Calorie content and nutritional value of buckwheat per 100 grams
Buckwheat has two beneficial properties: nutritional value and moderate calorie content. In terms of protein content, it is considered the leader among all cereals, and in nutritional value it is second only to oatmeal. Therefore, buckwheat dishes are useful for people who play sports and lead an active lifestyle. From this article you will learn how many calories are in 100 grams of buckwheat and what valuable substances it contains.
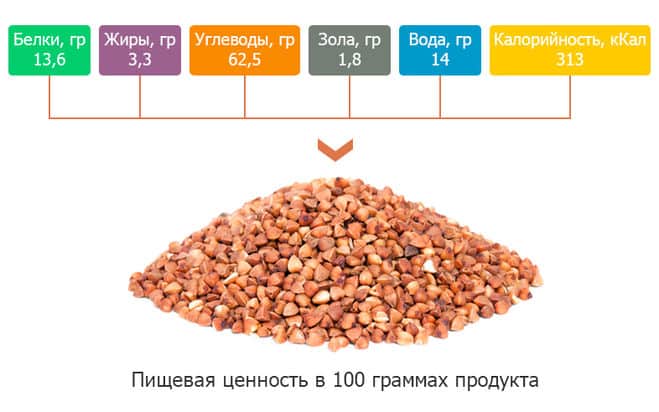
Calorie content and nutritional value of buckwheat per 100 g
There are three types of dry buckwheat: kernel, done and cereal. The kernel is a whole grain, peeled from the husk, and is most often used to prepare crumbly porridges. Prodel, otherwise called chaff, is crushed and crushed cereal. Dishes made from it are more tender and homogeneous. Cereals are more suitable for children's menus and nutrition for the elderly.
The calorie content of the core is higher than that of the limit and flakes, and varies from 305 to 350 kcal. It depends on the quality of the grain and the type of cereal. For characterization we will use the average indicator.
Reference. The calorie content of dry buckwheat is 313 kcal per 100 g. The protein content is 12.6 g, carbohydrates - 62.1 g, fat - 3.3 g.
The nutritional value of cereals changes during the cooking process. When cooked, it swells approximately three times, respectively, and the calorie content is distributed over 300 g of the finished product. The more water you take for cooking, the lower the calorie content of 100 g of porridge will be.
Reference. The calorie content of boiled buckwheat using 200 ml of water and 100 g of cereal is 104 kcal per 100 g of finished product. BJU of boiled cereal: proteins - 4.2 g, carbohydrates - 20.7 g and fats - 1.1 g
The energy value of the dish increases if you cook it using milk and butter. Salt does not affect calorie content.
When cooking The amount of fiber is reduced almost threefold, and vitamins remain in minimal quantities. To preserve beneficial substances, it is recommended to steam buckwheat with boiling water. To do this, you need to rinse the cereal and pour hot water overnight, for example, in a thermos.
Reference. The calorie content of steamed buckwheat using 300 ml of water per 100 g of cereal is 78.3 kcal per 100 g of the finished product. Protein content – 3.2 g, carbohydrates – 15.5 g and fat – 0.8 g.
Buckwheat suitable for dietary nutrition. It does not contain simple carbohydrates that contribute to excess weight. The complex carbohydrates included in its composition release energy gradually during digestion. Thanks to this, there is no feeling of hunger for a long time.
Buckwheat is considered the leader in protein content among cereals. 100 g of ready-made porridge accounts for 5.6% of a person’s daily requirement. Proteins are highly digestible, which makes this cereal indispensable in the diet of athletes for the development of muscle mass.
Porridge contains a minimal amount of fat - only 1.3% of the daily requirement. There are no harmful saturated fats at all.
The high fiber content (about 10.5%) helps buckwheat to effectively cleanse the body, helping to normalize digestion.
Buckwheat is not considered a cereal crop because it is the seed of the buckwheat flower. Therefore, buckwheat protein, unlike wheat, does not contain food allergies. gluten.
Composition of cereals

The content of vitamins in buckwheat is within the range typical for grain crops. Cereals are rich in B vitamins, which, when consumed together, enhance each other’s effects. These vitamins do not accumulate in the body and must be taken daily.
