How to grow currants on a trunk yourself: step-by-step instructions
A spreading berry bush is the most common form of currant in the garden. However, it may look different. The standard form can be grown in the form of a miniature tree, with a main trunk and a crown of fruit-bearing branches.
The formation procedure can be carried out with all varieties of berries: black, red And yellow.
Types of standard currants
Black currant got its name thanks to the dark color of the berries. Its fruits are the sweetest, however, such a berry plant will require more attention. In addition to standard procedures, the bushes need shelter from the winter cold, otherwise their fragile shoots will freeze out.
The most popular varieties for growing:
- Commemorative;
- Sibylla;
- Stork;
- Premiere;
- University;
- Monastic.
 Red Ribes also got its name from the color of the berries. It is considered the most unpretentious berry of the “family” - for good growth and a bountiful harvest, it only needs basic care. Due to its undemanding nature, beginners are recommended to start with it, and the following varieties should be considered as the first plantings:
Red Ribes also got its name from the color of the berries. It is considered the most unpretentious berry of the “family” - for good growth and a bountiful harvest, it only needs basic care. Due to its undemanding nature, beginners are recommended to start with it, and the following varieties should be considered as the first plantings:
- Red Cross;
- Rondome;
- Natalie;
- Accordion;
- Viksne;
- Chulkovskaya.
yellow currant In the modern agricultural market it is represented by the Imperial Yellow variety. It has large and juicy berries with golden skin. Such currants are distinguished by their aesthetic appearance - they are often planted on the site as an ornamental plant.
Pros and cons of standard form
The standard form has a number of significant benefits:
- uniform illumination;
- pest resistance;
- convenience of location on the site;
- the high position of the crown reduces the risk of infection with a fungal pathogen;
- ease of berry farming technology;
- ease of harvesting;
- beautiful appearance of the plant.
To the significant shortcomings should be attributed to: poor resistance to frost and relatively high invasiveness of the plant.
Self-cultivation of standard currants
A standard bush can be purchased or grown with your own hands. Landing on your own is a troublesome task, but the procedure is not considered particularly difficult. The whole process consists of preliminary preparation, planting a standard seedling and further formation of the crown.
Pre-landing activities
Preliminary preparation affects the planting site and the seedling.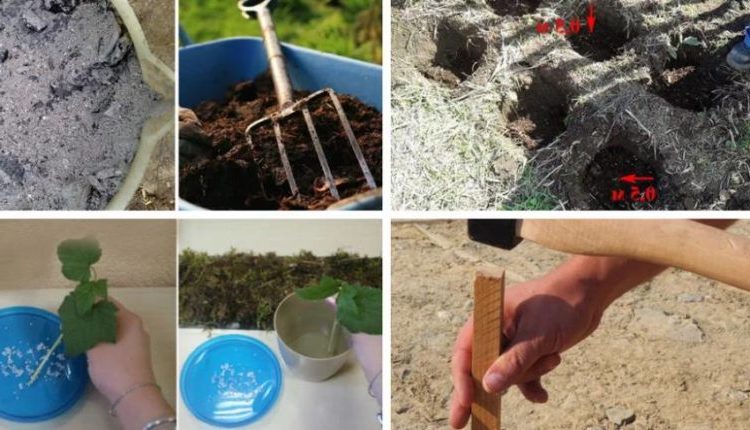
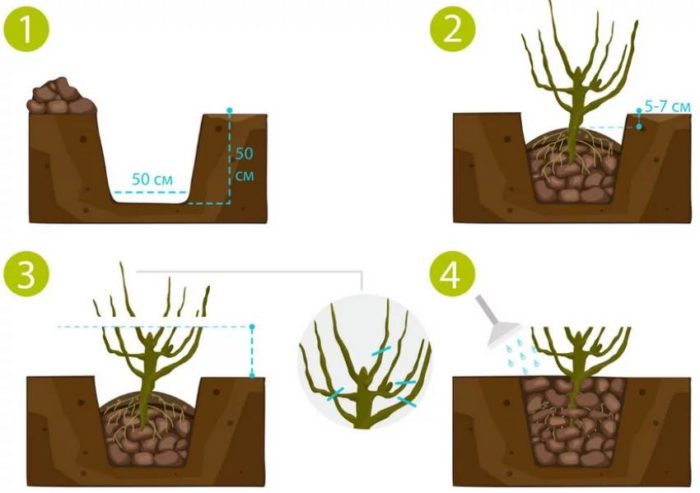
The selected area must be cleared of weeds and debris. The hole for planting must be prepared in advance: dig a hole (50 cm deep and 50 cm wide), put a nutrient mixture of compost (10 kg) and wood ash (200 g) on the bottom, drive in a support post (15 cm from the center of the hole).
