Is it necessary to pinch bell peppers: arguments for and against, a guide to the correct formation of a bush
Bell pepper is a capricious crop, demanding on climatic conditions, soil composition and care. It is not easy for an inexperienced gardener to grow a rich harvest on his plot.
One of the recommended methods for increasing yield is pinching bushes. The article will tell you whether you need to pinch bell peppers and how to do it correctly.
Do I need to pinch bell peppers?
There is no clear answer to this question. Those who cultivate this vegetable make decisions based on the purpose and growing conditions, as well as the characteristics of the variety. First, let's figure out why pinching is done in general.

The meaning of the procedure
Pinching involves removing the apical buds (growth points). This is one of the agricultural techniques aimed at shaping the plant along with removing excess shoots and foliage.
Important. Thanks to pinching, upward growth is stopped and the development of stepsons is activated, which give the bush a spherical appearance.
Pinching is carried out to stop the growth of new stems. Thus, the bush directs all its forces to the ripening of already formed fruits. If this is not done, then the plant will form many small and thin-walled fruits.
Varieties that require pinching
Domestic and foreign breeders have developed a wide variety of crop varieties. Some of them need to be pinched. In this case, the seed manufacturer directly indicates on the packaging how and when to form a bush.

These are, for example, vigorous hybrids that grow up to 2-3 m in height. The bushes of these plants have lush greenery and without formation they will grow and develop poorly. These varieties include Aries, Bosun, Orange miracle, Forward, Elephant, Bourgeois, Merchant.
Important. All varieties of sweet pepper are divided into indeterminate (having no restrictions on the growth of green mass) and determinate (the growth of the bush stops during the fruiting period).
Indeterminate crop varieties need to be shaped to limit growth green mass, better ventilation and accelerated fruit ripening.
Small determinate varieties form compact bushes 60-70 cm high. These are, for example, Brother Fox, Eroshka, Chardash, Pinocchio F1. They do not require mandatory formation and, if the growing technology is followed, they grow well and bear fruit without pinching.
Attention. With thickened plantings of determinants, the formation of bushes still needs to be carried out. This will provide air and light access to all plants.
Compact ornamental varieties also do not need growth restrictions, intended for growing on balconies and window sills. These are varieties such as Treasure Island, Watercolor, Curiosity, Carat, Etude. Medium-sized bushes should be removed only from barren shoots, which will improve their lighting and natural ventilation.

In what cases is pinching necessary?
When answering the question of whether to pinch or not, it is also worth taking into account weather conditions. With high humidity combined with high air temperature, the formation pepper bushes are carried out to prevent fungal diseases.
If the summer turns out to be dry and hot, then you should not thin out the green mass of bushes. Lush foliage shades the bushes from the sun and prevents the evaporation of soil moisture.
If you don't pinch the peppers
Neglecting the pinching procedure when growing tall varieties leads to the following consequences:
- poorly developed root system - as a result, the bush receives insufficient water and nutrients;
- decrease in yield indicators - new shoots grow from internodes, on which additional fruits are formed;
- without pinching, tall varieties actively increase green mass, the bush grows powerful, and the fruits become small and thin-walled;
- Without shaping, the bushes grow greatly, they become crowded, and the plants begin to hurt.
If the seed manufacturer recommends shaping the plants, you should not ignore these recommendations.
Timing of the procedure
They begin to pinch off the tops after 5-7 leaves appear.. As a rule, at this time the bushes grow to 15-20 cm and begin to branch, dividing into two branches.
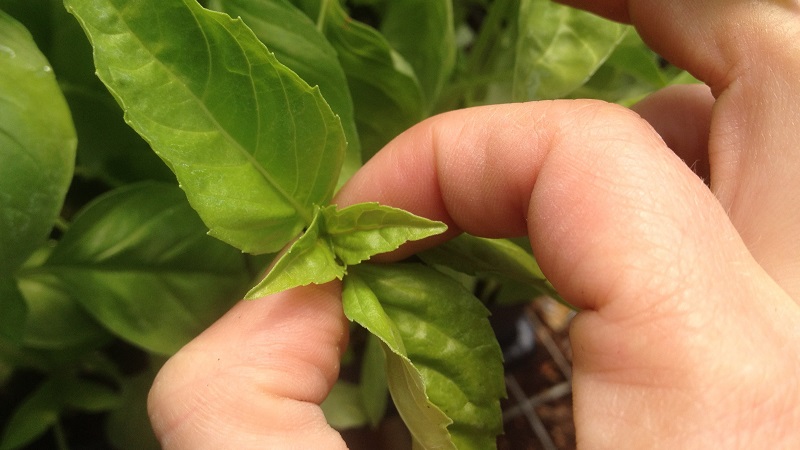

