When and how to prune grapes correctly in spring for beginners step by step: instructions and diagrams
With proper care, grapes can bear fruit for several decades. Even an old vineyard can be revived with the help of rejuvenating pruning. In spring, young plants are pruned for shaping, using suitable patterns, and damaged and dry branches are pruned. In the article you will find step-by-step instructions for beginners on how to prune grapes in the spring.
Purposes of spring grape pruning
The culture has a unique ability to direct nutrients to young shoots. This property has been developed and improved over centuries. In the wild, the branches stretched upward, trying to receive the maximum amount of solar energy. For this reason, in the middle and lower parts of the bush, the eyes develop slowly and sometimes do not produce shoots at all. That is why winegrowers regularly prune their grapes.
Spring pruning of grape bushes is aimed at increasing fruitfulness and giving a neat shape. Proper pruning improves ventilation and sun exposure. This is one of the main tasks of a gardener, neglect of which leads to thickening of plantings, reduced pollination, and peas of berries.
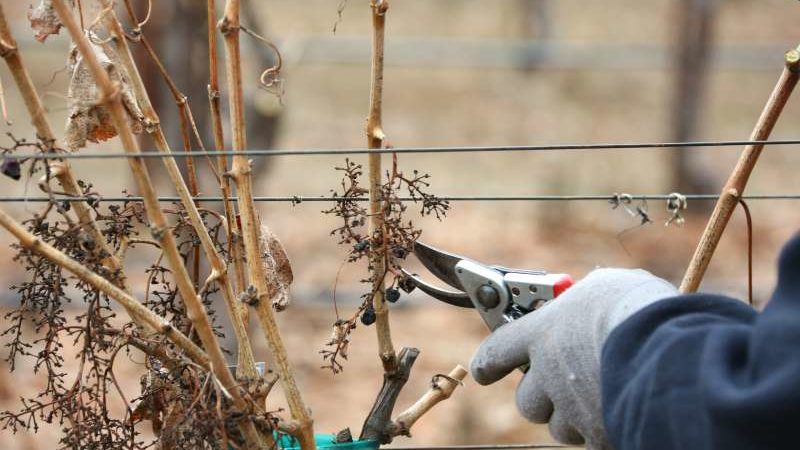

Advantages and disadvantages of carrying out the procedure in spring
Benefits of spring pruning:
- increase in yield by 60-80%;
- molding bushes of the correct shape;
- increased frost resistance;
- improving plant nutrition and maintaining photosynthesis;
- simplified care and harvesting;
- ensuring free access to the vine from all sides.
This method has no disadvantages. The main thing is to start working before the sap flows, otherwise the plant will die due to large loss of moisture.
When to prune in spring
The timing of pruning grape bushes is extremely important for bud ripening, yield and quality of berries. Spring pruning is divided into early and late.
Early pruning is done after the snow melts. As soon as the air warms up to a stable +5°C, winegrowers arm themselves with tools and begin to work. During this period, sap flow has not yet begun, so the cuts will quickly dry out and tighten. In extreme cases, the procedure can be performed before the first buds swell.
Late pruning is carried out when the sprouts reach 5-6 cm in length. This procedure is performed in regions where there is a high probability of return spring frosts. Late pruning is recommended only if absolutely necessary, and even better, postponed until autumn. It severely depletes the grapes and slows down the growth of new shoots.
Reference. In the regions of central Russia (Moscow region), grape sap flow begins in the 1st-2nd decade of April, in the southern regions - at the end of March.
Favorable days
Favorable days for pruning according to the lunar calendar for 2020:
- March - 11.12, 16-18, 24-26;
- April - 11-14, 21.22;
- May - 10, 11.
Favorable days for pruning according to the lunar calendar for 2021:
- March - 17-19, 22,23, 26-28;
- April - 13-15, 19, 24-17;
- May - 12-17, 24-26.
Types of pruning
Among the types of pruning of grapes, there are formative, rejuvenating and sanitary.
Formative pruning helps regulate the bush's load of vines and berries. In the first year of development, the seedling does not need special care.For proper growth, it is enough to trim the growing shoots. The seedling is tied to a support and left alone until the next season. In the second year of development, they choose a suitable pruning scheme for shaping the bushes and adhere to a single course.
