Why do currants dry out along with the berries and what to do about it
Currant ripening begins in June and continues until August. Most gardeners grow several bushes at once - with red and black berries. Currants are distinguished not only by their bright taste, but also by their beneficial composition; they are especially rich in vitamin C. Caring for the bush is simple and does not require special skills. However, sometimes the bushes begin to wither, the leaves turn yellow and crumble, and the shoots and berries dry out. What to do in this case and how to find the cause, we will consider further.
Reasons for drying of currants and berries on branches and what to do about it
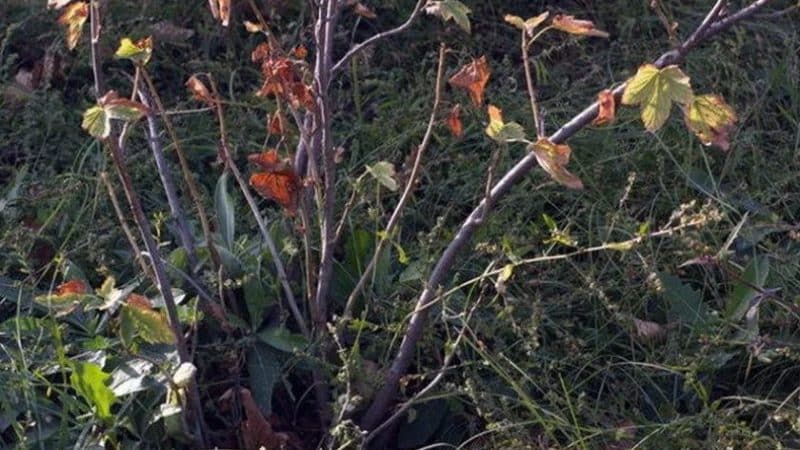

To understand why red and black currant branches with berries dry out, you need to establish the reason. These could be diseases or pests, improper care, or sudden changes in weather.
Once the cause is discovered, it is eliminated - treatment is started or agrotechnical procedures are adjusted. The sooner you begin to eradicate the cause, the higher the likelihood of preserving the berry harvest.
Growth conditions and care
Currants are unpretentious in care, but if the growing rules are violated, summer residents will be left with dry bushes and small berries. They grow it along fences, but many make a common mistake - they plant the bush close to the fence. Because of this, the currants do not have enough space to grow healthy. The recommended distance between the bush and the fence is at least 2.5 m, between plants - no more than 2 m.
Currants cannot be grown in lowlands or on open hills. In the lowlands, cold air infuses, which harms the root system, and at the heights there is always a lot of snow. Gardeners choose a flat or slightly hilly area for the shrub, located away from underground and groundwater. Otherwise, currants often suffer from fungal diseases and infect nearby growing crops.
Due to the characteristics of the root system, currants do not tolerate drought, so summer residents pay special attention watering. The frequency and intensity of the procedure depend on the climate and growing region. On average, currants are watered once every 10 days; 3-4 buckets are used per bush. To prevent moisture from evaporating, the tree trunk circle is mulched with a layer of 5-10 cm. If the summer is rainy, the amount of watering is halved.
Attention! The cause of drying out may be a lack of microelements. The berry bush needs nitrogen-phosphorus-potassium fertilizers. These elements are obtained from urea, manure, ammonium nitrate, double superphosphate, and nitroammophosphate. During the summer, currants are fertilized four times. Fertilizers are applied in liquid form, after watering the soil.
Diseases and their treatment
Currant diseases are divided into viral, bacterial and fungal.
Causes of infection: wet weather, freezing of the soil, inappropriate planting location, selection of weak varieties. Sometimes diseases occur due to a lack of microelements or thickening of plantings.