For a seedling, the main attention falls on preparing the root system. The roots are carefully cleaned of soil and immersed in a solution of a root growth biostimulator for several hours. Experienced gardeners recommend a mixture of drugs such as Agromix Epin Maxi and Kornevin.
Planting seedlings
Step-by-step scheme for planting seedlings:
- place the seedling in the hole;
- straighten the rhizome;
- fill the space in the hole with water;
- fill the hole with soil;
- water again generously.
Formation of a trunk
The procedure for forming a currant trunk is carried out using two methods: own root and on a third-party rootstock.
You should consider the features of each method and determine the most comfortable and suitable one.
Rooted
For this method you only need a currant bush. The process itself is scheduled for early spring, trying to be done before the kidneys “awaken.”
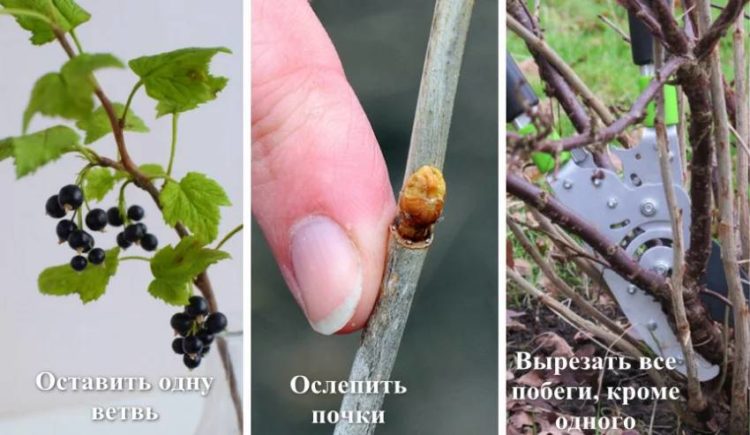
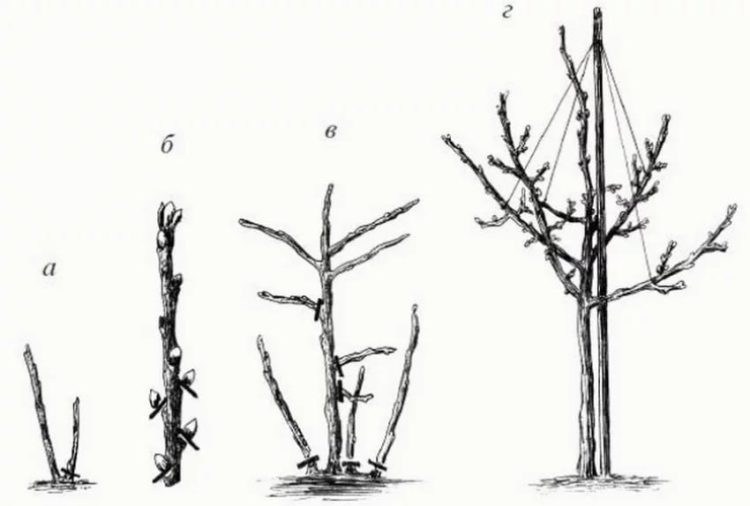
Step-by-step formation process:
- On the main bush, choose a straight shoot no shorter than 90 cm and pinch the top.
- The buds on the branch are blinding, leaving the top 4 intact.
- The remaining shoots are cut out.
- During the season, the lateral shoots are completely removed.
- The remaining buds are pinched over the third or fifth leaf.
- The following year the procedure is repeated.

On rootstock
Modern gardeners prefer to use the method on the rootstock. For the process, a suitable rootstock bush and scion cutting are taken. By the time the procedure is carried out, the rootstock should reach 80 cm with a tip thickness of 0.5 cm. Thinner shoots may not cope with the scion. The cutting itself must have 4 healthy buds.
Work algorithm:
- The buds on the trunk are blinding.
- The lower edge of the cutting and the upper edge of the scion are smoothly cut diagonally.
- The sections are carefully connected to each other.
- The junction is tightly wrapped with film or electrical tape.
- For the next 3 years, the lateral shoots on the scion are pinched after the 3rd leaf, and all shoots and buds on the rootstock are removed.
