacrimation during cutting, and the pungency of the onions depends on the amount of sulfur absorbed by the vegetable from the soil. Therefore, on soils rich in salts of sulfur-containing compounds, the most pungent and “evil” onions grow.
Duane Mellor, in his study based on the study of different varieties of onions, concluded that sweet, red salad varieties contain fewer sulfur compounds than classic white onions and, accordingly, are less irritating to the eyes when cutting.

Sensitivity to onion lachrymator
Why don't onions sting everyone's eyes? The reason lies in the individual structural features of the visual apparatus. Statistically, men have fewer receptors on the surface of the skin and mucous membranes, so they can more easily endure irritation when cutting onions. The older a person is, the thicker the surface of the epithelium of the mucous membranes and the lower the sensitivity to irritating factors.
The response to onion lachrymator varies in various eye diseases. With keratoconjunctivitis sicca, called dry eye syndrome, sensitivity to sulfur compounds in onion juice is sharply reduced until it disappears completely. In inflammatory and infectious processes, on the contrary, there is an increased secretion of tear fluid in response to lachrymatory substances.
How to cut onions without tears
In addition to using safety glasses and gauze, experienced cooks We recommend using the following simple lifehacks for chopping onions:
- Use a sharp knife. If the knife is not sharpened enough, the onion cells are crushed, releasing more onion juice and more lachrymator.
- Soak the bulbs for half an hour in cold water. Water decomposes the sulfur-containing lachrymator, so less of it is released when cutting.
- Wet the knife with water while slicing. The principle of operation of this life hack is the same as in the previous paragraph: water decomposes 1-sulfinylpropane. The more contact the bulb has with water, the fewer tears.
- Chop onions under a hood or fan. Directed air flow will reduce the concentration of volatile compounds in the air.
- Do not cut the onion to the spine. More sulfur compounds accumulate at the base of the bulb, so this part causes more tearing.
Practice shows that some folk methods of reducing lacrimation when cutting onions are ineffective:
- take water into your mouth while slicing;
- grease the board with lemon juice or sprinkle with salt;
- light a candle next to the cutting board;
- plug your nostrils with cotton wool;
- talking or singing while cutting.
Using a scientific approach, rather than old superstitions, you can minimize discomfort when preparing your favorite dishes with onions.
Conclusion
Bringing tears to those who decided to “add onions” is a plant’s defense mechanism developed in the process of evolution. The cause of lacrimation when cutting onions is the lachrymator substance 1-sulfinylpropane, produced from cysteine and methionine during enzymatic reactions.
Lachrymator decomposes with water on the surface of the mucous membrane of the eyes with the formation of a small amount of sulfur-containing acids. These compounds are instantly neutralized by the components of the tear fluid, without harming health, but they disrupt the pH that is comfortable for the eyes.
To make cooking your favorite dishes enjoyable, use a sharp knife, soak the onions in water before cutting, work under a hood and do not cut the onion to the root. If you are intolerant or allergic to onions, use personal eye and respiratory protection.