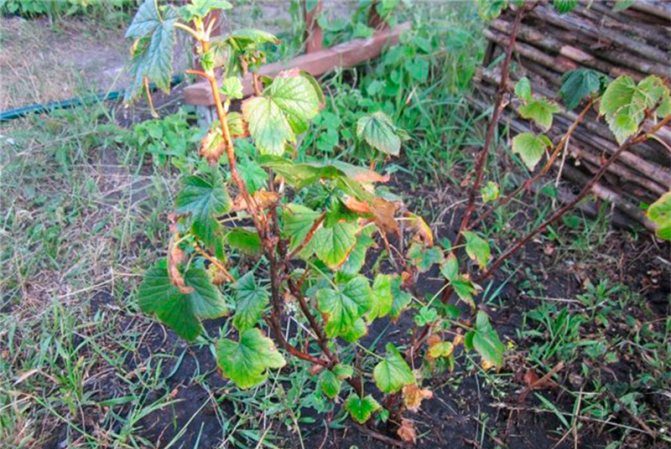

Nectria drying of shoots
It occurs due to the fungus Nectria ribis, which penetrates the soil along with water. Young shoots and adult branches are covered with reddish dots, which over time turn into brown tubercles.
When the fungal spores mature, it causes the branches to turn black. Currant leaves turn yellow, branches dry out and die.If signs of nectar drying are detected, the affected branches are cut back and burned at a distance from the garden plot. The remaining branches are treated with a solution of copper sulfate - 100 g of the substance per 10 liters of water.
Attention! Copper sulfate solution also serves as a prophylactic. To protect young plants from disease, before planting, currant roots are soaked for 5 minutes in a 1% solution. The procedure protects not only from nectar drying, but also from scab, powdery mildew, and aphids.
Anthracnose
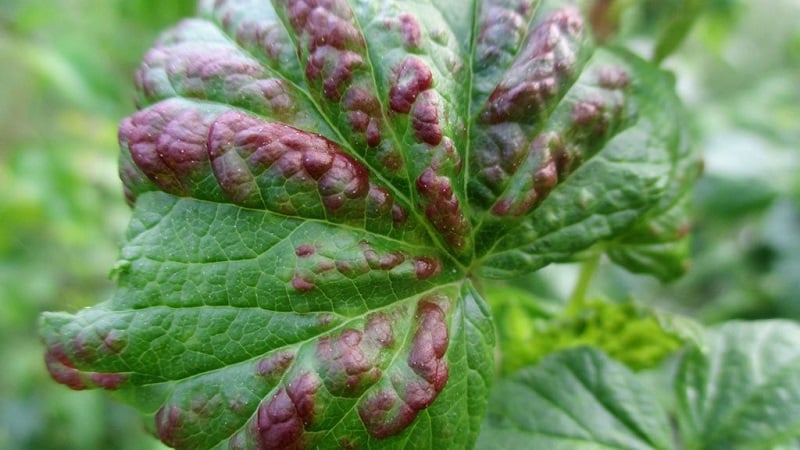

The fungal disease affects adult and young plants and is common in all regions of the country. Brown spots appear on the leaves, which increase in size over time. The petioles and shoots dry out and lose their ability to bear fruit. The peculiarity of anthracnose is that most often it affects red currant bushes.
The spread of the disease is facilitated by rainy and hot weather, non-compliance with planting rules - sometimes gardeners forget to disinfect the soil and treat garden tools with Bordeaux mixture. Anthracnose is treated with a solution of colloidal sulfur - 30-40 g of the substance are diluted in 10 liters of water. The bushes are treated the first time after the disease is detected, the second time after 10 days.
Columnar rust
The disease manifests itself in the middle of the growing season as yellowish spots on the leaf blades. After 2-3 weeks they turn brown, and after another 5-10 days they dry out and fall off. The shoots become sluggish and dry, the berries become deformed and stop developing.
Infected leaves are torn off and burned, and the remaining ones are treated with fungicides - “Agrolekar”, “Gamair”, “Rubigan”. Before processing, study the recommended dosage and precautions.
Pests and their control
If the currants dry out along with the berries, the reason may lie in the appearance of insect pests. Some overwinter in the ground and come out when the weather warms up, while others end up in the area with rain or winds.