Rejuvenating pruning is carried out from the moment the first signs of aging of the bush are detected. This is indicated by poor development of shoots, decreased yield and peas of berries. Sometimes winegrowers resort to extreme measures and completely prune the bush, performing a complete “reboot” of the plant. The procedure is carried out in summer or autumn, following the scheme:
- The base of the bush is dug 10-15 cm deep.
- Next, the ground trunk is completely cut off at a height of 5-10 cm.
- The cut is treated with wax or garden varnish.
- The trimmed bush is covered with loose and fertile soil.
- In the spring, the soil is removed, after which the young shoots quickly grow and gain strength.
Sanitary pruning is performed in the spring. The bushes are carefully inspected after hibernation and dry, diseased and damaged branches are removed.
How to prune grapes correctly
Over hundreds of years, winegrowers have determined several general rules for pruning crops, guided by which even a person without experience can cope with the task.
Required materials and tools
List of tools for pruning grapes:
- The pruner is used to trim one-year and two-year branches with a diameter of up to 1.5 cm, as well as thin sleeves. To get even, neat cuts, gardeners use pruners with two blades.
- The bow saw is used for pruning perennial shoots with a diameter of 7-8 cm.
- The hacksaw is suitable for cutting branches with a diameter of 8 cm.
- A lopper is a type of pruner. The tool is suitable for branches in hard-to-reach places.It is attached to a stick, a certain branch is hooked and it is cut off by pulling a twine tied to a lever.
- A budding knife is used for budding eyes.
- The grafting knife is suitable for grafting vines with cuttings.
Before use, instruments are sharpened if necessary and disinfected in medical alcohol or a strong solution of potassium permanganate.
Reference. Sleeves are perennial branches that form throughout the life of the plant and increase in size each year due to the shoots left behind when pruned.
Step-by-step instruction
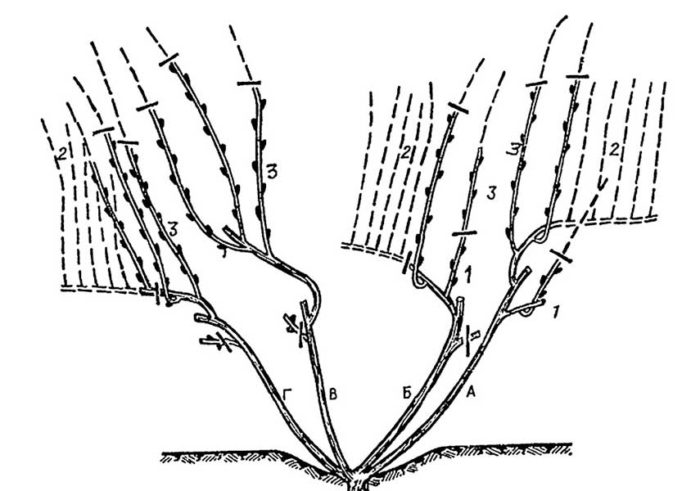
Trimming rules:
- The cut is made at an angle of 90° perpendicular to the branch. This allows for faster healing due to a smaller wound area compared to cutting at an acute angle.
- Diseased and dead vines are completely removed.
- 7-12 eyes are left on the shoot.
- Annual shoots that bear fruit are carefully cut off, trying not to damage the wood. Sections are made at the base of a perennial shoot, leaving a stump of 0.5 cm.
- Healthy shoots with a diameter of 6-10 mm are left for fruiting. Thin and thick shoots (with a circumference of more than 10 mm) must be cut off.
Trimming schemes
Grape growers use several schemes for pruning grape bushes:
- according to the Guyot method;
- fan;
- Moscow small fan;
- horizontal cordon.
Pruning using the Guyot method
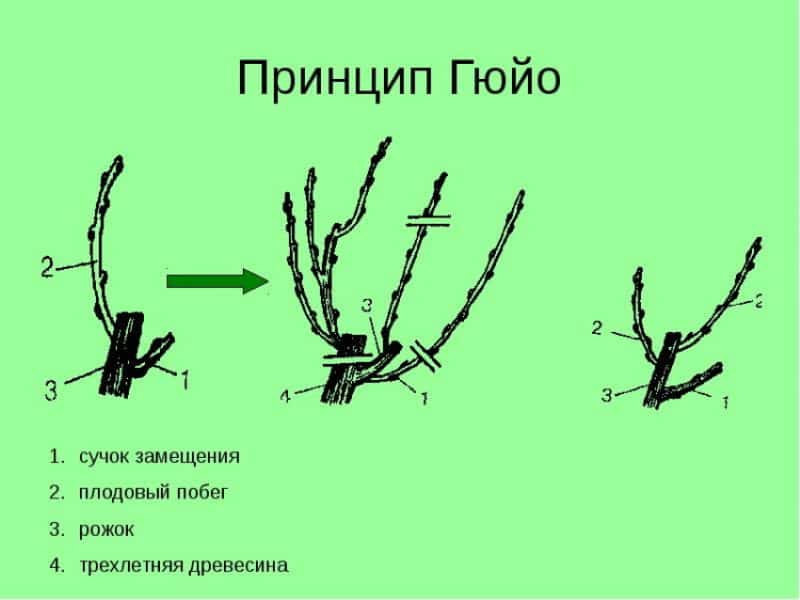
This simple scheme is aimed at growing one strong shoot. In the fall, all young shoots that have grown over the summer are cut off, and the main shoot is shortened by 5-6 eyes.
