What to do if potatoes burst and crack in the ground, why does this happen?
Sometimes, when harvesting, gardeners notice that individual potato tubers are deformed and look unattractive. There are many reasons for this phenomenon - from non-compliance with agricultural technology to crop diseases. Let's take a closer look at why potatoes burst in the ground and whether it is possible to save the crop in such a situation.
Why do potatoes crack or burst in the ground?
There are many reasons for the appearance of cracks in potato tubers: the results of diseases or attacks insect pests, violation of agricultural practices, influence of weather conditions.
Potatoes that have cracked in the ground when stored can cause contamination of the entire crop.

Sudden change in temperature
One of the main reasons for the formation of cracks in tubers is often unfavorable weather during the formation of the underground part of the vegetable.
A sharp transition from drought to prolonged rains and cool temperatures increases the liquid content of potatoes. Because of this, the pulp cells begin to grow more actively, unlike the peel, which cannot withstand pressure and bursts. Later, the injury site heals, forming defects in the form of cracks.
Poor quality planting material
The tuber culture is prone to rapid degeneration. Each subsequent harvest, in the absence of an annual change of seed material, is increasingly exposed to infection by pathogens.
Potato tubers change shape, the skin deteriorates, and yield decreases. As a result, low-quality planting material becomes prone to cracking.
Violation of agricultural technology
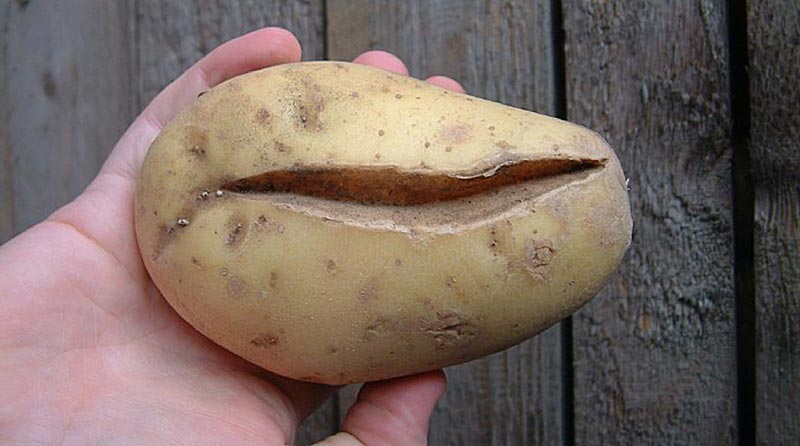

To preserve the quality of the crop, it is important to comply with all requirements of agricultural technology.
The reason that potatoes crack in the ground is failure to comply with:
- light mode;
- watering regime;
- disembarkation dates;
- wrong choice of soil type.
If planting material was introduced into the soil before it warmed up to +8°C, the green mass of plants will stop developing and there will be no harvest.
Diseases
Potato diseases are different: some affect only the underground part, while others have a detrimental effect on the tops and tubers. If prevention is not taken care of in a timely manner, the crop is at risk of cracking.
Attention! Some types of pathogens remain in the soil for several years and only when favorable conditions begin to actively multiply, affecting the crop.
Diseases, causing deformation of potatoes:
- fungal (scab, late blight);
- bacterial (ring rot, blackleg);
- viral (mottling, wrinkled mosaic, curling).
Diseases are often brought to the site along with infected planting material.
There are non-parasitic problems. As a rule, they arise under the influence of unfavorable physicochemical cultivation conditions. These include:
- lack or excess of nutrients;
- mechanical damage.
Pests
Dark spots, rotten pulp, burst and deformed skin on tubers are a consequence of vital activity nematodes, living in the ground and parasitizing potatoes.It is impossible to detect the pest, and signs of its presence appear only when the infestation reaches its maximum.
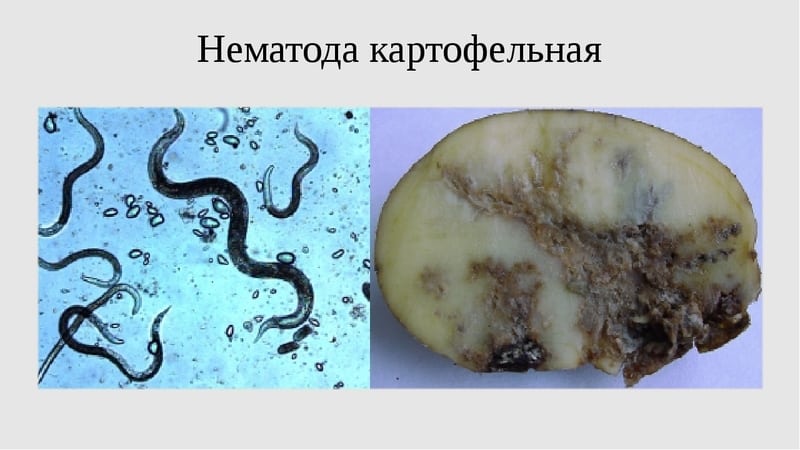
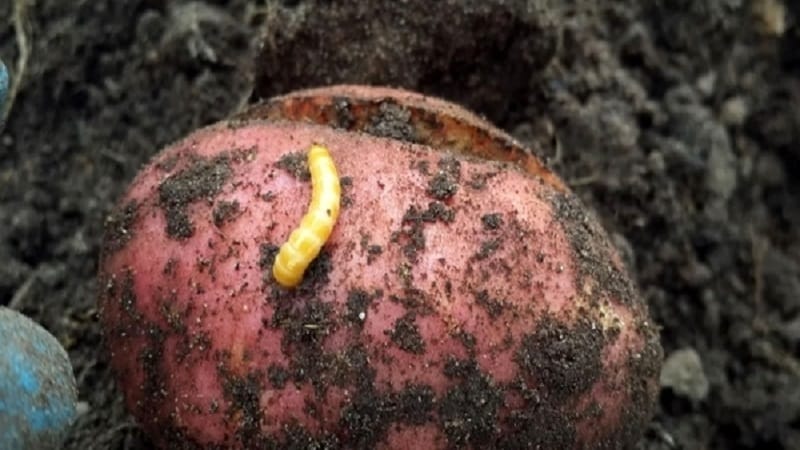
Another source of cracks in tubers is wireworms, which also affect the potato pulp, leaving thin passages inside it. Mole crickets can cause the peel to burst and deteriorate. When they encounter a culture, they gnaw through the core, thus making a way through it.