In terms of the amount of B1, cereals are ahead of many other products of plant origin. The main function of B vitamins is to maintain the normal functioning of the nervous and immune systems.
| Name | Amount of mg per 100 g of dry product | % of daily value |
| Vitamin B1 | 0,43 | 28,7 |
| Vitamin B2 | 0,2 | 11,1 |
| Vitamin B6 | 0,4 | 20 |
| Vitamin B9 | 0,032 | 8 |
| Vitamin PP | 7,2 | 36 |
| Vitamin A | 0,002 | 0,2 |
| Vitamin E | 0,8 | 5,3 |
Buckwheat contains the maximum amount of vitamin PP, compared to other cereals.. When consumed, blood circulation processes improve, blood vessels dilate, and the body is cleansed of toxins.
The set of micro- and macroelements in cereals is also diverse. Thanks to the high magnesium content, metabolism is normalized and sugar levels are regulated. Sodium, potassium and silicon maintain water-salt balance in the body. High iron levels prevent anemia. And phosphorus, like calcium, affects the formation of the bone skeleton.
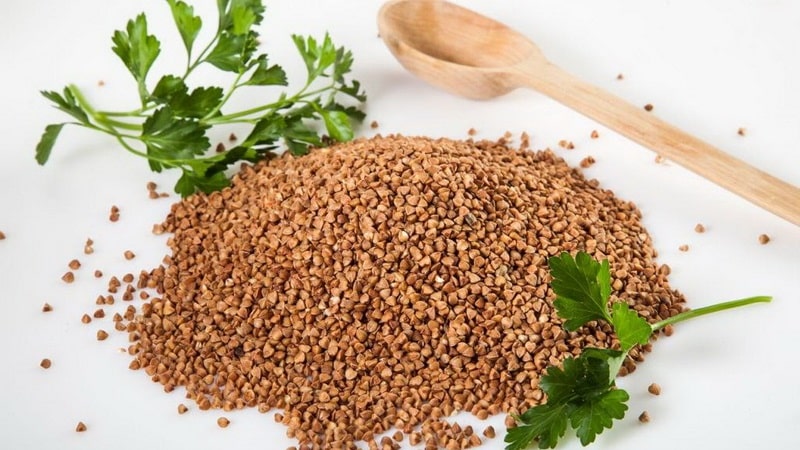

| Name | Amount of mg per 100 g of dry product | % of daily value |
| Macronutrients | ||
| Potassium | 380 | 15,2 |
| Calcium | 20 | 2 |
| Sodium | 3 | 0,2 |
| Magnesium | 200 | 50 |
| Phosphorus | 298 | 37,3 |
| Silicon | 81 | 270 |
| Microelements | ||
| Iron | 6,7 | 37,2 |
| Zinc | 2,05 | 17,1 |
| Iodine | 0,003 | 2,2 |
| Copper | 0,64 | 64 |
| Manganese | 0,156 | 78 |
| Chromium | 0,004 | 8 |
| Cobalt | 0,003 | 31 |
| Molybdenum | 0,034 | 49,1 |
Buckwheat protein, unlike the protein of other cereals, contains amino acids of non-plant origin. This composition is found in meat and dairy products. Cereals contain three of the eight amino acids important for metabolism: lysine, threonine and tryptophan.
Lysine is involved in the formation of collagen, which repairs damaged body tissues.A deficiency of this amino acid leads to weakness, fatigue, and decreased muscle mass. Threonine is important for maintaining muscle function. Tryptophan is used to synthesize the “happy hormone” serotonin; its deficiency leads to depressive disorders.
Buckwheat also contains essential amino acids. The body cannot synthesize them on its own, but receives them only from food. These include valine and isoleucine. The valine content in buckwheat has a calming effect, reduces insomnia and nervousness. Isoleucine normalizes sugar levels, increases the body's endurance and accelerates muscle growth.
Conclusion
The content of macro- and microelements, amino acids and B vitamins allows the use of buckwheat in therapeutic diets for anemia, diabetes, and obesity. And the high content of protein and complex carbohydrates helps athletes and people leading an active lifestyle maintain muscle shape.