Reference. If the main shoot is weak, it is completely removed and molding is postponed until the next season.
In spring, the fruit arrow is tied to a trellis in a horizontal position. If there are two shoots left on the bush, they are tied up so that they look in different directions.In this way, it is possible to obtain a two-armed bush according to Guyot. The shoots of the fruiting vine are tied vertically to the second and third wires as they grow.
In the third year the vine produces its first harvest. In the autumn of the same year, the stem is completely freed from inflorescences and stepsons. The next season, the vine is lengthened by 10-12 buds, bringing their number to 20. In each subsequent season, the stages of the method are repeated.
Fan model
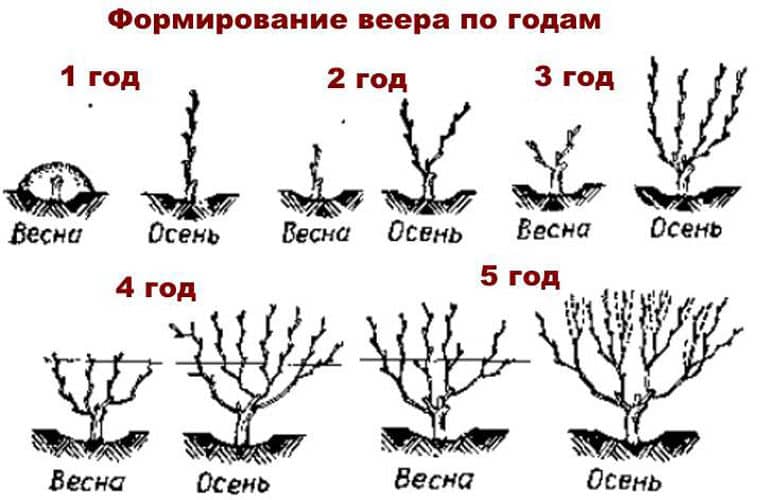
The fan pattern involves the molding of two short sleeves located in the same plane at different angles of inclination. Thanks to this molding, the vine can be easily removed from the trellis in the fall and covered for the winter. The grape bush is constantly renewed, and the yield increases.
Moscow small fan
With this molding scheme, the bushes are located at a distance of 70-80 cm, the row spacing is 1.5-2 m. This allows you to cover the bushes for the winter with grass and dry branches. The vine breathes freely, thanks to which it lives for more than 10 years. The scheme is often used in the northern regions.
Horizontal cordon
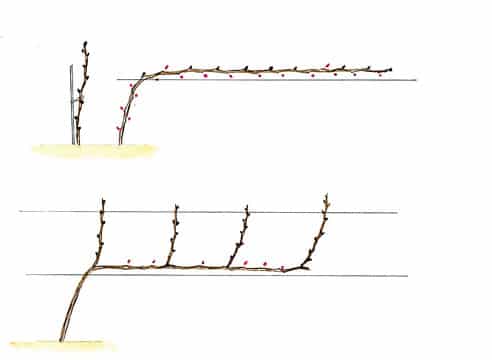
The essence of the scheme is to grow one shoot, which is cut off in the fall, leaving one eye at the bottom. In the future, a sleeve will grow from it.
The next season, the shoot is fixed at an angle to the bottom wire, the awakened eyes are broken out and the last one is left at the bottom. The upper eyes are also thinned out, leaving a gap of 30-35 cm.
In the autumn of the second year of development, the vine is pruned by 2-3 eyes, and the latter is shortened to the full length of the sleeve. In spring, the buds are broken out, leaving 2-3 shoots with an interval of 30-35 cm.