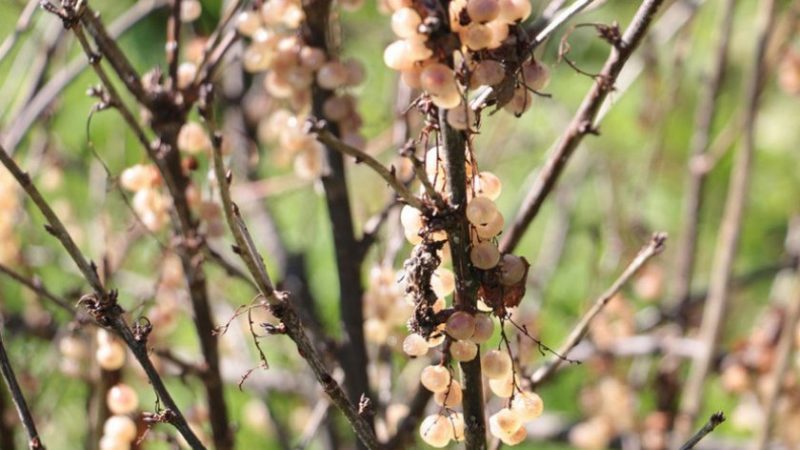

Ognevka
The caterpillar of this butterfly damages red and black currants by eating unripe fruits, which is why the latter ripen prematurely and dry out. The adult is a brown butterfly that lays eggs on leaves. One caterpillar can damage up to 15 fruits.
The insect is frost-resistant - with the arrival of autumn, it hides in the ground, and in the new year it comes out with warmth to complete the development cycle. If a pest is detected, it is recommended to remove the nests from the bush and destroy them. Next, the currants are treated with Karbofos - 60 g of the substance and 8 liters of water are required to prepare the working solution. 1.5 liters are consumed per bush.
Currant bud mite
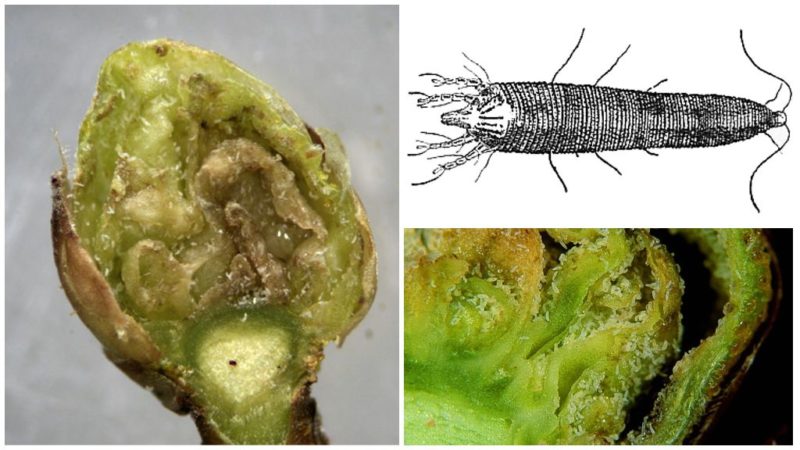
Female currants are dangerous for currants. kidney mite - white insects 0.3 mm long. If the pest appears on a currant bush, the plant will die with an 80% probability. Females overwinter in the soil and lay up to 100 eggs. It is easy to recognize damage - the berries on the currant dry out, the buds swell, and the leaves become deformed and lighten. The tick is carried by people, insects, birds, and wind.
To get rid of the pest, tobacco infusion helps - 400 g of dry leaves are poured into 10 liters of hot water and infused for two days. The infusion is filtered and diluted with water in a 1:1 ratio. Apply the product immediately after preparation - spray the bushes with a spray bottle. Tobacco solution is not suitable for storage.
Currant gall midge
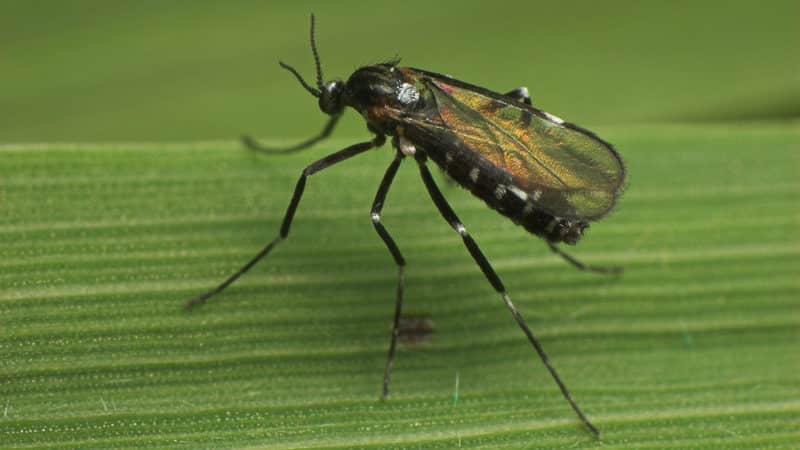

This is a small flying insect similar to a mosquito. There are leaf and shoot gall midges. Leaf attacks young shoots, shoot — overgrown old bushes. Gall midge larvae become active during flowering - the ovaries fall off, the bushes dry out, and the branches become brittle and brittle. If remedial measures are not taken in time, the currant will die.