To grow standard currants, the rootstock method is often used. During the process, the trunk is completely cleared of side shoots, and the scion serves as the crown of the future tree. To successfully carry out the procedure, it is better to use copulation, which promotes faster fusion of the scion and rootstock.
Planted shrubs can also be converted into a standard form using the bush reconstruction procedure.
Bush reconstruction
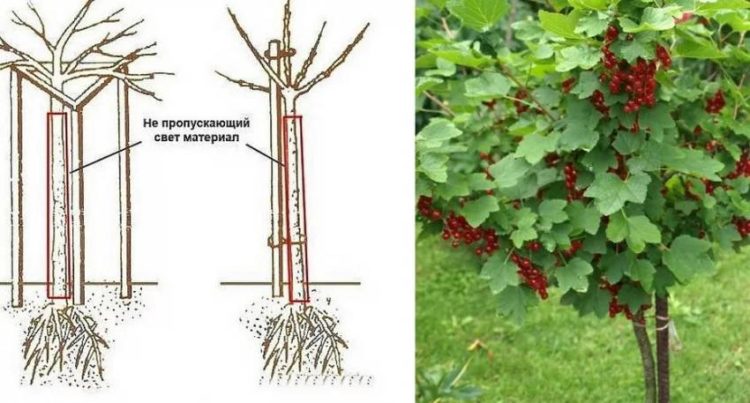
To transform an adult bush into a standard tree, you need to get rid of excess growth. The reconstruction process itself is carried out using two methods:
- using tubes, when after planting a special tight clamp is put on the root collar (this action prevents the growth of new shoots). The device covers the outer part of the neck and 5 cm of the underground part, does not allow light to pass through and prevents the formation of buds and branches;
- during planting, when a new seedling is immediately pruned with pruning shears, forming a trunk. The first 40 cm of the bush from the surface of the ground is cleared of shoots and buds; all shoots should be located only in the upper part. Then the upper buds are pinched to stimulate the growth of side shoots. The formed trunk is subsequently constantly cleared of growth.
Features of care
Standard-shaped currants require regular attention and careful agricultural technology. The main care measures are watering, feeding, crown formation and shelter for the winter.
Watering do not require a strict schedule; it is enough to monitor the drying of the soil and carry out the irrigation. The soil should remain moist to a depth of 1 m from the surface. The amount of water applied and the frequency of irrigation are affected by climatic conditions and soil composition. You cannot let the soil become too dry - currants do not tolerate drought.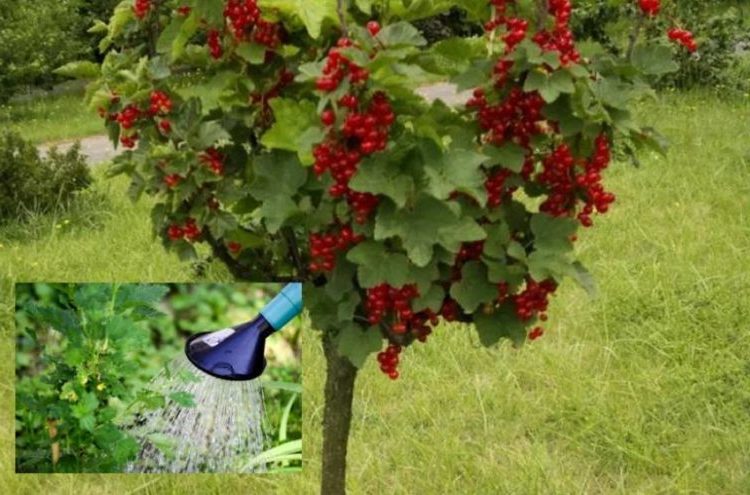
Feeding is applied according to the following schemes:
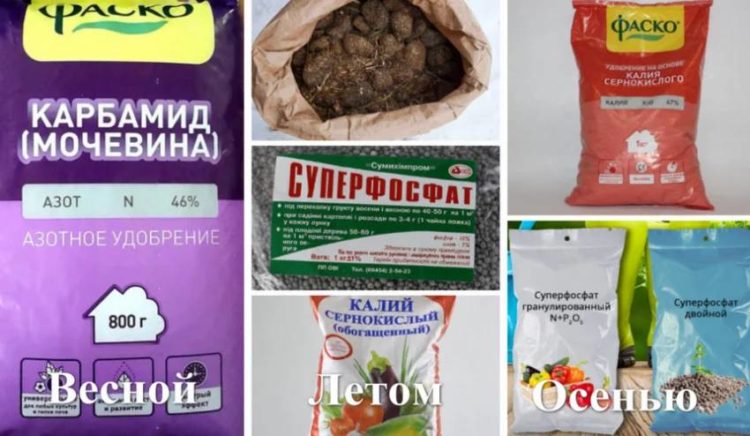
- At first spring - choice of 5 kg of compost or 50 g of urea (try not to exceed the indicated dose);
- in mid-summer - a dry mixture of half a bucket of rotted manure, 40 g of superphosphate and 10 g of potassium sulfate;
- at the beginning of autumn - a dry mixture of 50 g of superphosphate and 20 g of potassium sulfate.