A crown bud appears at this fork, which is removed to allow further development of the bush.. Each branch will form fruits and due to this the overall harvest will increase.
Attention. If you want to get pepper seeds, then leave the crown bud on 1-2 bushes. It produces the healthiest seeds.
Immediately after picking or transplanting the plant, you should not disturb it.. After all, pinching is a trauma for the bush and the plant does not need additional tests during this period.
Another sign that it’s time to start shaping – staining of the internode.
It can be useful:
Rules for planting peppers: preparation, timing and nuances of the process
Step-by-step instruction
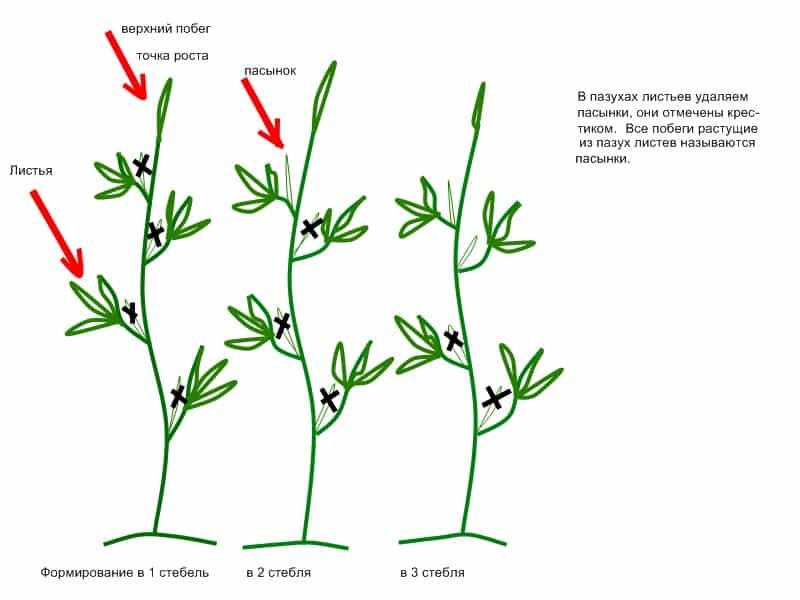
Pinching is a long process that continues until the bush grows to the desired height.. Schemes for forming plants into one, two and three stems are included.
There are several stages in the formation of a pepper bush:
- Pinching the crown bud at the first fork of the stem. This bud contains an inhibitor substance that does not allow the bush to fully bear fruit. When planting early, in order to slow down the growth of the plant, the bud is left for a while.
- Pinching off excess stems. 2-3 main shoots are left on the bush, which fully develop and set the shape. Leave the strongest branches. Pinching will give impetus to the formation of lateral shoots that form the bush.
- Removing fruitless shoots and lower leaves. Barren branches and excess foliage shade the plant and take away nutrients. Their removal improves air circulation and light access.
- Pinching skeletal branches. Skeletal shoots are pinched after enough fruit has formed on the bush. On average, 20-25 fruits are left on one bush. Thanks to this, the peppers will grow larger and meatier. Formed bushes with fruits are shown in the photo.
Pinching is repeated as new stems grow.. No more than 2-3 leaves and no more than one stepson are cut from one plant per day. If you remove more at one time, the pepper may become sick and die.
Tips and tricks
Recommendations from experienced gardeners will help beginners avoid problems during the procedure.:
- the plant is formed gradually - if you remove all the excess stems at once, it will wither and die;
- stepsons are removed as soon as they appear;
- pinching is not carried out immediately after watering, while the plants are still wet, as there may be pathogens in the water;
- After the procedure, the plants are also not watered for several days - this way they will recover faster;
- removed stems and leaves are removed from the garden bed;
- form only healthy plants, sick ones may not survive the tests and die;
- use a sharp, disinfected instrument to remove stems and leaves;
- It is useful to treat the cut areas with crushed activated carbon for disinfection.
Conclusion
Forming bell peppers is the removal of excess growth points in order to increase productivity. Each gardener decides for himself whether to prune or not. At the same time, the varietal characteristics of the crop and growing conditions are taken into account.