Unsuitable or clayey soil
The formation of proper potatoes is influenced by the ability of the soil to pass water and air.
Heavy clays and loams retain high humidity for a long time, but they have little oxygen. This leads to the fact that the roots of the plant do not receive enough nutrients, and because of this, the tubers lose their standard shape, burst and crack.
Important! The culture develops well in sandy loam, loose and light soils.
Sandy soils lose water very quickly, which does not have the best effect on potatoes, which will not grow well in such conditions.
Incorrect watering mode
A sure way to ruin the future harvest is to incorrectly water.
Failure to comply with the irrigation regime in dry weather conditions leads to cracking and rotting of tubers. Uneven flow of liquid into the soil contributes to improper formation of potatoes.
The negative effect on crop quality is enhanced if liquid accumulates in the ground faster than it drains. Most often, an incorrect watering regime causes cracking of early varieties of potatoes.
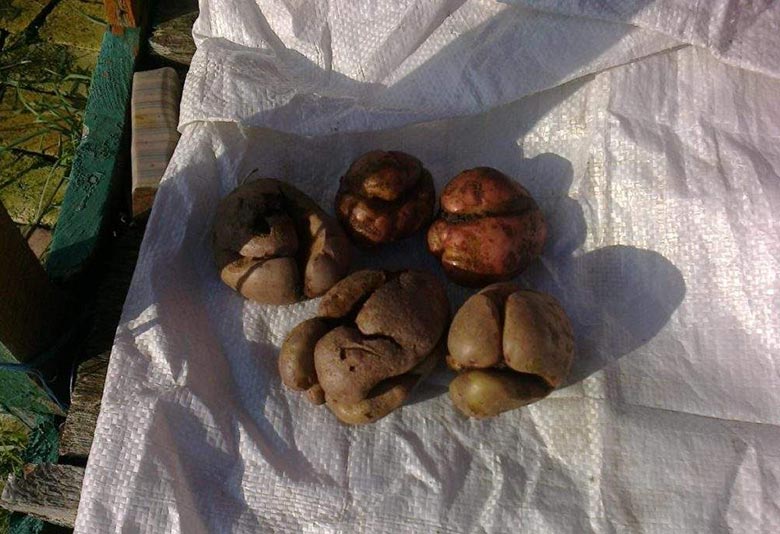

Methods for removing factors that negatively affect potatoes
Preventing tuber cracking is effective only with an integrated approach.Selective application of recommendations in practice will not help remove factors that negatively affect culture.
The development of agricultural technology together with the suppression of the vital activity of pathogens and pests helps to obtain high-quality results during prevention.
If soil contamination becomes known even before potatoes are planted, it is better to assign quarantine status to the site. The harvest collected on such land is not transported or sold. The potatoes themselves are not grown in this place for up to 3 years.
How to prevent cracks in potatoes
It is quite possible to prevent improper growth and deformation of tubers.
To do this, it is necessary to observe a set of preventive measures related to proper agricultural cultivation techniques and prevent the occurrence of diseases and pests.
Proper agricultural cultivation technology