In the autumn of the third year of development, two shoots appear on 2-3-eyed shoots.The lower shoots are pruned by 2-3 buds to obtain replacement branches, and the upper shoots by 5-6 buds to obtain fruiting shoots.
Standard spring pruning
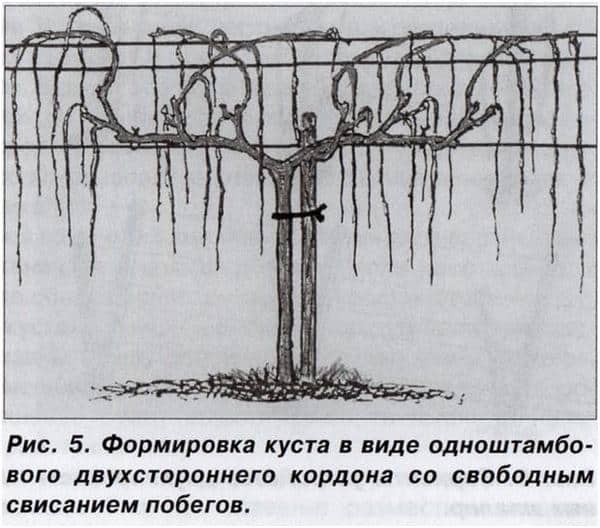
The procedure corresponds to the age of the grapes. The method is used when cultivating covering varieties.
Trimming scheme:
- In the first year after landings seedlings are cut to two eyes to obtain two shoots. The remaining shoots are removed completely.
- In the second year of development, the main shoot is shortened to 50-90 cm. To be on the safe side, another shoot is saved and cut to two buds.
- In the third year, all shoots on the trunk are removed, except for the top two. Each of them is cut to two eyes and fixed to a support. In the fall, four shoots that have grown over the summer are cut off: the lower shoots are cut to two buds on all sides, the upper shoots are cut to 5-15 buds.
- In the fourth year of development, fruit-bearing branches are cut off, shoots from replacement knots form new fruiting links. To do this, on each side of the bush, one shoot is cut to 5-15 buds, the second to two buds.
Standardless spring pruning
This type of molding has its own subtleties and is used for uncovered grapes:
- A year after planting, dry, diseased branches are removed, leaving 10% of all young shoots, which are cut at a height of 2-3 cm above the second bud.
- In the second year, 60% of the young shoots are cut off, leaving 2-3 of the strongest ones.
- In the third year, the lower vine, acting as a replacement knot, is cut to two eyes, the fruit shoot (upper part) is cut to 7-14 eyes. Two vines are left on each sleeve, the rest are cut off.
Spring pruning of fruiting grapes
This type of pruning requires compliance with several nuances.In order to prune the fruit-bearing bush and not damage it, winegrowers remove shoots that have completed fruiting, weak, damaged, thin and fattening shoots. Ripe branches with a diameter of 6-10 mm are left on the bushes.
Special pruning of damaged bushes
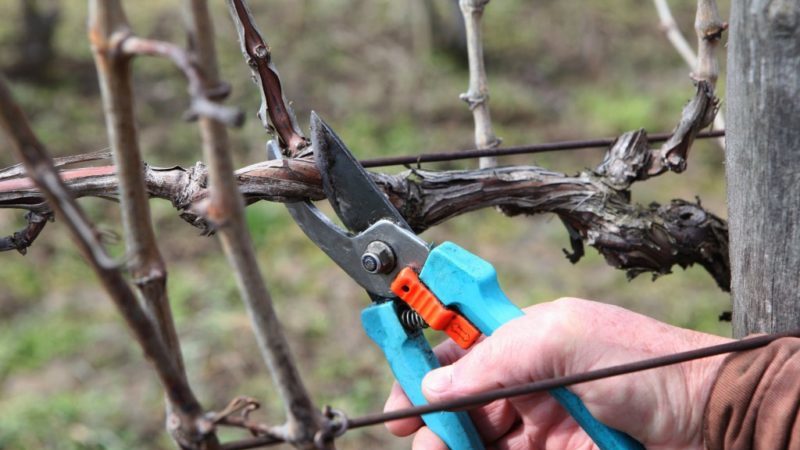

Spring pruning is carried out not only for the purpose of shaping the bushes, but also to restore the vine after winter, after unexpected return frosts and other weather surprises. Proper pruning can bring even severely damaged grapes back to life.