They get rid of gall midges using the drugs “Karbofos” or “Aktellik” or use a folk remedy - mustard infusion. To prepare, 100 g of mustard powder is poured into 5 liters of water. Leave for 24 hours and dilute in water in a ratio of 1:5. Spray currants early in the morning.
Attention! Many insects are difficult to see on bushes - some are disguised as the color of the leaves, others reach only 0.1 mm in length. Therefore, experienced gardeners advise regularly inspecting plantings - checking the leaves on both sides, shoots, and the base of the bush.
What to do if the cause cannot be found
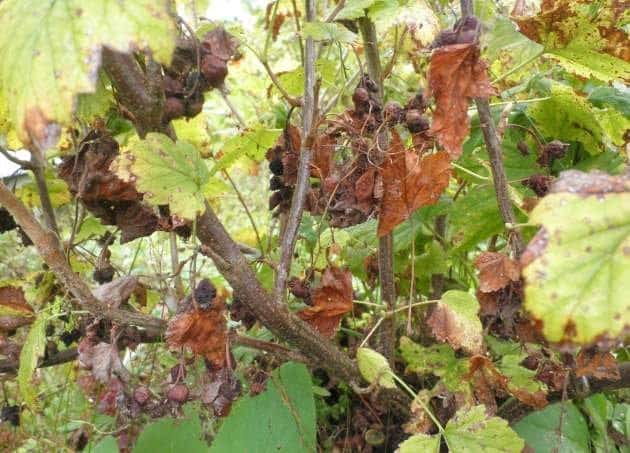

If the cause of drying out of bushes and berries has not been identified, it is recommended to carry out sanitary pruning - remove dry and damaged branches. They may show rot, stains, and a waxy coating. Leaves with red, white and yellow spots are also trimmed - these are signs of disease. Lastly, dried and moss-covered shoots are removed. All removed shoots are burned to avoid the spread of diseases and insects.
It is important to pay attention to care. Perhaps the reason for drying lies in the lack of fertilizers. If there are no currants fed more than two years, rotted manure is applied under the bush (preferably at the end of April). If the bush dries out in the summer, it is recommended to water it with a solution of chicken manure. Also during this period, attention is paid to watering, loosening, and mulching the soil.All these procedures are aimed at strengthening the immune system and the healthy development of currants.
Prevention measures
In order for currants to bear fruit consistently and delight with the harvest every year, special attention is paid to preventive measures. It is better to prevent problems from occurring than to waste time and effort fixing them.
Experienced gardeners recommend:
- Select a variety in accordance with the growing region (early - for the Urals and Siberia, mid-ripening - for the middle zone, late - for the southern regions).
- Plant currants in hilly sunny areas, protected from wind and groundwater. Favorable neighbors for currants are blueberries and gooseberries.
- For planting, select two-year-old seedlings, disinfect them and soak them in a growth stimulator (Epin, Kornevin).
- Cover shrubs for the winter to protect them from frost and wind.
- Once every 10 days, spray the bushes with a soap solution - 5 liters of water require 250 g of grated laundry soap.
- Carry out sanitary pruning annually, formative pruning once a year, and rejuvenating pruning once every 5 years.
- Once every 10 days, loosen the soil to a depth of 5 cm. This procedure retains moisture and improves root nutrition.
- Mulch the plant with sawdust, pine needles, leaves and grass.
- Alternate organic and mineral fertilizers.
Conclusion
Drying of currants is a consequence of diseases or pests, errors in choosing a planting site and growing. Red and black currants suffer from nectar shoot drying, columnar rust, anthracnose, gall midge, and bud mite.
Sometimes the reasons lie in a deficiency or excess of nutrition and moisture.To avoid drying out, gardeners regularly inspect currant bushes and carry out preventive measures: they cut off old and dry shoots, mulch the plantings, and spray the currants with a soap solution.