The following measures will help to obtain high yields and protect crops from pathogens and insects:
- Careful selection of planting material. Potatoes grown from varieties with immunity to pests and diseases will be the most resistant to cracking. The tubers should be no smaller than a chicken egg, without signs of infection or deformation.
- Compliance with crop rotation, which consists of alternating with other crops.
- Planting a barrier strip of vegetables. This prevents the migration of pathogens.
- Selection and preparation of suitable soil. To do this, dig up the ground, add rotted sawdust and coarse sand (one 10-liter bucket per 1 m2), reduce acidity with ash, chalk or lime, plant green manure after harvesting.
- Compliance with the irrigation regime. In hot summer conditions, moisturizing is carried out up to 2 times a week.The crop becomes especially sensitive to moisture during the period of vegetative mass accumulation. After tubers form, the intensity of watering is reduced.
Loosening the soil, removing weeds and fertilizing potatoes are also included in the list of agrotechnical measures.
Disease Control
Potato skins are a habitat for pathogens that often remain dormant throughout the winter.
Therefore, before planting, tubers must be treated with fungicides:
- "Fitosporin";
- "Colfugo Super";
- "Phenorama Super";
- "Vitaros";
- "Mancozeb";
- "Maxim"
- "Wistom";
- "Bactofit".
Fungal diseases will be eliminated by spraying the planting material with Bordeaux mixture (100 g of copper sulfate and 150 g of quicklime per 10 liters of water) or a copper solution (1 tbsp. powder per 1 liter of water).
Pest Control
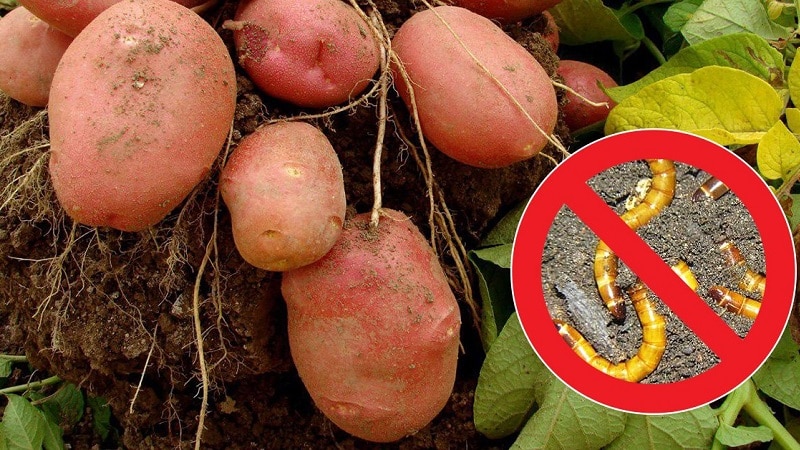

Destroying pests that can lead to cracking of tubers begins before planting material is introduced into the soil.
Treatment with drugs will help get rid of nematodes:
- "Nemagon";
- "Phosfamide";
- "Carbation";
- "Bazudin."
Store-bought chemicals “Actofit” or “Entocid” will prevent the reproduction of mole crickets and wireworms.
Important! Enriching the soil with earthworms and replacing cow manure with bird manure will help in the fight against insect pests.
Plants with an insect-repellent smell are planted next to potatoes: garlic, coriander, marigolds and chrysanthemums.
Additional recommendations
In addition to standard methods of dealing with the problem, there are a number of additional tips that will help protect tubers from cracking:
- Bringing the seed to a state of uniform greening of the skin.
- Select a well-lit area.
- Triple hilling: with tops up to 10 cm in size, 2 weeks after the first and before the buds bloom on the green mass.
- Proper watering. If weather forecasters do not predict a dry summer, 2 waterings will be enough for the bushes for the season (a week after emergence and at the beginning of tuber formation).
- Loosening the soil after moistening.
- Providing drainage in case of regular heavy rainfall.
- Timely removal of weeds.
- With small plot sizes, alternating not crops, but potato varieties with different ripening periods.
- Cleaning and destruction of diseased bushes, including burning.
- Autumn deep digging of soil and planting of green manure.
What to do with cracked and burst potatoes
There are many statements that it is pointless to store deformed potatoes: not only will they not last long, but they will also be dangerous for healthy crops in the cellar.
Experience shows that cracked or burst tubers are perfectly stored in dry rooms and are still suitable for consumption.
Is it possible to eat this and save it?

Cracked potatoes without signs of rot or disease can be eaten without fear, but first of all. Appearance has no effect on taste.
Important! The cracked tubers are used to feed domestic animals, but are never used for planting.
To reduce the risk of contamination of the rest of the crop, the cellar is cleaned, whitened with lime and disinfected before planting. Deformed specimens are stored separately. For greater safety, bursting potatoes are treated with Alirin-B or Gamair.
Conclusion
The problem of cracking and deformation of potatoes is completely solvable.They approach its elimination in a comprehensive manner: they follow the rules of agricultural technology, monitor the condition of the soil and the level of moisture, and carry out the prevention of infection and the spread of pests on the site.
Store damaged specimens in a clean, dry cellar separately from the rest of the crop and use them as food first.