Frostbite in winter
If the bushes are very frozen in winter, first inspect the buds and make cuts, moving from the base to the top. If the eyes are green, then everything is fine. Dark brown or black coloration indicates damage.
If less than 80% of the kidneys are dead, A larger number of buds are left on the fruit links than with conventional pruning. The harvest will be harvested thanks to the additional shoots on the fruit-bearing branches remaining after the autumn pruning.
If more than 80% of the kidneys have died, perform sanitary pruning in two stages. To do this, before the buds open, remove frozen shoots and sleeves. After the greenery appears, cut off unnecessary growth.
With 100% kidney death They examine the stepsons, which are characterized by increased frost resistance. If the buds on them are dead, they begin to form fruit links from shoots (shoots from the underground part of the trunk) or tops (fatifying shoots).
When the entire above-ground part has died, a “black head” cut is made: they dig up the bush to a depth of 25-30 cm and cut down all the branches to a healthy node, and cover the stump with a 5 cm layer of soil. Soon young shoots will appear from the trunk. The strongest of them are left, the excess growth is cut off.

Frostbite of roots
Partial frostbite or complete death of the root system of grapes occurs due to a winter with little snow. To check the condition of the roots, it is recommended to dig up the soil in several places and make cuts. Healthy roots have a gray-white cut, frostbitten ones are dark brown.
If the frostbite diameter of the root is no more than 2.5 mm, there is no threat to the life of the plant; the main thing is that the main part of the rhizome remains intact. In case of partial frostbite, it is recommended to reduce the load on the vine by pruning the fruit shoots.
Hail damage
If, after a strong hail, the grapes have lost most of their leaves, young shoots are cut to 1-2 eyes. New shoots need to be thinned out to stimulate the growth of spare eyes, which will produce a harvest the following season.
Consequences of cold snap
Spring frosts often coincide with the awakening of the buds, so the death of young shoots, annual vines and buds is not uncommon. In this case, winegrowers perform short pruning of last year's branches to stimulate the growth of young shoots and new buds.
This is interesting:
How to water and feed grapes in spring: instructions for beginners
The best fertilizers for grapes in spring and the rules for their application
What properties should uncovered grape varieties have and which ones are considered the best?
The nuances of pruning depending on the growing region

For each region, there are preferred methods for pruning grapes:
- the Moscow small fan scheme is suitable for the northern regions;
- horizontal cordon formation is practiced in the northwestern climate;
- pruning using the Guyot method is only suitable for the southern regions (Kuban).
Features of pruning young and old plants
Young grapes are pruned to give the crown a standard or bush shape, adjusting the number of shoulders and sleeves. Pruning of adult plants is carried out in order to get rid of dry, diseased, damaged branches. On old bushes, 2-3 young shoots are left to replace the old vine.
Care after pruning
Any pruning causes extreme stress. Many wounds appear on the bushes, and the grapes spend a lot of effort to restore the integrity of the integument. Particularly dangerous are cuts with a circumference of more than 1.5 cm. A large amount of damage weakens the plant and often causes its death.
Compliance with a number of rules will help the plant quickly restore its vitality:
- To make even cuts when pruning thin shoots, it is recommended to use sharp pruning shears. A bow saw is suitable for removing thick branches, and a hacksaw can handle old thick branches.
- It is advisable to place all cuts on one side. To achieve this result, it is necessary to place replacement shoots on one side during annual pruning. Thanks to this arrangement, all branches will receive their portion of nutrients.
- To prevent moisture from retaining on the surface of the cuts, uneven edges are cleaned with a garden knife. Excess water penetrates into the deep layers of wood and leads to the development of putrefactive processes.
- After trimming a thick shoot, the height of the stump should be less than 1 cm, otherwise it will become covered with cracks.
- Thick and old branches are cut at an angle of 90° so that wounds heal faster.
- Annual shoots are cut 1-2 cm above the lower eye.
Conclusion
Spring pruning of grapes increases productivity and helps give the bushes a neat shape.Proper pruning improves ventilation and solar heating. Neglect of pruning leads to thickening of plantings, reduced pollination and peas of berries.
Winegrowers use different schemes: according to the Guyot method, fan pruning, horizontal cordon and Moscow small fan pruning. The standard pruning method is used when growing covered grapes, while the standardless pruning method is used for non-covering grapes. In addition, in the spring, sanitary and anti-aging pruning will be performed to restore the vitality of the plant after winter.