 Formation during the first three years involves strengthening the standard form and specialized pruning. Detailed diagrams are presented above. After a 3-year period, the bush undergoes annual sanitary pruning. It is better to schedule the procedure at the beginning of spring in order to be in time before the moment of “awakening”. The following are subject to removal:
Formation during the first three years involves strengthening the standard form and specialized pruning. Detailed diagrams are presented above. After a 3-year period, the bush undergoes annual sanitary pruning. It is better to schedule the procedure at the beginning of spring in order to be in time before the moment of “awakening”. The following are subject to removal:
- old branches that no longer bear fruit;
- shoots randomly thickening the crown;
- injured sprouts;
- shoots with signs of disease;
- root shoot.
 The step-by-step process of pre-winter shelter is as follows:
The step-by-step process of pre-winter shelter is as follows:
- Cleaning and weeding of the tree trunk circle.
- Moisture-charging irrigation with a consumption of 40 liters of water per 1 sq.m.
- Wrapping the bush with agro-canvas.
How to propagate standard currants
Reproduction of the standard currant bush is carried out cuttings. The procedure is carried out in mid July in a certain order:
- A shoot with 5 buds is cut out from the central part.
- Plant the cuttings in the ground, deepening up to 4 buds.
- Water regularly.
- In autumn, the seedling is covered with spruce branches.
- In spring, the side shoots of the cuttings are blinding.
- At the beginning of summer, the bush is fertilized with nitrogen, in August - with potassium and phosphorus.
- The next year, the top of the central shoot is pinched at a distance of 90 cm to the ground, the lower buds are blinded, leaving only the 4 uppermost ones.
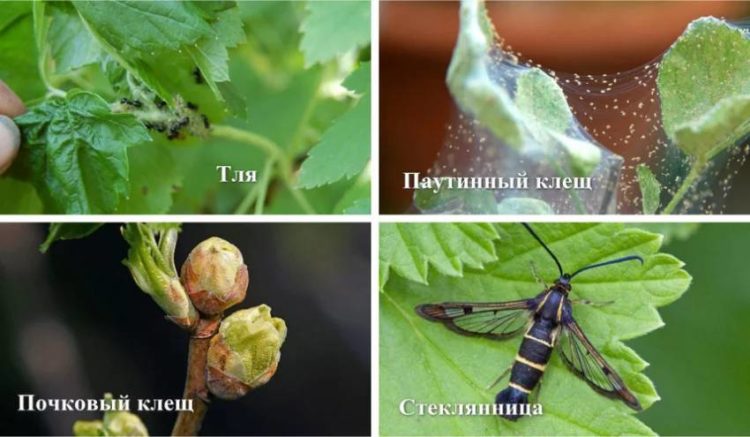
Diseases and pests: prevention and control methods
Currants have strong immunity, resistant to diseases and pathogens. However, some varieties are more susceptible to infections and parasites.The gardener should immediately respond to all signs of currant disease. The most dangerous diseases include:
- powdery mildew;
- anthracnose;
- glass rust;
- terry;
- septoria.
 Common pest species will be: aphids, spider mites, glass beetles, currant gall midges, bud mites, and berry sawflies.
Common pest species will be: aphids, spider mites, glass beetles, currant gall midges, bud mites, and berry sawflies.
 To reduce the risk of infection and spread of dangerous diseases and parasites, it is necessary to carry out preventive treatment and currant support.
To reduce the risk of infection and spread of dangerous diseases and parasites, it is necessary to carry out preventive treatment and currant support.
Effective preventive measures include:
- regular moderate watering;
- timely application of fertilizing and fertilizers;
- spring sanitary pruning;
- autumn digging of soil in the berry garden;
- spraying with specialized protective agents.
Conclusion
Growing standard currants is a troublesome undertaking that requires time and effort. However, the manipulations performed are not complicated and the process will most likely bring pleasure to the gardener. As a result, an ordinary bush will turn into a beautiful tree with juicy sweet berries.